Hosta - boarding and leaving
Content:
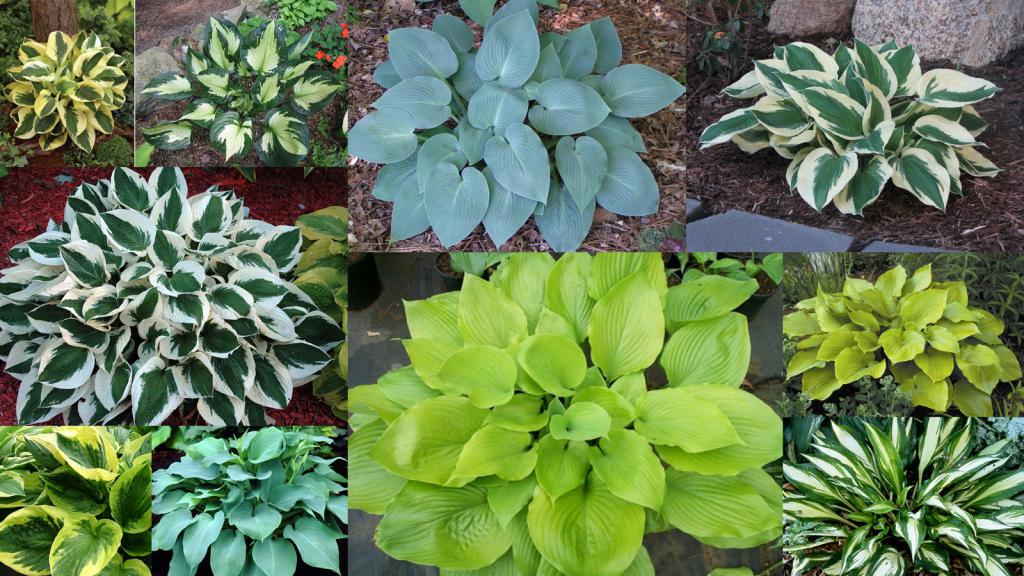
When breeding perennials in the country, most gardeners prefer this flower - the host, or funkia. If the host is cultivated, planting and caring for an unpretentious plant is available even to a beginner. In order for the culture to please with its decorativeness, knowledge of the rules of how to care for a host is appreciated.
Transfer after purchase
Perennial herbaceous culture, numbering more than 40 species, grows in the Far East and East Asia. For a bush, a place near a reservoir is preferable.
The correct choice of place is responsible for the well-being and life span of the flower. A perennial is able to grow in a flower bed without replanting for 20 years. It serves as a sure base for a flower bed of continuous flowering.
If hostas are engaged in breeding, planting and care in the open field are ideal for spring: from the 3rd decade of April to mid-May (after the threat of return frosts).
It is advisable to prepare the soil in the fall: dig up the flower garden on a shovel bayonet and add organic matter.
Summer residents are interested in when and how they plant the host. Many gardeners practice planting from late summer to the first half of September. If the flower is planted at a later date in the fall, it may not take root until frost arrives. The soil is intensively watered before planting.
Cultivation of crops in the garden is carried out in unprotected soil, bushes are planted on flower beds near hedges or together with ground covers and ferns. Some growers grow hostu in tubs, flowerpots, containers. They decorate the site with original compositions.
A perennial plant is not afraid of cold weather. Cultures or rhizomes bought in pots are planted in the garden in the spring when the air warms up to + 12 ... + 14 ° С. Adult gardeners do not need shelter for the winter season.
The host does not like stagnant water, waterlogged soil, strong winds. Water the flower early in the morning at the root.
Optimal location
For landing, hosts are preferable:
- a place in partial shade that shelters from the winds;
- humus soil, with drainage, moist, with a neutral or slightly acidic pH level. The hosta flower grows poorly on heavy clay and sand. The soil mixture should include in equal proportions humus, peat, vermiculite, leaf turf. Crops like fertilization.
It is advisable to locate the flower garden in a draft-protected area: the lawn behind the house or by the pond, in the northern zone of the garden. But variegated varieties need sunlight to maintain their vibrant color. For blue and gray varieties, shade is suitable, they have enough light for 2 hours a day. It depends on the partial shade what the leaves will grow, while the development of the bush slows down. The host will be harmed by the bright sun throughout the day - leaf burns are possible.
Choosing a location is a key component of success, which tells you how to land the host correctly. The sun is responsible for the correct color, but it accelerates aging or completely destroys the foliage. The most suitable localization is shade and partial shade.
Growing in full sun is not suitable for plants. Certain varieties require a lot of sunlight and special care: a constantly moist substrate to replenish water supplies due to rapid evaporation.
To grow a plant in the sun, you will need:
- specially prepare soil containing compost, peat;
- apply mulch to protect the soil from overheating and moisture evaporation.
When growing a crop in a sunny flower garden, the color of the leaf plate will change under the following conditions:
- yellow hosts will get white foliage;
- in blue varieties, the leaves become greenish.
Yellow varieties cope with a large amount of ultraviolet radiation in the morning and at noon. It is preferable to grow multi-colored varieties in partial shade. Pigment-free varieties (Color Glory, Supernova, George Smith, Tokudama Aureonebulosa, Dance with Me) are located on a flower bed without solar access.
Step-by-step planting process
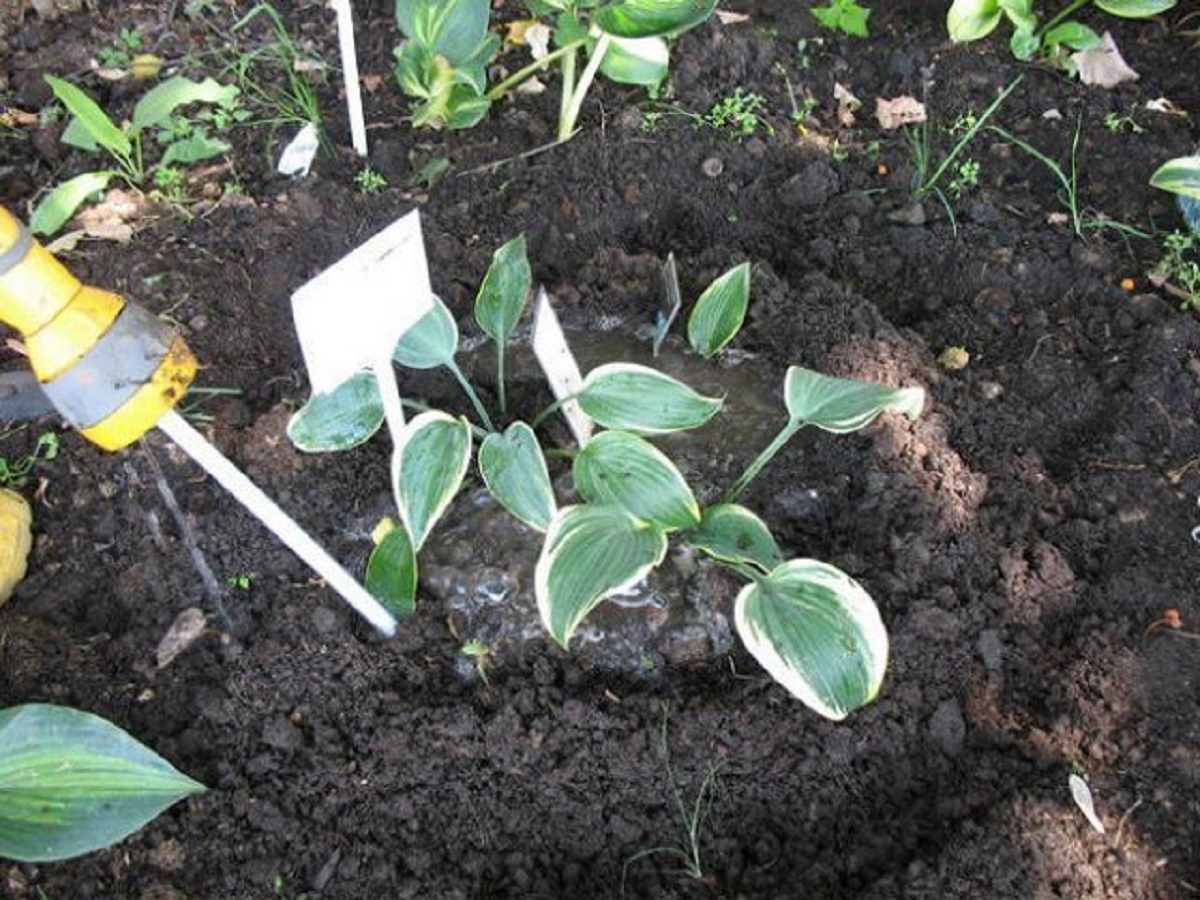
When planting hosts in an open flower garden, they are guided by a step-by-step scheme. Would need:
- Dig holes in 40-60 cm increments for normal species and 90-100 cm for tall species.
- Fill the hole 2/3 with peat or compost.
- Water the seedlings, remove them from the flowerpot along with a lump of earth, inspect the cuttings for damage or root rot.
- Place the seedlings in the holes.
- Straighten the roots, cover with earth, water.
- Add mulch to the soil near the seedling - sawdust or bark.
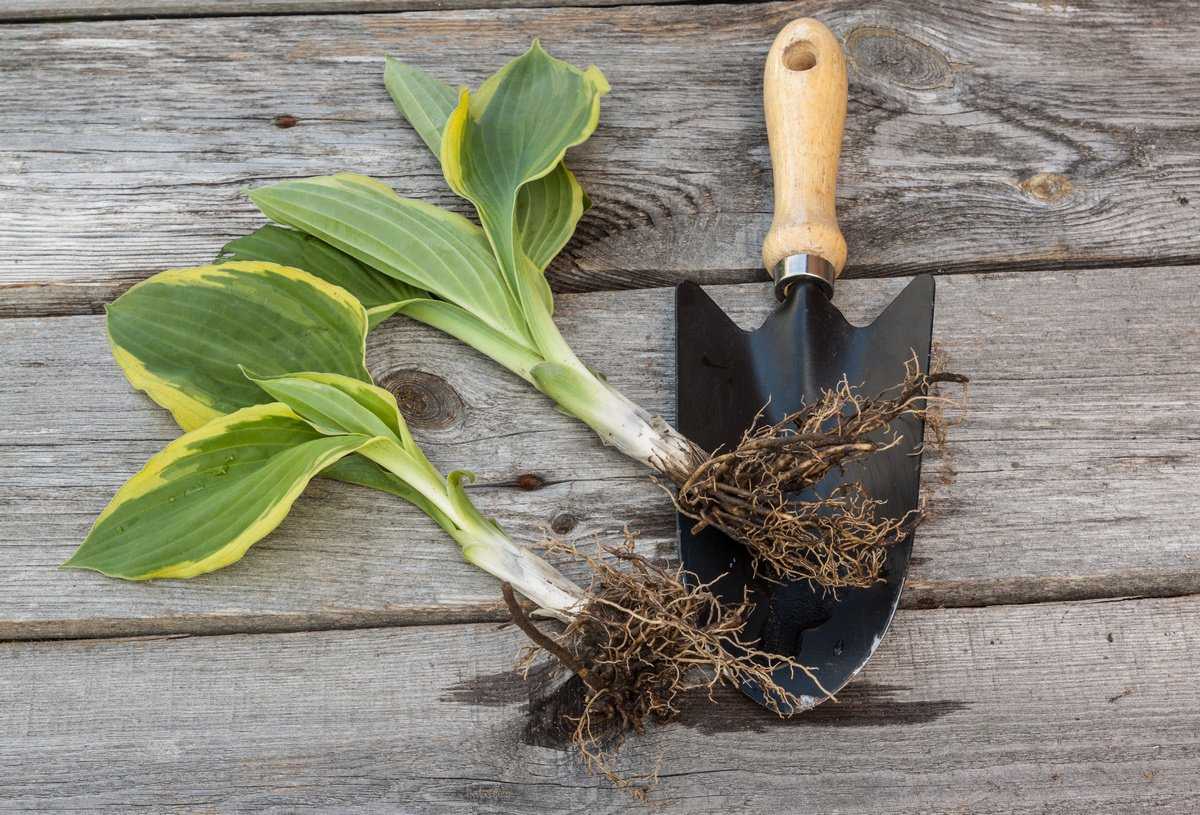
Planting material for disembarkation is carefully selected. 10-12 cm roots are elastic. It is desirable that the seedling has 2 or 3 buds.
When planting, the buds are located at the level of the soil. If necessary, add additional soil under the root.
Planting a crop in unprotected soil in spring is determined by meteorological conditions and air temperature. In the Urals, it falls at the end of the spring or the arrival of the summer season, in the Krasnodar Territory, work begins in the last decade of April, in the Moscow region - until May 15.
Outdoor care
Watering mode
Hosta care involves drip irrigation. He is responsible for the beauty of foliage, size, filling with energy. In the absence of an opportunity, the hosts carry out watering, trying to avoid getting on the leaf plates.
The manipulation will prevent the wax from being washed off the sheet surface. This is of great importance for blue varieties, in which the wax determines the color. Gentle spraying reduces the risk of fungal infections and foliage sunburn.
It is useful to water the plant in a timely manner, the soil must constantly be slightly moistened.
A favorable time to water the flower is before 11 o'clock in the morning. If it is cloudy outside, it is allowed during the day. Otherwise, he will get burns if water drops fall on the sheets.
Top dressing
When the hosta grows up, care determines its appearance. The introduction of dressings affects the decorative effect of the flower. It is advisable to feed the plant three times during the growing season:
- at the stage of growth;
- in the flowering phase;
- after flowering.
Often, feed with nitrogen (N), potassium (K), phosphorus (P) is used. Humus is also introduced, which is fed in the fall. Organics are preferred over mineral dressings. The main thing is not to overdo it. Too frequent or intense feedings are the cause of burns.
This factor affects the color of the foliage, its weight, elasticity. The flower does not need abundant feeding. Fertilize several times during the season or use prolonged-release feeds.
It is important to respect the proportions of the ingredients when fertilizing the host. Excess nitrogen leads to lightening and dilution of the pigment, therefore, they make recharge in 2 stages: in early spring, while the leaves are formed.In the phase of juice separation and recovery from hibernation, fertilize with humus. As a mineral component, agents with a nitrogen content plus calcium nitrate are used, which are introduced during the formation of the first shoots.
According to the responses of summer residents, it is preferable to apply a handful of fertilizers per crop for large plants, less for small plants, a teaspoon is enough for miniature flowers.
In the spring-summer season, the coloration of the hosta depends on the balance of the contained nutritional components (phosphorus, potassium, nitrogen) in the ratio: 1: 1: 1, 1: 1: 2 or 1: 2: 1.
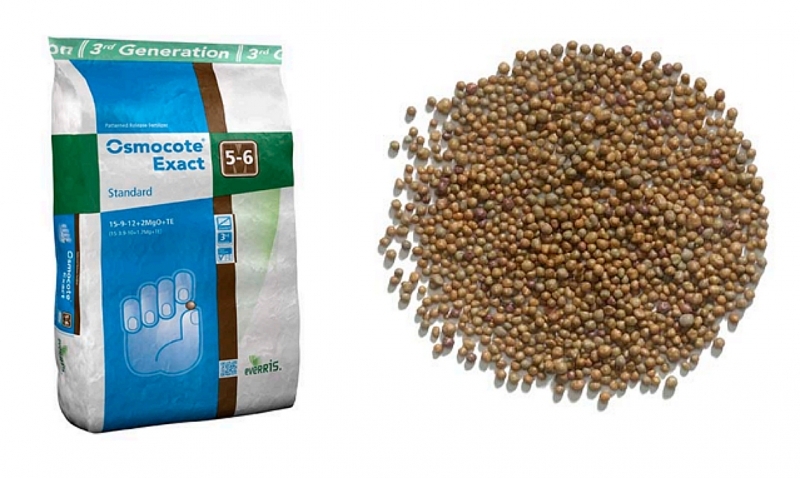
This period is suitable for the use of make-ups with a long-lasting effect, for example, Osmokot.
In addition, it is important to fertilize crops 2-3 times with foliar feed. Chelated nutrients are ideal. Foliar feed with a predominance of nitrogen is suitable for plants with green or yellow foliage.
These preparations are used with caution for blue hosts. They help transform it from blue to green culture. For blue varieties, fertilizing with balanced NPK is appropriate.
Organics are rich in micro- and macronutrients. It guarantees the safety of the flower. Top dressing is difficult to use, in order to maintain the required NPK ratio, changing the color of the foliage cannot be avoided.
When planting hosts in fertile soil, they do not think about fertilizers for 3-4 years. The use of organic matter falls on the 5th year late in the fall, with the onset of spring it is introduced in the form of mulch:
- herbs;
- compost;
- straw;
- peat;
- overripe manure.
When the growth and pallor of adults deteriorate, granular fertilizer is applied to the loosened soil, where the components are contained in the same volume. Then the flower is intensively moisturized at the root.
It is easy to find in stores special fertilizers in liquid soluble form with micro- and macronutrients for deciduous ornamental crops. They are suitable for a flower, contribute to the correct development, improvement of expressiveness and texture, contrast of heterogeneous foliage.
During flowering
If the hosts are engaged in cultivation of the flower, care and cultivation during flowering provide:
- weed removal and systematic loosening;
- feeding with liquid-soluble fertilizers;
- regular hydration: twice a week, in case of drought, increase the volume;
- release from old flowers;
- pest control.
Growing a large number of plant species on a flower garden increases the threat of getting crops affected by diseases and harmful insects. It is useful to carefully select planting material, periodically inspect the flowers.
To preserve the appearance of the hosts, arrows and buds are removed.
During the rest period
When the plant finishes blooming, timely removal of peduncles is carried out, preventing the bush from loosening.
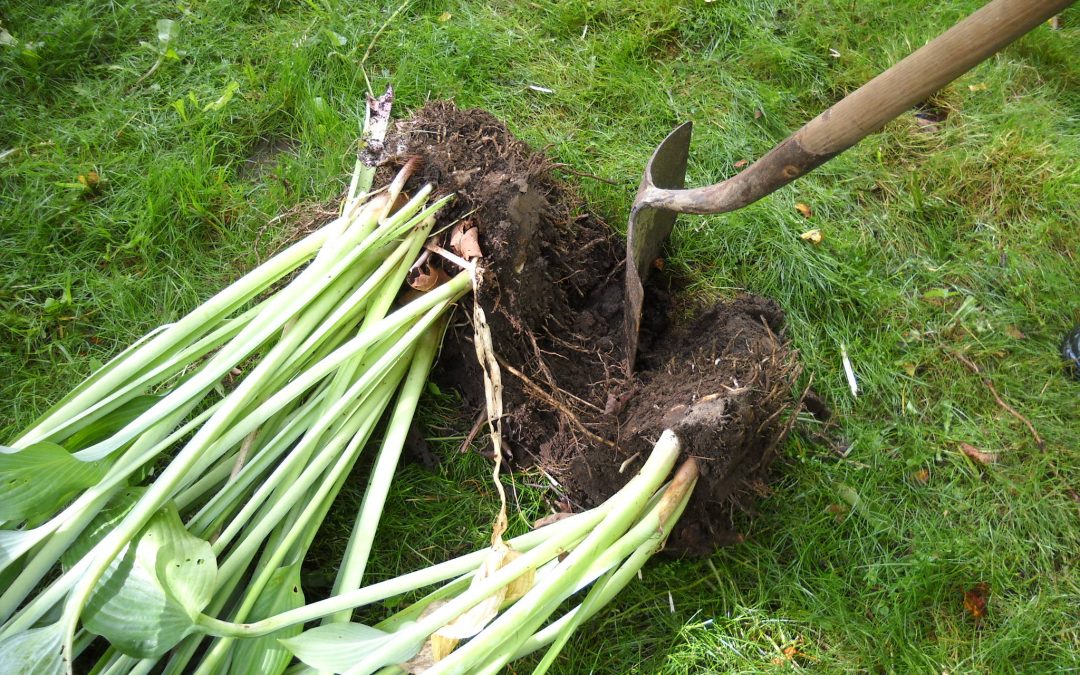
Every year in the fall, adult specimens, which grow strongly, are transplanted. Flower reproduction is carried out by dividing the bush. The host is watered intensively, dug up and divided into segments. Each piece includes 2 sockets as well as spines.
The plant is planted until mid-September. While the cold weather comes, the seedlings should take root and prepare for wintering.
The soil for transplantation is chosen fertile and breathable. Wells with cuttings are moistened and mulched with sand or sawdust.
Preparing for winter
Correct preparation of the flower for winter is appreciated. You will need to cut off the flowering shoots, sprinkle the soil near the hosta with foliage, sawdust, peat. Foliage pruning is not carried out.
The fallen snow is used to additionally cover the bushes. Cover the host with spruce legs. It is undesirable to cover the culture with a film - the access of oxygen is blocked, conditions are created for the survival of pests.
Some gardeners transplant the hosta into a flowerpot for the winter and grow it at home on a windowsill.However, the opinions of florists differ as to whether the host can be a room culture. According to individual summer residents, the flower feels great only in an open flower bed. Other growers say with confidence about the possibility of growing hostas as a potted plant, if the rules of agricultural technology are followed.
Removing foliage is a controversial issue among gardeners. In warm areas, foliage is removed at the root to protect the plant from parasites hiding in the greenery. In the north, it is preferable to leave the leaves as protection from frost.
The queen of a shady garden opens up great opportunities for gardeners in landscape design. The unassuming flowers of the host will decorate the summer cottage and will delight the owners and passers-by for a long time, if you follow simple tips and recommendations for care.