Garden chrysanthemum - planting and growing
Content:
Garden chrysanthemum is often found on household plots throughout the Russian territory, its second name is "Chinese". The culture is characterized by a variety of colors of buds and sizes - from miniature to tall, striking with its luxurious crown.
Garden chrysanthemum - what kind of flower is it, what family it belongs to
The basis of modern chrysanthemum varieties is Chrysanthemum morifolium, which is a representative of the Aster family (Asteráceae). The shrub belongs to the varieties that bloom with the arrival of autumn. It perfectly tolerates cold and does not lose its buds even with the first frost.
The first information about the culture was found in the works of Confucius, in the 5-6th century BC. At that time, she looked more like her wild counterparts and had medium-sized flowers, painted in a yellow tone. The plant became the progenitor of modern hybrid varieties, today there are about 3 thousand species of them.
A perennial shrub has a thick and branched root system, from which powerful shoots emerge. Stems grow to 25-120 cm, densely covered with leaf plates. Green foliage grows from 7 to 15 cm in length and from 4 to 8 cm in width. Plates located on the upper and lower tiers differ in volume and shape. Some subspecies have long or short petioles; pubescence predominates on the seamy side.
Plant varieties, popular winter-hardy varieties, what they look like
Experts distinguish several classifications of chrysanthemums due to the different approach to their selection. The Chinese version is considered complete and versatile.
Classifications by flower size and height
According to the Chinese version of Chang Shu-lin, the division is carried out by size, into small-flowered and large-flowered subspecies. It is customary to distinguish about 25 classes:
- the first subgroup includes 8 types;
- to the second - 17 units.
Classification by the shape of inflorescences
The division is made according to four options, due to the presence of tubular and reed flowers in the inflorescences:
- flat;
- anemone;
- tubular;
- spoon-shaped.
Selection by varietal characteristics complements the description with the number of certain buds, the ratio of their size, for other qualities. There are seven subgroups of plants with different petal colors:
- white;
- bronze;
- yellowish;
- green;
- red;
- cream;
- purple.
There are bicolor varieties, with different tones of inner and outer petals. According to the description of Wang Mao-shen, 9 variants of inflorescences can be distinguished in culture:
- hairy - with slight pubescence on the lower parts of the corolla;
- radiant - radically symmetrical, more like feathery;
- terry - the inflorescence is symmetrical, the outer corollas are long, and the inner ones are short;
- osmanthus - similar to the osmanthus flower;
- feather-like - with a large, medium and small volume;
- hemispherical and spherical - flowers in appearance resemble balls;
- simple or semi-double - with wide rims and slightly curved tips;
- grasping - their corollas can be compared to thick tubes.
Flowering classification
In Japanese territories, the preference is given to the classification "Shinjuku" - the imperial park.
Its experts prefer to divide into wild and cultural types. The latter are additionally subdivided into decorative and suitable as food (when preparing salads). Terry chrysanthemums and others (for decoration and decoration) are divided according to the ripening period into winter, summer and autumn subspecies.
Perennials and annuals
Annual variants are characterized by small bud sizes (up to 4 cm in diameter) and several classes:
- keeled;
- multi-stemmed;
- sowing;
- crowned.
Annuals have a long flowering period: from late June to November. The buds wither along with the persistent frost. The culture comes in different sizes: 25-70 cm.
Compared to single-season, bush perennials are larger in growth, can reach 150 cm. They are grown both in personal plots and in pots. Large-flowered varieties are used as cutting material. The division is carried out according to the period when they will bloom: early, middle and late type.
Perennial chrysanthemums: planting and care in the open field
To get a beautiful and healthy plant, you must first familiarize yourself with the literature on how to grow chrysanthemums in the garden, take care of a flower in the country or in a greenhouse.
It should be noted that these flowers are resistant to drought and cold, do not require special care in the garden. The list of exceptions includes only new hybrids with large flowers, which need to be looked after more carefully: water and fertilize more often.
Location selection
How to plant chrysanthemums correctly: the culture is completely dependent on light, with a lack of it, the quality of flowering may suffer. Shoots begin to stretch, buds begin to shrink, in areas where other crops can live peacefully.
The result will be an ugly and creeping shrub. In order for him to maintain an ideal crown, it is necessary to plant the young on the sunny side, with protection from gusty winds.
How to prepare the soil and flower for planting
Understanding the question of how to plant chrysanthemums, one must not forget about the quality of the earth.
Requires sandy loam or loamy soil with good drainage. Before work, it is carefully dug up and enriched with humus. The soil should have a slightly acidic reaction; peat is taken for mulching. Heavy and clayey lands are prohibited - the shrubbery on them will quickly die.
Features of planting chrysanthemums before winter
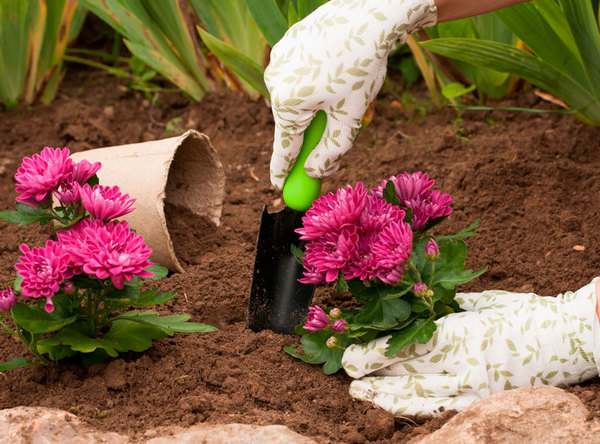
Pre-winter planting of bushes is carried out until September 15, young plants with closed roots are used for the procedure. This approach will eliminate the need for preliminary preparation. If the roots are bare, then 24 hours before disembarkation, treatment with Kornevin is carried out.
The landing procedure looks like this step by step:
- Dig holes 40 cm deep, leaving gaps between them at about this distance.
- River coarse sand or screenings - 5 cm are laid out on the bottom.
- The substrate is altered with humus.
- Planting is carried out without burying the shoots.
- For tall shrubs, prepare a support.
Watering rules and humidity
Long-lived bushes can live for a long time during drought, but are sensitive to its lack. Insufficient irrigation leads to fragmentation of buds and a decrease in their numbers. With insufficient watering, the shoots are covered with bark, and with an excess of water, the roots rot.
Irrigation is carried out when 5-7 cm of the top layer of the earth dries up. In hot weather, the soil is moistened more often, in cold weather - less often.
Top dressing and soil quality
The lack of mineral elements provokes faded and lethargic buds, and timely fertilization helps to extend their life and increase the total amount. The subcortex is carried out according to the schedule:
- after disembarkation or in spring - with nitrogen mixtures;
- in the middle of summer - potassium-phosphorus solutions.
Pruning and replanting
For some subspecies, an increase in their branching is required: with the development of 10 to 20 cm, pruning is carried out. Cut off tops (5-7 cm) are used for rooting. The remaining shoot should have at least 3 or 5 pairs of leaves.
Transfer works are carried out on May or September days. They are made for rejuvenation of shrubs, reproduction, or when forming a certain version of a flower garden.
Wintering a flower
Careful preparation for winter is not required for perennial chrysanthemums (winter-hardy) planted in the southern regions. For the northern regions, activities are carried out:
- hilling shrubs;
- pruning to 10 cm at the end of October;
- shelter with agrofibre after the arrival of stable frosts, with fixing it with weights (boards, bricks).
Features of flowering plants
Different culture variations may differ in terms of bud formation and their characteristics.
A period of activity and rest
At the beginning of the flowering of the shrub, the apical buds are the first to open, then the process covers the entire plant (from top to bottom). The duration of budding is from 2 weeks to several months.
Types and shape of flowers
Chrysanthemums are tall, dwarf and medium in size, the tallest require support.
Separate, prone to falling, shrubs are tied up with the arrival of spring.
Post-flowering care
Withered buds are carefully cut off, leaving flower stalks before the arrival of frost. Attempts at complete excision will lead to serious problems: the rhizomes will not be able to lay buds for the next season due to a lack of nutrients, the source of which is the green part.
Flower reproduction methods
Gardeners prefer to use cuttings, seed method and division of the mother bush.
Propagation by cuttings
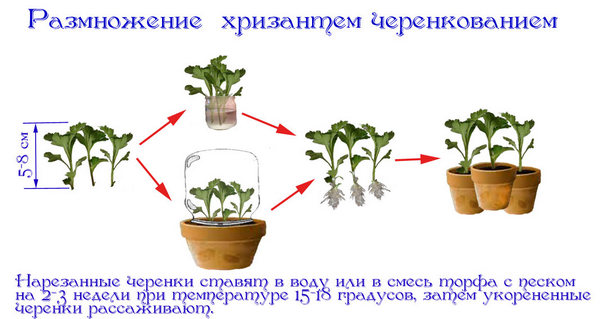
To obtain scraps, bouquets or adult shrubs are used. In the first case, you need to remove the flowers, and put the cuttings in water. After a few weeks, they will form roots and can be planted in open ground.
Self-cutting of material from the bush is carried out in May.Healthy specimens are suitable for the procedure, cut shoots are sent to a depth of 5 cm (to previously dug areas). From above they are covered with a piece of plastic bottle. By the end of the month, the seedlings that have taken root will give the first leaves.
Propagation using seeds
The seed method involves planting material for seedlings. After 2-5 weeks (the time depends on the varietal characteristics) the first shoots will appear. Until the days of May, seedlings are grown at home, then sent to a personal plot.
How to plant a chrysanthemum and achieve its flowering: seed material in the middle lane almost never ripens. To obtain it, cut shoots with buds, send them to a flowerpot with water. After a while, the seeds will ripen safely.
Growing problems, diseases and pests
Known diseases include:
- viral lesion by dwarfism, greening of inflorescences, mosaicism - pathologies are incurable, the affected shoots are excised and burned;
- powdery mildew - appears during a cold and rainy season, deficiency of phosphorus-potassium elements or an excess of phosphorus, the diseased shrub is treated with fungicidal solutions;
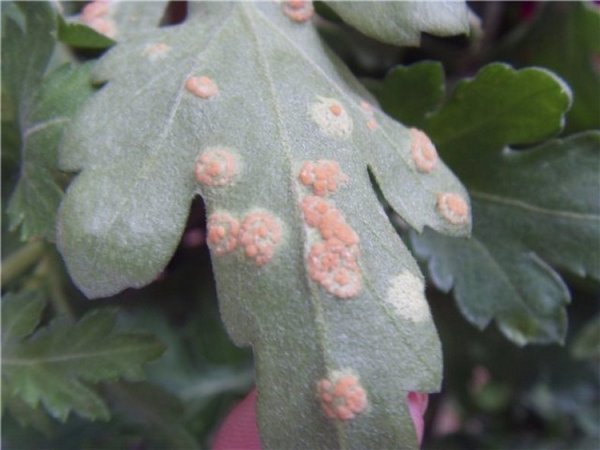
- rust - comes along with warm and humid weather, is determined by a yellowish-greenish spot on the foliage, which eventually turns into a brown color, therapy includes treatment with Bordeaux liquid and Topaz;
- septoria - spreads from the lower areas to the upper ones, manifests itself with black spots, occurs when there is a lack of sun and waterlogged soil, requires a reduction in watering and improved lighting;
- gray rot - determined by the characteristic grayish spots on the green part of the plant, with a transition to a brownish tone, treatment is carried out with fungicides.
Known parasitic insects are:
- nematode - damages not only the green parts of the shrub, but also the roots, requires prolonged treatment of plants with special agents: Phosphamide, Mercaptophos;
- spider mite - due to the sucking of the juices of the bush by the parasite, it begins to dry quickly, its presence can be determined by the cobweb covering the stems and foliage, processing is carried out by Fitoverm or Aktelik;
- aphids - the parasite often carries viral pathologies and is one of the reasons for the death of a shrub, the plant requires repeated treatment with insecticides.
The perennial garden chrysanthemum belongs to the luxurious decorations of the personal plot, but you can also love small indoor varieties. Which option is better: you can plant street mixes or potted chrysanthemums with burgundy buds. Each person has their own preferences, which is why it is impossible to give an exact answer to this question.