Phlox diseases and their treatment: why leaves curl
Content:
- Fungal infections - main types and treatment
- Verticillary wilting
- Cracking stems
- Annular leaf spot
- Necrotic leaf spot
- Drying and falling leaves
- Phoma (Latin Phoma betae)
- Slobbering penny
- Leaf rust (lat.Cronartium ribicola)
- Powdery mildew (lat.Erysiphaceae)
- Nematodes (Latin Phyllotreta cruciferae)
- Septoria or leaf spot (Latin Septoria phlogis Sac)
- Slobbering penny (lat.Philaenus spumarius Larve)
- Phlox: pest control and disease prevention
- Leaf blight
- Variegated
- Jaundice
- Threadiness of leaves
- Variegated petals
- Rattle
- Slugs
- Cruciferous black flea
- Caterpillars
- Preventive treatment of planting material
- Disease prevention
The name of herbaceous dwarf shrubs - phlox is translated from Greek as "flame". They are popular with flower growers not only for their bright flowering, but also because they are hardy, unpretentious. The main problem when growing phlox can be the need to protect plants from diseases and pests.
Fungal infections - main types and treatment
Gardeners do not always immediately pay attention to phlox diseases. Beautifully flowering lush plants may not lose their decorative effect, but at the same time on their leaves there will already be spores of fungal infections, pest larvae.
The causes of phlox diseases can be:
- unsatisfactory plant care;
- unfavorable climatic conditions;
- long term cultivation in one place;
- non-compliance with the rules of agricultural technology.
Fungal infections often appear on phloxes with the help of pollinating insects that carry pathogens on their bodies. Spores of fungi on flowers can be carried by the wind, which spreads microorganisms not only between plants growing nearby, but also over long distances.
Phloxes can get sick and die at any stage of their development. It can be very difficult to cure them. But gardeners never refuse to fight for the plants to bloom and delight their owners.
Verticillary wilting
The disease is provoked by microsclerotia of fungi of the genus Verticillium, which live on plant debris in the soil for up to 15 years.
The disease breaks out with foci. The main symptoms of the disease are the loss of turgor, that is, the filling of the leaves with moisture, their yellowing, darkening and drying out, a change in the color of the stems. The fungus enters plants through the root system, then moves to stems, petioles, leaves, and sometimes reaches fruits and seeds.
You can see the mycelium of the fungus on the cuts of the stems in the form of a weak grayish bloom. The mycelium clogs the conducting vessels and does not allow nutrients and moisture to penetrate into the vegetative and generative organs of phlox. Most often, verticillary wilting of plants begins to hurt at the stage of preparation for laying the inflorescence.
It is possible to prevent the appearance of the disease by preventive measures - removal of plant residues, autumn-spring digging of the earth, soil treatment with biological products and fungicides.
Plants can be treated with drugs:
- "Trichodermin",
- "Glyocladin",
- Fundazol,
- "Maksim",
- Vitaros.
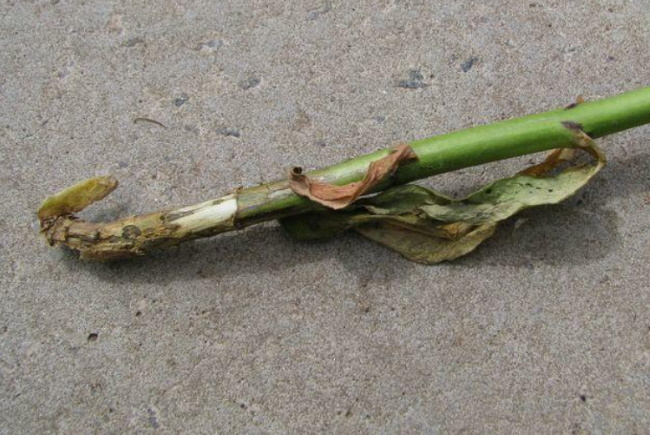
Cracking stems
Sometimes phlox diseases and their treatment are caused by an imbalance between the amount of moisture that is needed to support the plant and the capabilities of the root system, which is not able to absorb and raise the required volume of water.
The result is drying of the leaves and cracking of the lower zone of the stems. The tissues of the stems are exposed and hardened. With a sufficient reserve of nutrients and moisture in the soil, the plant suffers from a lack of them. Most often this occurs during the period of active growing season - enhanced growth of green mass by flowers.
Having figured out why phloxes dry from below and the stems crack, it is only necessary to organize feeding of plant roots to increase their strength. Watering the root zone of phlox with solutions of drugs that increase root formation, such as Kornevin, Epin, Amber Acid, and complex mineral fertilizers help to develop the root system.
Annular leaf spot
The viral diseases that affect phlox are not specific only to these flowers.
Ring spot of leaves in phlox is caused by viruses of tomatoes, and they are transferred from plant to plant by insect pests - nematodes Longidorus. The disease manifests itself in the spring and causes the cessation of growth of the bush, deformation of the leaves. On the leaf plates, areas of yellow color with characteristic ring patterns are formed.
Having found the reason why phlox leaves curl, the entire diseased bush is removed from the site and burned. From the plot of land on which the phlox grew, the surface layer of the soil is removed to the depth of the roots, the hole is treated with preparations containing chlorine (household "Whiteness") or formalin.
Necrotic leaf spot
Before treating phlox for diseases that cause necrotic spotting on the leaves, it is necessary to understand why brown spots appear on phlox.
The disease is caused by the cucumber mosaic virus (VOM), due to which growers lose up to 100% of the harvest of tomatoes, cucumbers, and peppers.
The fight against PTO is carried out everywhere, because it is common wherever vegetable crops are grown. The virus exists on the remains of wild-growing weeds, is carried by insects to cultivated plants, then returns to the soil with plant debris.
PTO is destroyed together with the diseased plant. Only the elimination of diseased plants from the garden plot will prevent the spread of the disease to healthy flowers. The soil and gardening tools are disinfected.
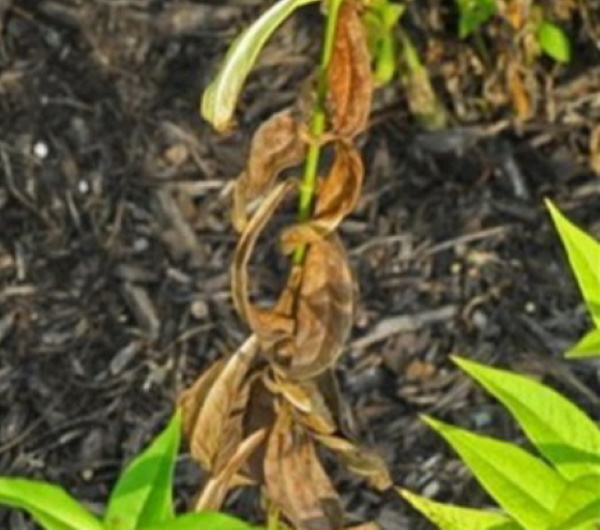
Drying and falling leaves
The main factors affecting the condition of phlox leaves are very dense plantings, irregular watering and feeding, high acidity of the soil.
Bushes shed their leaves, which the root system is unable to provide with the substances necessary for their life. After the establishment of a normal level of moisture and acidity of the soil, the introduction of complex fertilizers, thinning of the bushes, the growth of green mass resumes.
In order for the plants to stop dying, it is necessary to stop their withering. You will need to spray phlox leaves with a solution of Bordeaux liquid at the rate of 1 tsp. dry mix for 7 liters of water. Root top dressing is carried out with a phosphorus-potassium mixture (1 tbsp of each fertilizer is diluted in 10 liters of water). Dry ash is scattered on the soil under the bushes of plants, which, when irrigated, gradually penetrates into the soil and gives the roots the trace elements in it.
Phoma (Latin Phoma betae)
The appearance of numerous brown, loose phoma spots at the base of the stems and on the root collar indicates why the leaves of phlox are curled.What to do in case of strong development of phlox phomosis is indicated in the description of the preparations "HOM" and "Abiga-Peak". These contact fungicides are designed to kill Phomaphlogis fungal organisms that cause phomosis.
Those plants that do not lack phosphorus and potassium show resistance to the disease. Excessive application of nitrogen fertilizers leads to a weakening of immunity and the insecurity of flowers from disease. Preplanting dressing of seedlings and cuttings of phlox in a solution of "Fitosporin-M" increases resistance to phomosis.
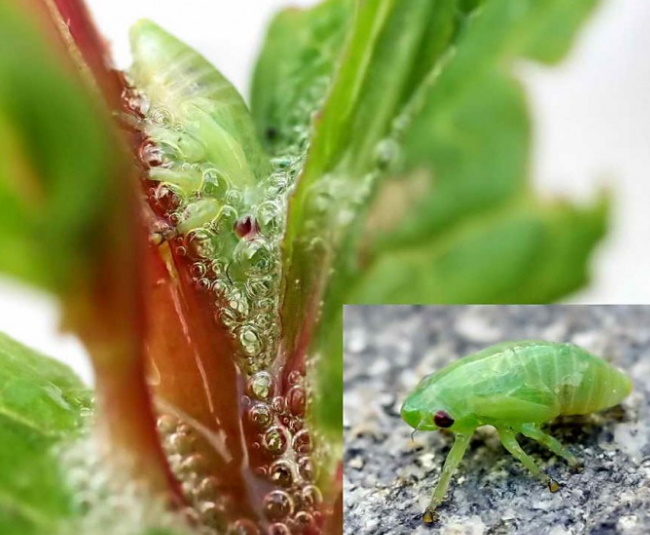
Slobbering penny
Phloxes suffer not only from pathogens, but from insects parasitizing on its bushes.
Cicadas of various colors, which are called slobbering pennies, cause significant damage to phlox bushes. Pennitsa secretes a viscous liquid in which its larvae develop. The pest lives off the tissues and sap of the plant.
Lack of nutrition leads to the fact that the leaves of phlox shrivel, curl, the buds stop growing, the shoots dry out. Treatment of flower bushes with Inta-Vir, Aktara, Tsvetofos means will be an effective way to combat the pest.
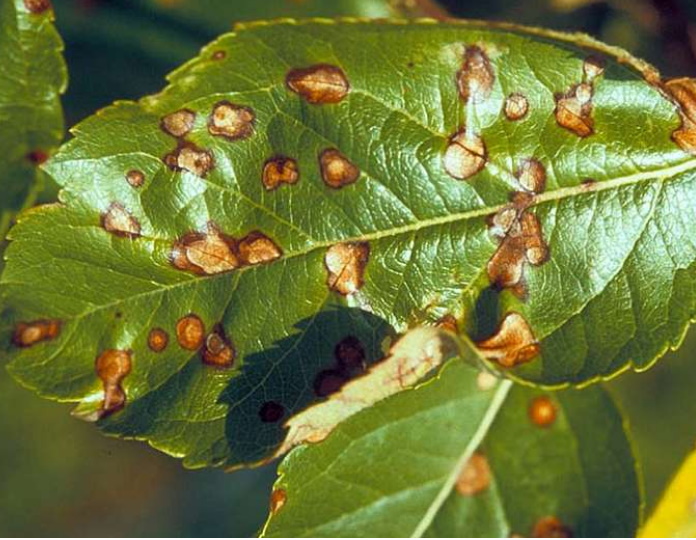
Leaf rust (lat.Cronartium ribicola)
A disease in which numerous and constantly increasing orange-brown spots appear on the leaves is said to be rust. The disease is extremely serious. In fact, at the moment, if rust appears on phloxes, it is not known how to treat it. There are no chemicals or traditional treatments.
Therefore, the bad, diseased leaves are torn off and destroyed. When rust spreads to the entire bush, it is uprooted and burned.
If the fight against the disease begins at the appearance of the very first symptoms, then the use of 1% ferrous sulfate, drugs "Oksikhom", "Skor" it can be stopped.
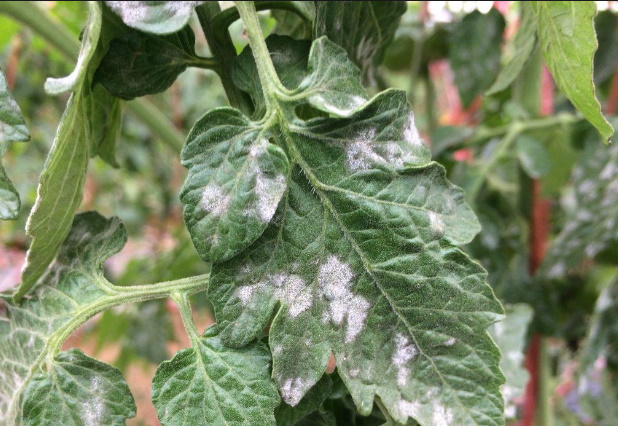
Powdery mildew (lat.Erysiphaceae)
The disease, which is provoked by a fungus from the Erysiphoid family, is called powdery mildew.
A harmful fungus settles on weakened plants suffering from a lack of moisture, is active with the onset of changes in temperature and humidity.
The causative agents of the disease live in the ground, therefore, the lower leaves of phlox are the first to suffer from powdery mildew - spots of white plaque appear on their seamy side, similar to a thick cobweb. Then the developing myceliums turn brown. Dark spots increase, move from leaves to stems and buds.
Plants are treated with agents with a high exposure rate:
- "Soon",
- "Topaz",
- Ridomil Gold,
- "Hom".
Plant treatments are carried out not only during an outbreak, but also for prophylaxis.
Nematodes (Latin Phyllotreta cruciferae)
Measures to combat nematodes on phlox involve the removal of affected bushes along with a lump of earth.
The nematode larvae live in the soil and invade the roots of phlox. At the site of penetration, friable swellings are formed, which are called galls. Adult worms infect stems by feeding on their tissues.
Bushes inhabited by nematodes first stop their development, then they turn yellow, dry out and die of flowers. Through tissue damage, all kinds of pathogens carried by wind and water are colonized in plants.
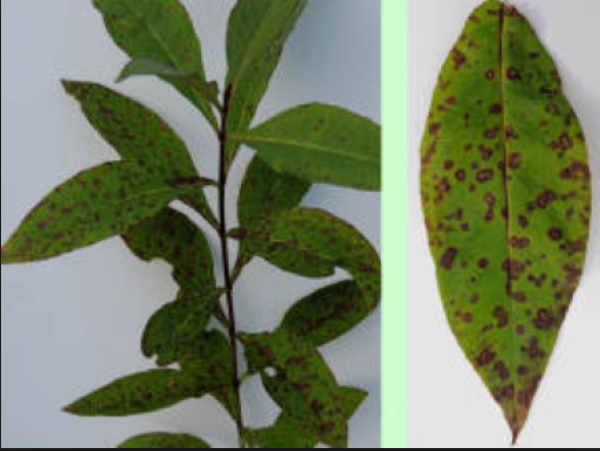
Septoria or leaf spot (Latin Septoria phlogis Sac)
During the period of growing green mass, gray spots may appear on phlox, indicating that the plant is infected with septoria spores.
The disease has a second name - white leaf spot. It is familiar to many gardeners and gardeners, because many perennial crops are susceptible to disease during periods of high humidity and high air temperatures.In the process of development of the disease, gray spots turn yellow, a reddish border appears around them.
For treatment, the means with which the leaves and stems are treated are used. The active substances of the preparations work not only on the surface of plants, but also penetrate into the stems. Protection also extends to new shoots that appear after treatments with such agents as "Oksikhom", "Acidan".
Slobbering penny (lat.Philaenus spumarius Larve)
Pests live in gardens on cultivated plants, meadows, forests, parks.
If the colony of pests is not numerous, then the fight against it can be carried out manually, breaking off the leaves and stems with signs of penny nesting - the formation of a foamy sticky substance inside which insect larvae live.
But it is difficult to keep track of adult insects, they can jump off the bush and hide. Therefore, numerous insect colonies are destroyed using chemical insecticides. Folk remedies, such as decoctions of stalks and flowers of tansy, wormwood, garlic, can scare off an adult insect, but it will not be possible to destroy its larvae.
Phlox: pest control and disease prevention
The prevention of phlox diseases and their protection from pests will be successful if, before planting phlox seedlings in a permanent growing place, work is carried out to decontaminate plants and soil from pathogens and insect larvae.
Adequate watering and timely feeding will increase the resistance of plants to diseases and pests.
In the fall, it is necessary to dig up the soil to a depth of 30-40 cm. Fallen leaves and plant debris should be removed from the garden, preventing pathogens from wintering in them. Plants can be planted next to phlox, which, with their pungent smell, will scare off pests.
Plants must be periodically treated with chemical agents intended for the prevention of diseases - fungicides "Maxim", "Vitaros", "Topaz", "Skor".
Leaf blight
The causative agent of the disease is fungi from the genus Alternaria (Alternaria tenuis).
First of all, they populate phlox leaves, forming brown rounded spots on them. After some time, the number of spots increases, they join into a single spot, the leaf plates dry up, the leaves fall off, the stems of phlox are completely bare. For the prevention of disease in the spring, flowers are treated with systemic fungicides, in particular, for this purpose, you can use "Fundazol".
Variegated
This disease is incurable, it occurs due to the effect of the mosaic virus on the formation of coloring pigments in the petals.
The virus eliminates the varietal traits of flowers. Variegation is transmitted by insects with sap and pollen. It also spreads with phlox seeds. Virus infection can be determined by comparison with reference plants.
Jaundice
When the fact of underdevelopment of phlox bushes, curliness and chlorosis of leaves appears, experienced gardeners diagnose: microorganisms from the class of bacteria - mycoplasma, settled on phlox.
Experiences that phlox leaves turn completely yellow, how to treat ailments, why phlox do not bloom, are justified.
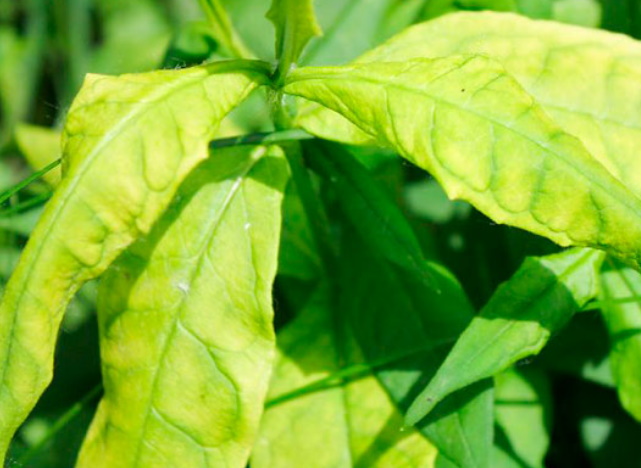
But there is a solution to the problem of how to treat phlox chlorosis if it has arisen due to improper flower care. The yellow tip of a young leaf on the phlox stem indicates that it lacks iron. With an increase in the number of such leaves, plants are fed with complex fertilizers, because it is difficult to determine without laboratory studies what minerals plants need.
Threadiness of leaves
Signs of a change in the external structure of the leaves, the transformation of their leaf plates into thread-like formations with wavy edges indicate that the plant has been attacked by a cucumber mosaic virus or is inhabited by nematodes.
In the latter case, the change in leaves mainly occurs in the center and at the top of the stem. Plants infected with the virus do not bloom, do not increase in growth, and die quickly.
Variegated
The disease is characterized by the appearance of white streaks on the leaves and petals of flowers. Affects the flowering time and the shape of phlox leaves.
Diagnosis of the disease is difficult, it is determined by the external indicators of the pattern and color of the petals. On diseased plants, the patterns are unevenly located. The disease is inherited and worsens the varietal performance of flowers.
Rattle
Indicators of the disease are rings and half rings, stripes, semicircular spots that appear on the leaves against the background of a change in their color from green to light yellow. The number of spots increases, the growth of plants stops. The cause of the disease is the pathogen Tobacco rattle virus.
Slugs
Mollusks, which include land slugs, love to eat young leaves and shoots, phlox buds. In addition, they are carriers of infectious agents.
It is impossible to see slugs during the day, they hide in the ground, under stones, and other shelters. If you lay out traps in the garden in the form of pieces of thick cardboard, slate, then you can manually collect these pests.
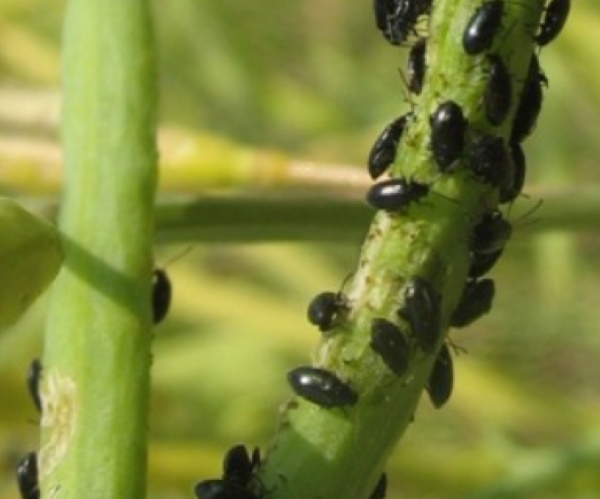
Cruciferous black flea
Pests from the leaf beetle family - black cruciferous fleas - live in the surface layer of the soil, parasitize on the branches and leaves of cruciferous plants.
From early spring, they eat the shoots and leaves of phlox, in the summer they add buds and flower petals to their diet. The phlox bush can die from numerous injuries.
To destroy the pest, the soil and bushes are powdered with a mixture of tobacco dust and wood ash, dry slaked lime.
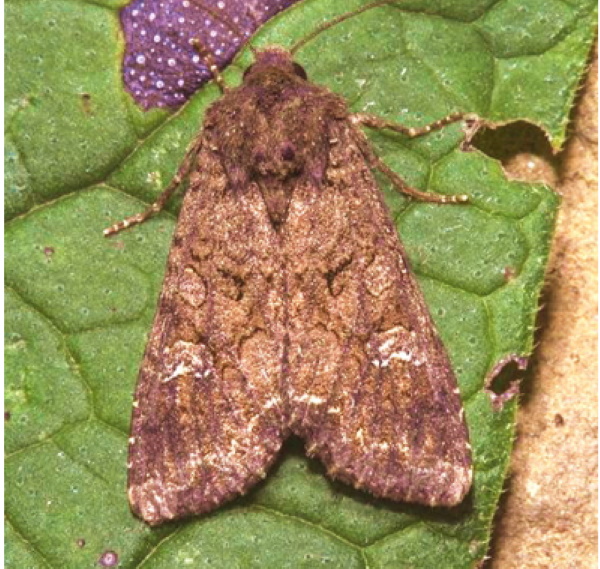
Caterpillars
Members of the Noctuidae family - various species of scoop butterflies - lay their eggs on plant stems.
Caterpillars emerging from eggs eat the buds, flowers and stems of phlox. To exterminate pests, use the preparations "Karate", "Fastak", carry out manual collection of insects.
Preventive treatment of planting material
Cuttings, seedlings, phlox seeds are treated with drugs that prevent the formation of rot, destroy various types of pathogens.
These drugs include biologics:
- "Aktofit",
- "Lepidocide"
- "Phytodoctor",
- Fitoverm.
Disease prevention
To keep the plants from getting sick, they need to be well cared for. The soil in areas where flowers grow is regularly weeded, freed from plant residues, if necessary mulched to maintain sufficient moisture in the root zone of plants, fertilized, and measures are taken to protect against pests - carriers of infections.
Diseased bushes destroy and disinfect the soil. In order to prevent the spread of pathogens, regular inspections of plants are carried out, leaves and stems with the slightest signs of disease are removed.
Although phloxes are rather unpretentious plants, if you do not allocate time and money to care for them, it is unlikely that it will be possible to achieve that such representatives of these flowers bloom in the garden, which everyone, without exception, would admire.