Rhododendron University of Helsinki
Content:
Rhododendron University of Helsinki is the most frost-resistant variety of the entire genus. It easily tolerates temperature changes and a sharp cold snap. Feels good and blooms magnificently even after the most persistent frosts. But there are some nuances in planting and caring, which are described below.
History of origin
The history of the variety begins at the University of Helsinki, which at that time collaborated with the Mustila Arboretum. The cultivation of the variety lasted from 1973 to 2000. Only those specimens that were available in the Helsinki Arboretum and survived severe frosts in the period from 1930 to 1973 were involved in breeding.
Initially, 53 plants of the short-fruited rhododendron subspecies were taken for selection, for pollination of which 48 hybrid and 23 pure species were chosen. As a result of reproduction, 22 thousand seedlings were obtained, of which only 14 thousand copies were selected for further participation in the program. Severe frosts could not survive 5,000 seedlings. Of these, the most resistant plants were again selected, of which there were only 80, and then they were subjected to microchannel propagation. At this point, nine new frost-resistant varieties were registered.
Description and characteristics
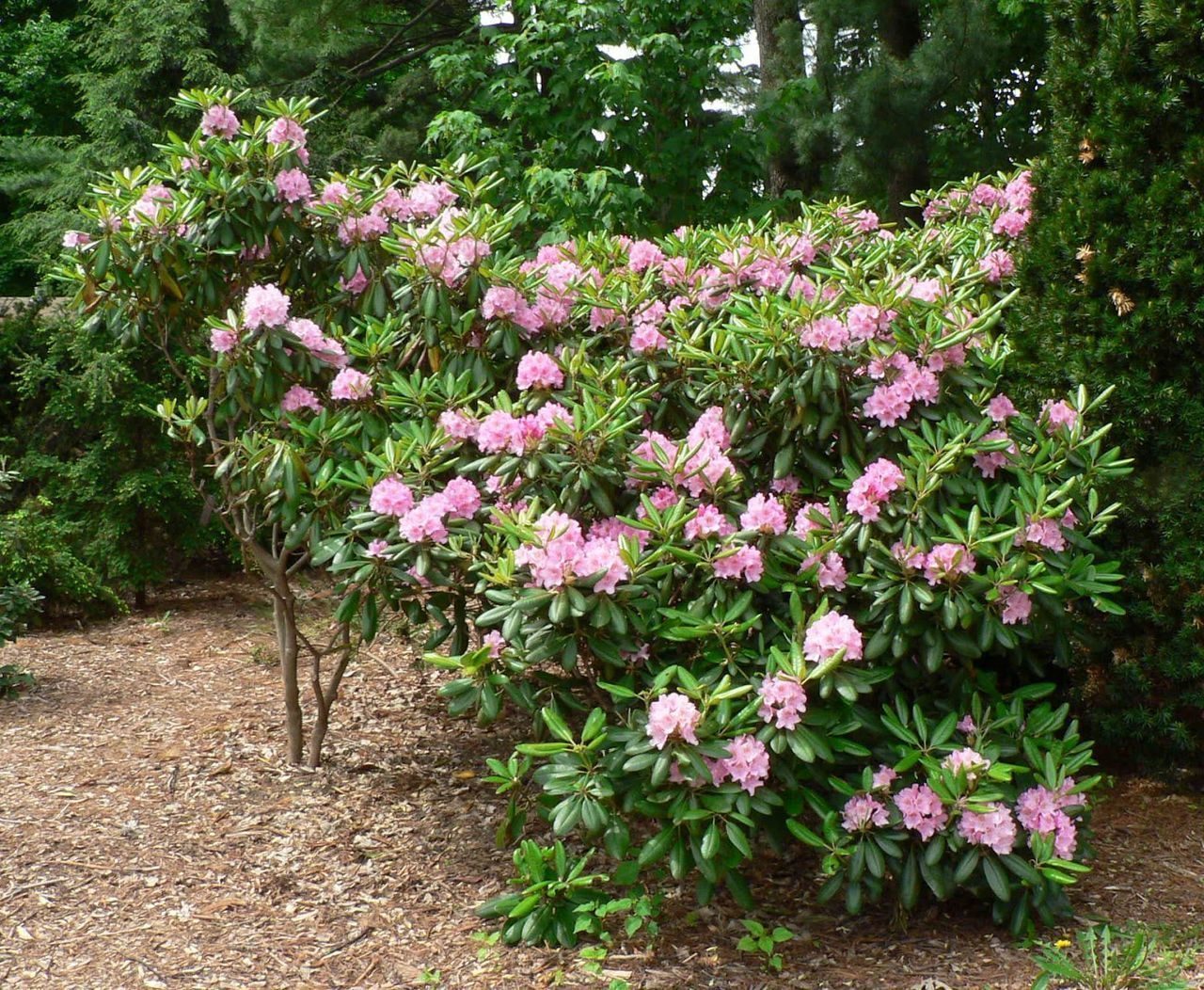
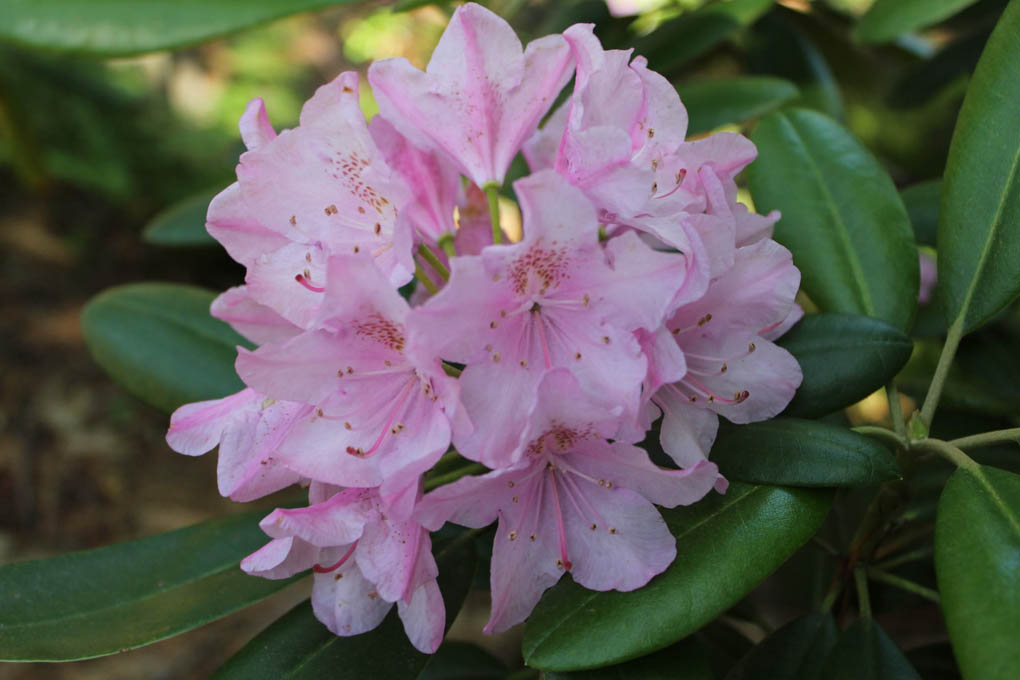
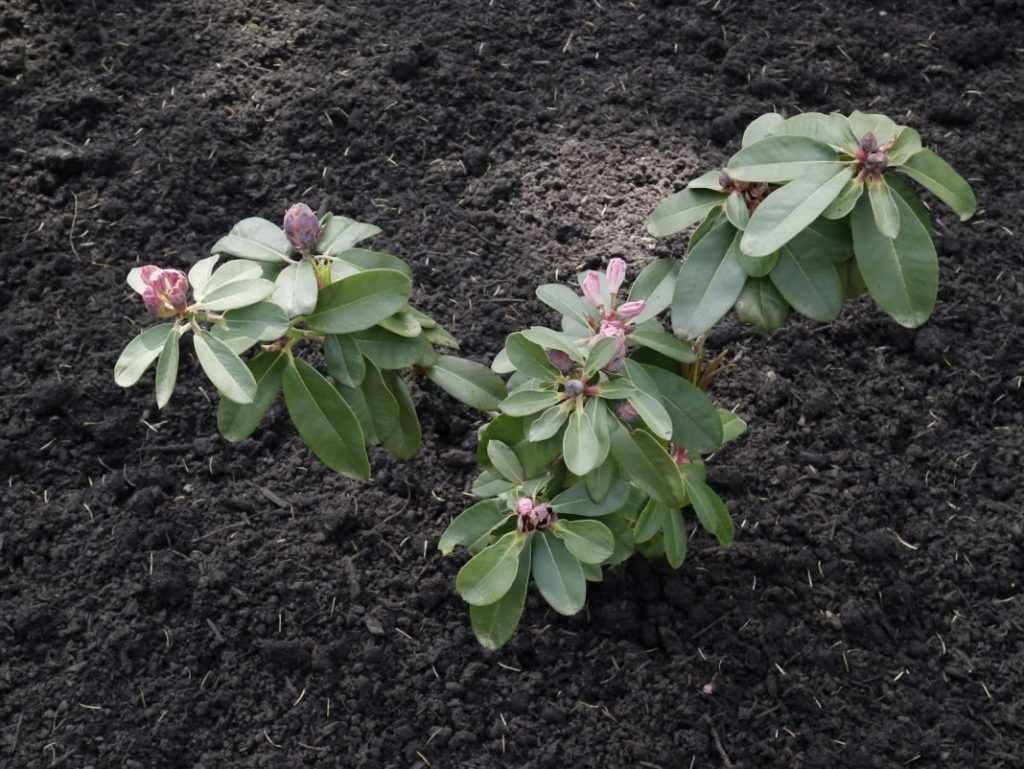
The maximum plant height is 2 m, by the age of 10 the plant rises by 1-1.5 m. It has a spherical crown, the average diameter of which is 1-1.5 m. The rhododendron leaves are dark green, oblong, reaching a length of 15 cm. inflorescences are on average 15 flowers. The buds are pink, six-petaled, have red spots inside.
In natural conditions, in particular, in the south of Finland, the evergreen rhododendron blooms in mid-June, in the northern regions this period begins later. Even after enduring the cold winter, the Helsinki rhododendron will bloom magnificently again.
Medicinal properties
Rhododendron University of Helsinki will not only decorate the local area, but also relieve the owners of ailments.
Therapeutic properties of the plant:
- bactericidal;
- diaphoretic;
- calming;
- antipyretic;
- pain reliever.
The leaves contain essential oils, tannins, ascorbic acid, rutin, arbutin, andromedotoxin, ericoline, phytoncides, etc.
Flower tea will help with colds, diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, urolithiasis, in the fight against staphylococci and bronchial asthma.
Tincture of leaves and flowers can be rubbed in with neuralgia, osteochondrosis, polyarthritis, sciatica, used for douching with erosion of the cervix.
Application in the garden
On the garden plot of Helsinki University, rhododendron is used to decorate paths, alpine slides. Can be combined with any ornamental plants, looks good with juniper and thuja.
Grows better in the shade than in the sun.When creating a composition, it must be borne in mind that the crown of the bush is dark green.
Care and cultivation of rhododendron
Planting and caring for rhododendron Helsinki University starts with choosing a good location. The soil must be acidic - pH 4.5 to 6.5. A porous, moisture-absorbing soil is suitable. In hot weather, the Helsinki rhododendron requires frequent watering, since its root system is shallow. Mulching will help to facilitate the task of moistening the soil. So that the roots do not interfere with each other's development, it is recommended to grow the bushes at a distance of 1.5 m from each other.
Cropping flowers
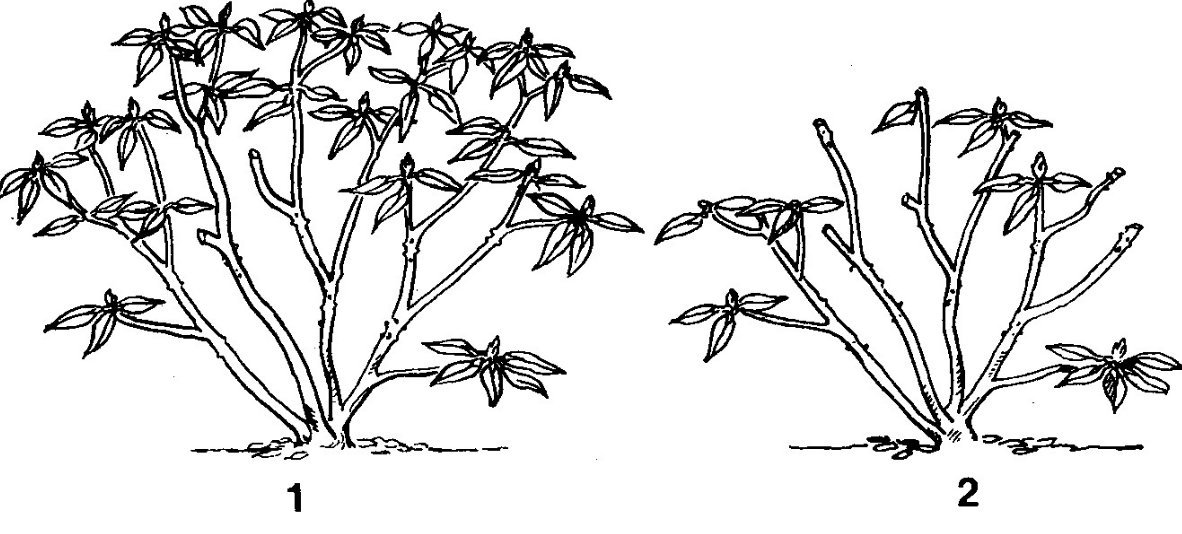
Only young shrubs of University's rhododendron need pruning. In the first year of life, all buds and damaged branches are cut from the plant. This is necessary so that nutrients are more directed towards the development of the root system.
In the future, trimming flowers and crowns can be skipped. The variety has the correct shape and does not need to be artificially formed. To rejuvenate the bush, only the removal of old, dried shoots is practiced. It is allowed to remove no more than 25% of the total mass of the bush. The places where the branches are cut are processed with garden varnish.
There is no need to wait for the plant to discard wilted inflorescences by itself, it is also better to cut them off immediately. This will help maintain the strength for flowering next year.
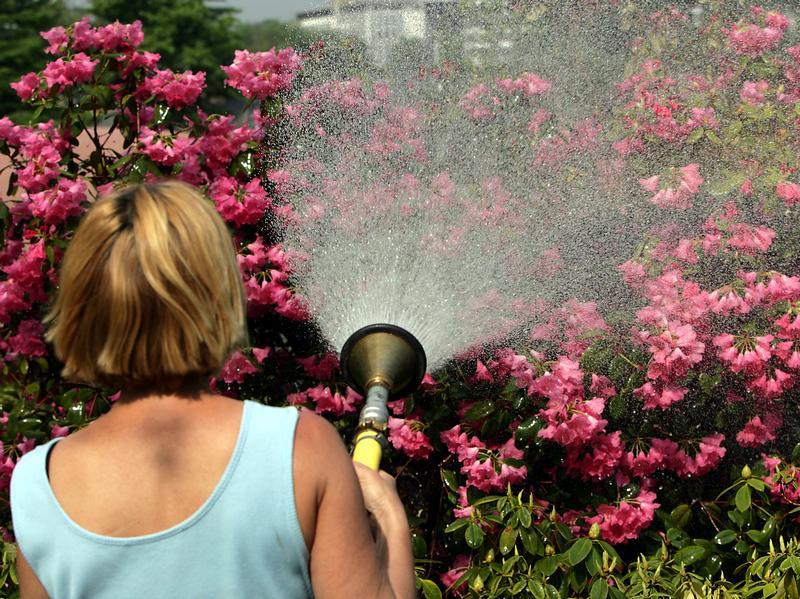
Watering and feeding
Rhododendron University of Helsinki loves a lot of moisture, so in the heat, 1 bush will need about 10 liters of water 3 times a week. Every evening the plant is sprayed. In autumn and winter, watering is almost not required, only as the soil dries up.
Water for irrigation is used soft, unsalted, acidified if possible.
In spring, the plant is fed with potassium and phosphorus (1: 2). It is important not to overfeed young specimens, so the fertilizer is twice less concentrated.
Fertilizers containing potassium, magnesium and calcium are diluted with a ratio of 1.2: 1000.
The fertilization scheme is as follows:
- 50 g per 1 m² of magnesium sulfate and ammonium sulfate is introduced in early spring;
- 20 g of potassium sulfate and superphosphate, 40 g of ammonium sulfate are introduced in June;
- 20 g of potassium sulfate and superphosphate are introduced in July.
A good option is a top dressing made from semi-rotted cow dung, which is diluted with water in a ratio of 1:15. Before applying the fertilizer, it should be infused for several days.
Preparing for winter
In winter, plants are not dug up, they tolerate frost well. However, to avoid drying out the leaves, the shrubs are covered with burlap or other textile material that allows air to pass through.
Reproduction
In nature, the plant propagates by seeds, at home it is easier to use cuttings or layering.
Cuttings
Semi-lignified shoots are cut up to 8 cm long, the lower leaves are cut off. The cuttings are placed in a vessel with a root growth stimulator for 16 hours. For rooting, a mixture of peat and sand in a ratio of 3: 1 is used. The cuttings are covered with a jar or transparent film. Rooting period is from 1.5 to 4 months.
Layers
An easier and faster method is used right on the land. For reproduction by layering near the mother shrub, a groove is pulled out, into which the middle part of the shoot is inserted and sprinkled with earth. The top of the branch is tied to an upright peg. When the twig takes root, it can be cut off and transplanted to another location.
Seat selection
The place for growing rhododendron is chosen shaded, in nature it grows in a pine forest, which lets in but reduces sunlight. Shrubs will do well on the north side of the site.
Diseases and pests
Hybrid rhododendron Helsinki University can be infected by the following parasites:
- slugs;
- snails;
- spider mite;
- shield;
- rhododendron bug;
- weevil.
Slugs and snails are collected from the bush by hand, with other pests the situation is more complicated. Small insects die after treating the shoots with fungicides, karbofos, but the weevil can be dealt with with diazonin.
Prevention of various problems
The best disease prevention for the Finnish rhododendron is the right choice of location and plant care. Rhododendron is more vulnerable if it grows in the sun, in alkaline soil, oversaturated with moisture or fertilizers.
As a preventive measure, at the end of autumn, the shrub is treated with a solution of Bordeaux liquid.
Rhododendron is not a plant for the lazy. Only by providing him with special care, you can wait for the results. Lush flowering will not leave indifferent any grower.