Diseases of nasturtium - why leaves turn yellow
Content:
- Diseases of nasturtium and their treatment
- Why do nasturtium leaves turn yellow, and what to do
- Why does nasturtium not bloom
- Why does nasturtium have sticky leaves?
- Why nasturtium dries up and how to save a flower
- How does nasturtium chlorosis manifest?
- What is powdery mildew in nasturtium (lat.Erysiphaceae)
- Gray rot (lat.Botrytis cinerea)
- Black rot of nasturtium (Latin Guignardia bidwellii)
- Signs of late blight
- Brown spot of nasturtium (Latin Phyllosticta petuniae Sp.)
- Causes of nasturtium disease
- Agrochemistry and plant protection
- Prevention and protection of nasturtium from pests and diseases
Not so long ago, nasturtium bushes began to be used to decorate flower beds. Until the 16th century, this plant was used as a spice with an unusual aroma. In the homeland of nasturtium, in Central America, the locals ate the roots of the plant. In Europe, the taste of leaves, flowers and fruits was first appreciated, and then flower beds in gardens were decorated with beautiful bright bushes with erect or creeping stems.
Diseases of nasturtium and their treatment
Medieval sailors returning from American voyages were treated for scurvy and colds with the seeds of nasturtium, which has the second name Capuchin (Latin Tropaéolum). Until now, the components of the plant are used in folk medicine, cosmetology, and cooking.
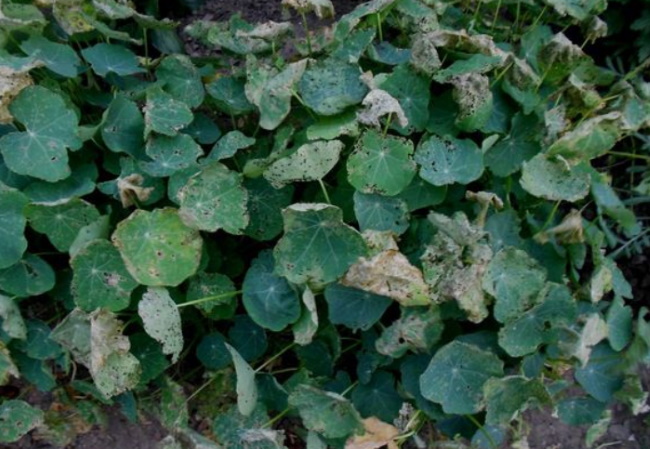
But the plant itself can also hurt - a lushly growing bush suddenly begins to droop, its stems wither, the leaves turn yellow, flowering stops, necrotic spots and rot appear. Fighting Tropaéolum diseases is not easy, but any disease can be made to stop if desired.
Why do nasturtium leaves turn yellow, and what to do
In favorable climatic conditions, thermophilic nasturtium grows as a perennial plant, but these plants cannot stand cold winters. Therefore, in temperate climates, Capuchins are grown as garden annuals, which can grow with a solid carpet, decorate the borders along the paths, and braid the gazebos.
Due to its attractive appearance - smooth, semi-double or double flowers and green, waxed leaves, ampelous nasturtium species are grown in hanging pots for decorating balconies and verandas. The color of the petals is dominated by shades of white, yellow, red, orange-pink.
Discoloration of petals and leaves does not always indicate nasturtium disease. The yellowing of the leaves of the lower tier is most often due to the fact that less sunlight falls on them, or the effect is associated with the aging of the plant.
Perhaps the weather is too hot or rainy outside - both of these factors affect the color of the leaves. In the first case, the sun burns the leaves and the plants lack moisture. Additional watering and shading of the bushes will help to correct the situation. In the second case, waterlogging of the soil leads to root rotting, that is, additional drainage is required.
In addition to natural reasons or due to disadvantages arising from care, yellowing of nasturtium can occur due to infection of plants with infectious diseases. When trying to understand why the leaves of nasturtium turn yellow, it is necessary to pay attention to the dislocation of yellowness.
If these are shapeless yellowish-green spots, leaves curl on nasturtium, then this may be a viral mosaic. Insects are carriers of viral diseases, in addition, seeds can become the source of the disease.
Why does nasturtium not bloom
Insufficient daylight hours, cold air, heavy clay soil, poor plant care, non-observance of cultivation techniques - these are the reasons why nasturtium may not bloom.
During a short daylight hours, a period of rest begins in the life of nasturtium. Plants planted in flower pots overwinter well in indoor conditions, but they will bloom only in spring. Changes in temperature - cold nights, hot days will affect the ability of plants to form buds.
Clay soil that does not allow water to pass through will worsen the condition of the root system. Flower beds overgrown with weeds, cracked soil crust, untimely feeding with nutrients - ignoring the rules of agricultural technology will not allow plants to develop fully.
Why does nasturtium have sticky leaves?
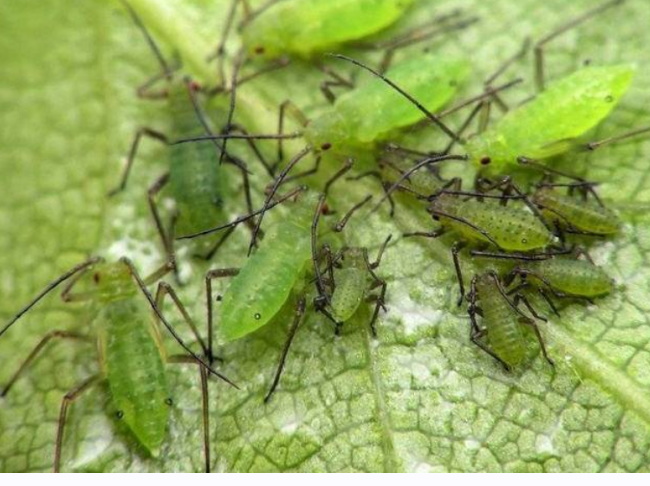
It often happens that with the establishment of a constantly warm weather, pests of nasturtium multiply in enormous quantities. These insects include aphids. Several thousand larvae can appear from one female in one season. Their transformation into adult aphids occurs very quickly. Therefore, a large family consisting of several generations of individuals can live on one plant.
Aphids feed on plant juices and produce a sticky, sweet substance. Because of it, the leaves of nasturtium become sticky, because a flower for aphids is a real delicacy. Gardeners plant capuchins to help aphids move from vegetable plants to their leaves. Then the flower bushes are treated with insecticides or simply burned together with aphids.
Why nasturtium dries up and how to save a flower
A flower that begins to dry in the summer at the height of all other plants is sure to be alarming. There can be several versions of the answer to the question why nasturtium grows poorly:
- poor care,
- heavy soils,
- disease,
- pests.
If it is impossible to eliminate all negative factors and after treatment the capuchin continues to dry, it must be destroyed.
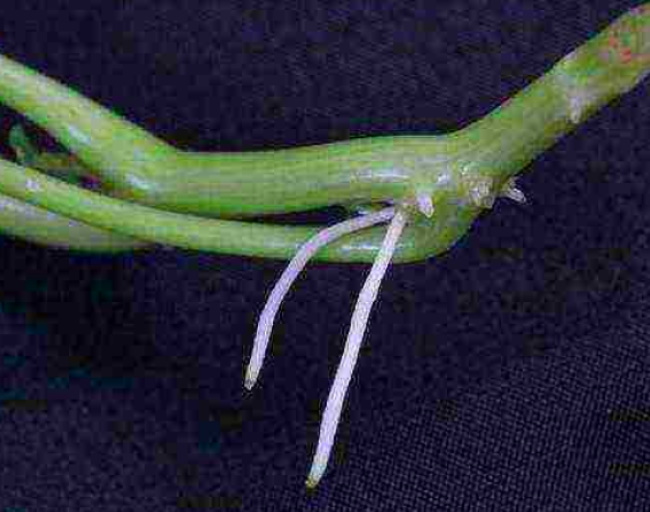
In this case, healthy strong stems are chosen on the bushes and cut into cuttings with 2-3 internodes. Leave 2 leaves. Shorten them by 1/3. The lower parts of the cuttings are treated with a rooting agent and placed in water to build up roots.
After the appearance of root shoots, the cuttings are planted in a mixture of sand and peat, and regular watering is continued. Gradually, nutritious soil and complex fertilizers are added to the pots, allowing the development of the root system of the cuttings.
In the spring, after the outside temperature reaches about 20 ° C, the rooted seedlings are transplanted into open ground or flower pots.
How does nasturtium chlorosis manifest?
The lack of iron in the soil or the inability of the roots to get the chemical element from the soil and send it to the leaves for photosynthesis leads to yellowing of the leaf plate.
A characteristic feature of chlorosis is green veins on the yellow background of the leaf. Nasturtiums shed their ovaries and flowers, curl the edges and reduce the size of the leaves.
For treatment, nasturtium is fed with preparations containing iron chelate, the Antichlorosis agent.
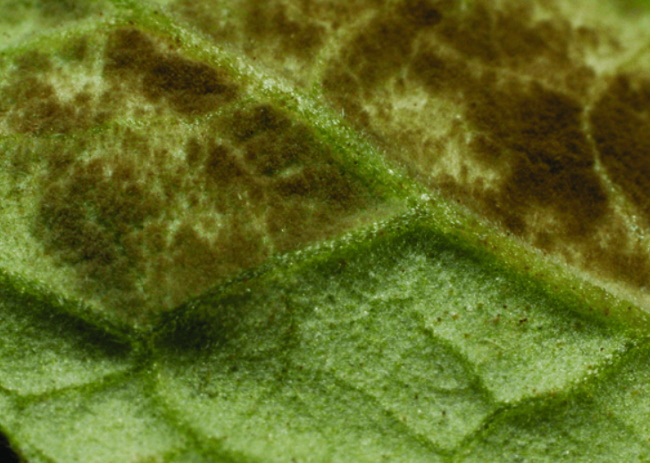
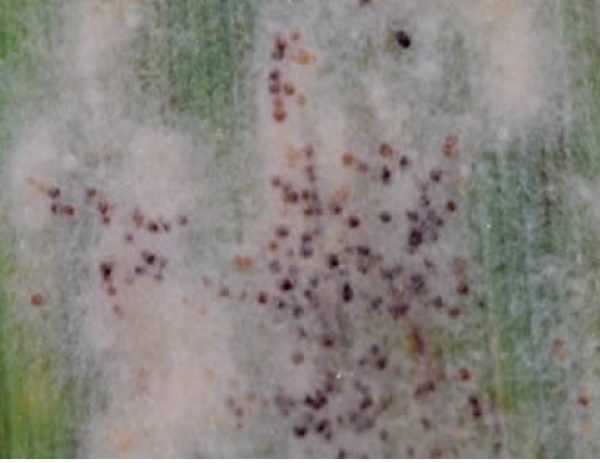
What is powdery mildew in nasturtium (lat.Erysiphaceae)
Powdery mildew is a fungal disease. It appears as spots of white bloom interspersed with dark brown spore balls on leaves and stems.
After a while, the plaque becomes dense and changes color to gray-brown. The mycelium grows, nutrition occurs at the expense of plant tissues. Nasturtiums wither, stop growing, their stems and leaves turn black. Flowers lose their appeal.
Treatment is carried out with drugs Fundazol, Skor, Vectra.
Gray rot (lat.Botrytis cinerea)
Disease comes to plants from the air. Gusts of wind spread the spores of the fungus Botrytis, which causes discoloration of stems and leaves, softening of tissues, decay of roots, and falling off of inflorescences.
The pathogen is easily transmitted through human hands after contact with an infected plant. The fungus is omnivorous: it settles on weeds, on all garden and vegetable crops, affects large fruits and small berries.
Methods for combating gray rot include the destruction of pathogens. First, all parts of the plants affected by the fungus are removed, then the nasturtium bushes are treated with Gamair, Alirin, Fitosporin-M.
Since the spores of the fungus live on the remains of plants in the surface layer of the soil, before planting flowers, it is necessary to prevent the disease - loosen, free from weeds and disinfect the soil in flower beds, pickle planting material.
Black rot of nasturtium (Latin Guignardia bidwellii)
The black rot pathogen Guignardia bidwellii is common in almost all countries with warm and temperate climates.
It spreads, like all mushrooms, by spores. White tiny dots that appear on the plant gradually expand, turn brown, then turn black. Impressed spots form on stems and leaves. Treating the disease is identical to fighting gray mold.
Signs of late blight
Fungi of the genus Phytophthora infestans are called plant eaters.
The mushroom begins its movement from below from the ground. Initially, brown spots with white bloom appear on the lower parts of the stems and leaves of the first tier. The mushroom is especially active in rainy, cloudy weather and when the soil is waterlogged.
The fight against the pathogen begins with preventive measures, without waiting for the onset of the disease. To increase the resistance of flowers, measures are taken to saturate the root layer of the soil with the necessary nutrients - fertilizers for nasturtium for abundant flowering.
To destroy the fungus, Fitosporin-M, Trichodermin are used.
Brown spot of nasturtium (Latin Phyllosticta petuniae Sp.)
Phyllosticosis - brown spot also belongs to fungal diseases. Pathogens of late blight and phyllosticosis compete with each other, therefore, these fungi do not settle on the same plant at the same time.
Pale olive specks of phyllosticosis appear when plantings are thickened and surface watering on leaves and stems. Therefore, the fight against the fungus consists not only in the use of copper-containing fungicides, but also in preventive measures to ensure sufficient gas exchange between plants.
Causes of nasturtium disease
Florists, faced with the fact that diseases and pests were found in nasturtium and knowing how to process plants, still need to understand the reasons for their appearance. This will help prevent the flowers from wilting in the future, will not give a reason to ponder why the leaves of nasturtium turn yellow, the buds fall off, and the roots rot.
- Temperature violation
Plants of the genus Tropaéolum are native to warm subtropical regions.And, although breeding work has led to the emergence of new varieties of nasturtium that are more resistant to cold weather, these flowers still need warmth. Otherwise, they weaken and begin to hurt, this can also be the reason why nasturtium does not bloom.
- Violation of watering rules
Too abundant watering with cold chlorinated water leads to rotting of the root system. Organic and mineral substances dissolved in water, which are used by the cells of leaves and stems for their vital activity, cease to flow to the tops of the plants. Without macro- and microelements, the production of chlorophyll stops, and the protection of plants from pathogens decreases.
- Lack of iron
Failure to comply with the timing of fertilization when preparing the soil for sowing seeds or planting seedlings leads to the fact that soil bacteria do not have time to process chemicals into a form that is easily digestible for plants. Plants cannot get substances - iron, copper, manganese, even if they are in excess. With a lack of iron, the leaves turn yellow, the buds fall off, the shoots dry out
- Diseases associated with excess moisture
Most fungal diseases of nasturtium are associated with the flow of excess water into the root zone, high air humidity, and abundant watering over the leaves.
Fighting fungi is possible if preventive treatments of soil and plants with biofungicides, disinfection of garden tools and structures, and protection of plants from the wind are carried out.
Agrochemistry and plant protection
The list of plant protection products includes:
- insecticides - chemicals that kill insects, along with eggs and larvae;
- fungicides are biological and chemical substances used to treat diseases.
How to treat with folk remedies
Plants very often protect each other from diseases and pests. Plants, which emit strong-smelling substances with their aroma, establish a barrier between insects and pathogens and flowers.
Phytoncide plants include nasturtium itself, as well as garlic, dill, wormwood, basil, lemon balm. From their stems and leaves, infusions and decoctions are prepared and treated with them on the soil surface near problem plants.
Serum is used to combat late blight. Its acidic environment prevents fungal spores from multiplying on the leaf surface. Water with the addition of a few drops of iodine has antimicrobial properties. Water extract from wood ash is used as fertilizer and for the prevention of fungal diseases.
Prevention and protection of nasturtium from pests and diseases
Diseases of nasturtium can be prevented by preparing the soil and choosing a planting site. In the dug up and thoroughly disinfected soil, pathogens of viruses and fungal spores, aphid and whitefly larvae, and the Colorado potato beetle will die. Loosening of the dried soil crust will allow not to disrupt gas exchange in the root zone.
Cleaning up crop residues will prevent the appearance of cabbage butterfly caterpillars. Regulated watering with settled warm water will prevent the development of spores of fungal diseases, hypothermia of the roots, and wilting of plants.
Nasturtium is an unpretentious flower that reproduces very well by seeds under local conditions.A description of the modern types of these flowers is now, thanks to the Internet, available to all gardeners. Any of these plants, if fertilized on time, protected from diseases and pests, will not only decorate the garden, but will become the pride of their owners.