Diseases of clematis and their treatment - what are the diseases of flowers
Content: [Hide]
- Diseases of clematis
- Why do clematis leaves dry
- Why does clematis fade
- Clematis leaves turn black: what to do
- Fungal diseases of clematis and their treatment
- Phomopsis
- Gray rot
- Fusarium
- Rust
- Powdery mildew (Erysiphales)
- Ascochitosis
- Alternaria, septoria, cylindrosporiasis
- Viral diseases of clematis and their treatment
- Insect damage to clematis
One of the most popular plants among florists is clematis. It attracts attention with luxurious flowers of different colors, depending on the variety. But, like most other plants, it can be sick, it can be affected by pests. In order for the fight against such problems to be successful, it is important to know what kind of diseases of clematis are and what to do with their development.
Diseases of clematis
Why do clematis leaves turn yellow, what should I do? If the lower leaves of clematis turn yellow and dry, there can be many reasons for this problem. Why does clematis turn yellow:
- climatic conditions do not correspond to the planted plant variety;
- incorrectly selected site for planting;
- watering is carried out during a period of strong sun activity;
- there is not enough space for the plant;
- excessive irrigation, stagnant moisture;
- applying an excessive amount of fertilizer;
- unprepared soil for planting;
- the development of fungal diseases;
- damage by pests.
If the leaves of clematis turn yellow, what should I do? - First of all, you need to find out the reason. After its elimination, the plant will grow and develop fully. Often, despite the care and the right place, the treatment with chemicals, the leaves continue to turn yellow, brown and dry out.
In this case, you should think about the correct feeding of the flower. Every year it renews its shoots, spends a lot of resources on long-term flowering. It needs replenishment with mineral elements: magnesium, sulfur, nitrogen, iron, manganese, zinc and copper.
With a lack of magnesium, spots first appear on the leaves, then yellowing and wilting begins. The tips dry out and curl. This happens if you plant a bush in sandy soil. To avoid this problem, you need to add magnesium sulfate.
If young leaves begin to turn red or yellow, brown spots appear, this may indicate a lack of sulfur. To replenish it, you need to feed the plant with calcium sulfate or ammonium sulfate.
If the upper part of clematis begins to turn yellow, gradually going down, this indicates a lack of iron or that the soil is calcareous. The fight against this situation is carried out with the help of fertilizers that will acidify the soil - sulfuric acid, iron chelate. When manganese, zinc and copper are deficient, the leaves can also turn yellow and dry out. You need to treat the plant with copper sulfate, humus, zinc sulfate.
Why do clematis leaves dry
Diseases of clematis are almost always manifested by negative symptoms on its deciduous mass. Rust is the most common reason for the leaves to dry out.First, spots appear on the leaves, after which they begin to curl, dry out and completely fall off.
Also, one of the reasons for the drying of the leaves is the growth of weeds around the plant. Insufficient watering can also provoke such a problem.
Why does clematis fade
Sometimes flower growers are faced with the question of why clematis withers. Common causes of the problem are:
- pests that are localized in the root system, rodents;
- lack of watering or excessive watering, in which the root system decays;
- lack of proper care - overgrowth of weeds;
- insufficient amount of nutrients in the soil.
Clematis leaves turn black: what to do
Also, lovers of ornamental plants may face such a problem as blackening of the leaves. The following reasons can cause this symptom:
- rust;
- necrosis;
- wilt;
- damage by pests;
- excessive watering.
If clematis leaves turn black, what to do:
- process with fungi;
- treat with insecticides;
- reduce the amount of watering.
Brown spots on clematis leaves
Most often, brown spots are the result of the development of rust. Also, such a problem appears with the development of gray rot.
Fungal diseases of clematis and their treatment
Verticillium wilting, or wilt
Clematis wilt is a very serious disease.
Wilt tends to spread quickly, as a result of which the plant dies. Most often, wilting begins to appear at a time when abundant flowering and maximum shoot growth begins. At this time, the root system is under increased stress and becomes vulnerable to the development of diseases. Excessive soil irrigation can also provoke the appearance of pathogenic flora. Wilt manifests itself with the following symptoms:
- wilting of the upper shoots;
- drying of leaves;
- brown shoots.
The fight against wilting should be carried out as quickly as possible. The first thing to do is remove the weeds around the bush. Next, treat it with a solution of Fundazole or Previkur. In spring and autumn, water the bush with a solution of wood ash, dolomite flour. If the infestation is too strong, the plant dies. It needs to be dug up and disposed of.
Phomopsis
Very often the plant infects the fungus Phomopsis. It appears as brown spots on large leaves; as it develops, the leaves turn black and fall off. The fungus also spreads to the shoots.
The bush is treated with fungicidal solutions. Fallen leaves and affected shoots must be disposed of. Water stagnation should not be allowed, if necessary, you need to transplant the bush to a sunny area.
Gray rot
With high air humidity, with prolonged rains, clematis can be vulnerable to the development of gray rot. Buds, leaves and stems are covered with gray-brown spots.
The causative agent of the disease is a fungal microorganism, its spores quickly spread to leaves and stems. The fight against the disease is carried out with the help of fungicides - Fundazol, Previkur.
Fusarium
Clematis undergoes fungal wilting caused by Fusarium. The mycelium of the fungus penetrates into the weakened tissues of the plant, disrupting the conductivity of blood vessels, metabolism. More often, such a disease appears on large-flowered species, on young plants.
Description of symptoms:
- rolling leaves;
- the appearance of brown spots on the edges;
- wilting of shoots and leaves.
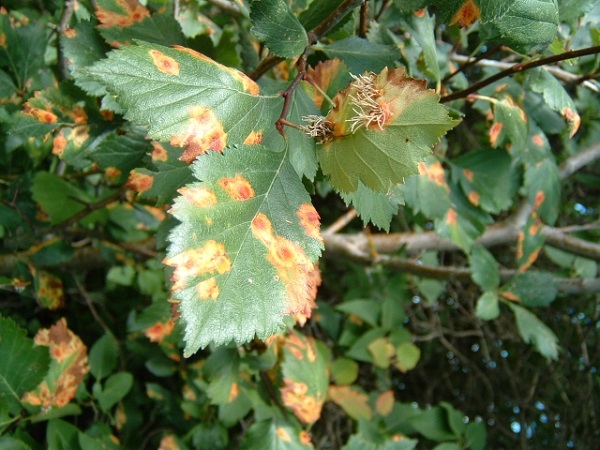
Rust
Affects ground parts of the plant.On the deciduous mass, the stems, bright orange spots appear. Gradually, these parts of the bush die off. The cause is fungal spores, weeds are carriers.
Treatment:
- remove all parts of the bush that have signs of the disease;
- treat with Fundazol, Previkur, Ridomil;
- treat with solutions containing copper.
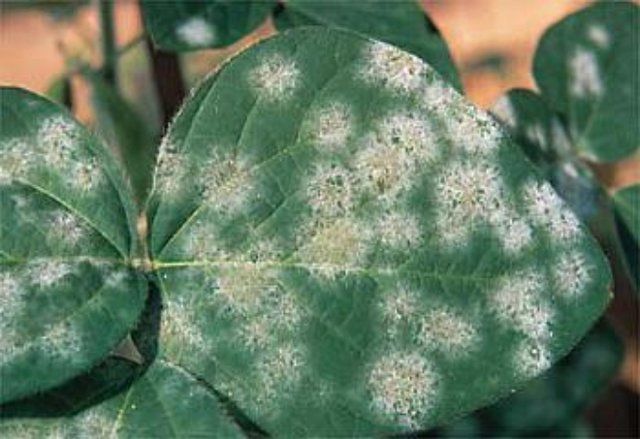
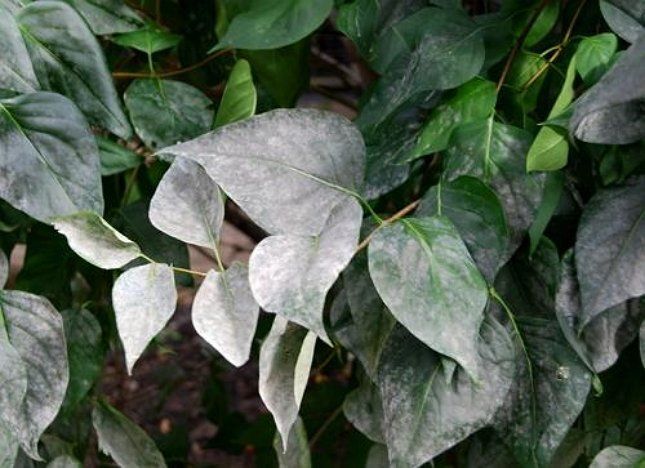
Powdery mildew (Erysiphales)
Clematis are vulnerable to powdery mildew.
Treatment:
- spraying with Fundazol, Previkur, Ridomil;
- treatment with copper chloride.
Ascochitosis
It appears as spots on the leaves in the middle of summer. The causative agent is a scochite mushroom. The result of his vigorous activity is dark brown spots.
Treatment:
- remove damaged parts of the plant;
- spray with a copper-containing preparation;
- treat with a solution of copper sulfate.
Alternaria, septoria, cylindrosporiasis
The causes of these diseases are fungi. Symptoms - the appearance of dry spots, the death of foliage and shoots.
Treatment:
- fungicide treatment;
- spraying with preparations containing copper.
Viral diseases of clematis and their treatment
Yellow mosaic
This viral disease is rare. It is manifested by the loss of foliage color, up to complete discoloration.
Insect damage to clematis
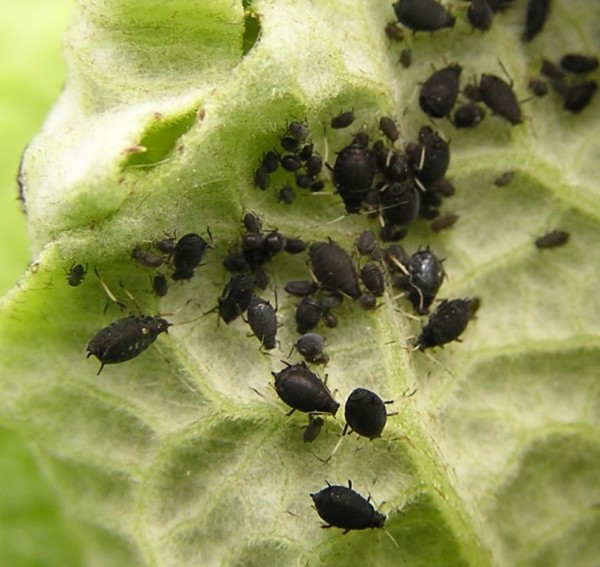
Aphids on clematis: how to fight
This pest affects all parts of the bush.
It hibernates on weeds or on neighboring plants, may hide on clematis.
If aphids appear on clematis, how to deal:
- tobacco dust treatment;
- application of the drug Antitlin;
- spraying with any insecticide.
Spider mite (Tetranychidae)
When affected by a spider mite, yellowing of the foliage, drying out of the buds, the appearance of cobwebs on them is noted.
The fight is carried out using:
- infusion of garlic;
- acaricides.
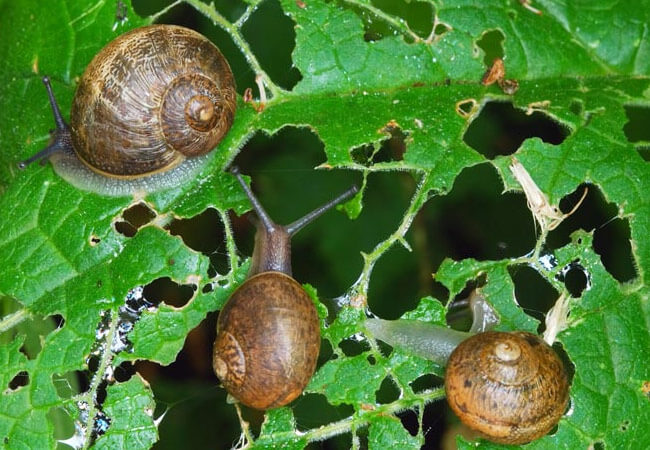
Snails and slugs
These pests are especially dangerous in spring, as they eat young stems and buds.
Control measures are:
- timely weeding;
- manual collection of pests;
- using baits - cabbage leaves, boards.
Nematodes
Microscopic worms called nematodes damage the root system of clematis. As a result, the leaves become pale, flowering stops, the plant dies. It is useless to take any measures against these pests. The affected plant must be dug up and disposed of. Prevention consists in planting near the bushes of marigolds and calendula.
End moth
A small butterfly that then turns into a caterpillar.
You can fight them with acaricides or insecticides.
Small true moth
It is a butterfly that also transforms into a caterpillar.
The fight consists in manually collecting caterpillars and pupae, in spraying the bushes before the beginning of the flowering period with Agravertin solution or other insecticide.
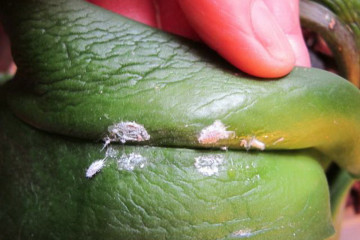
Mealybug
Mealybug or hairy louse feeds on young shoots, leaves, buds. The plant stops growing. The methods of struggle are as follows:
- soap solution treatment;
- processing with tobacco infusion;
- spraying with a solution of calendula pharmacy;
- the use of drugs Aktara, Callipso, Confidor, Fitoverm.
Shields
They feed on plant sap, after which the bush dries up. The methods of struggle are as follows:
- flushing plants with ethyl alcohol solution;
- the use of liquid potassium soap.
Bedbugs
The underside of young foliage is affected. Shoots stop growing, flowering stops. Destroyed with karbofos.
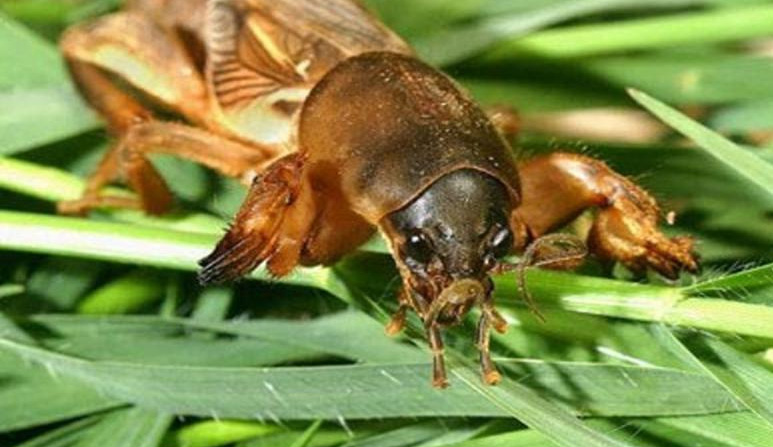
Medvedki
These are large pests that live in the soil.
They feed on plant roots. To destroy, insecticide Metarizin or soap solution is poured into holes.
Clematis can have a large number of diseases. These plants are susceptible to pests and are also sensitive to inappropriate weather conditions. However, there is a different treatment for every disease. Thus, today, with the modern abundance of store drugs and folk methods, clematis can be successfully grown.