Fruit moth on an apple tree - methods of struggle and folk remedies
Content:
An unpleasant guest - the apple moth - can seriously harm the garden. Correctly selected control methods will help get rid of the pest, preserve fruit trees.
Description of the pest
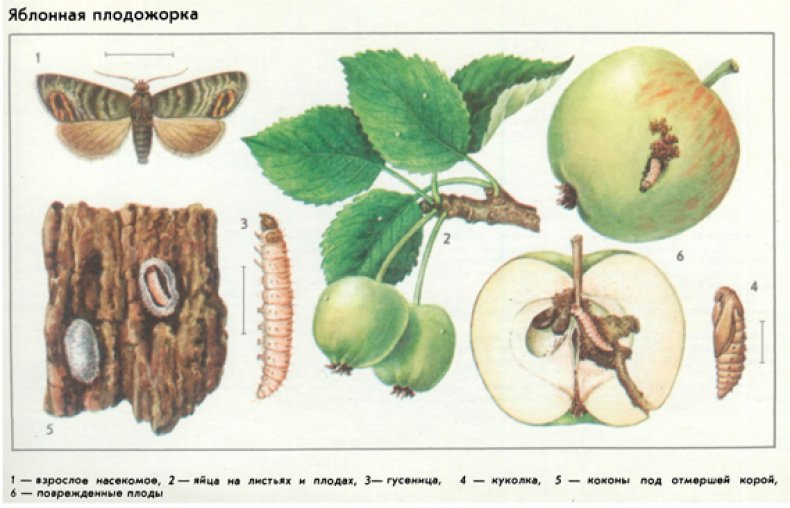
The insect belongs to butterflies, it is a representative of the Leafworm family, the Lepidoptera order. There are about 50 varieties of the pest; the apple and eastern moths are dangerous.
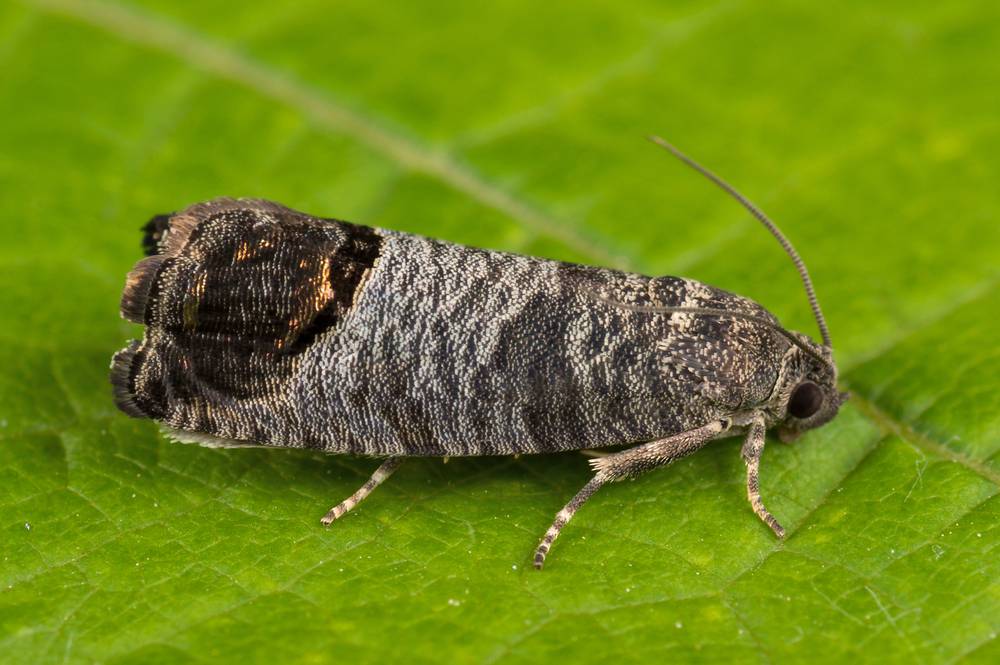
Apple moth
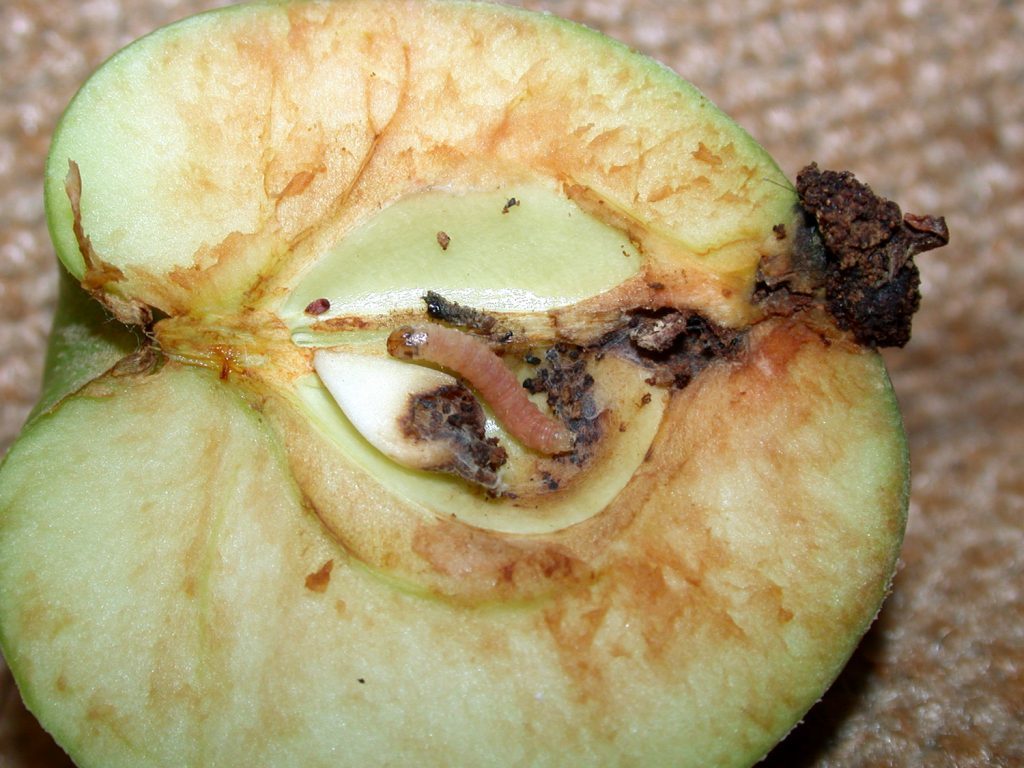
The apple moth lives in all regions of the Russian Federation, where fruit growing is developed. A gray or brownish nocturnal insect eats fruits, destroying 90% of the crop during the season.
Life cycle
The pest goes through several stages, from the larva to the moth.
Mature individual of the first generation
Sexually mature individuals fly into the gardens during the formation of ovaries, actively mate and lay eggs for 1.5-2 months. The pest fixes them from the outside and inside of the sheet plate.
Egg
An embryo begins to develop in it - from 9 to 12 days. For successful formation, a temperature of 20-22 degrees is needed.
Larva (caterpillar)
Young growth appears on the 15th or 17th day after the end of flowering, after 1-3 hours it moves to the fruits. Further development begins:
- the pest covers the fruit with cobwebs;
- in half an hour finds a weak spot and gnaws;
- having penetrated into it, turns his head towards the exit and closes the passage with a mixture of cobwebs and pulp;
- after 48 hours it sheds;
- after 2 days it sheds again;
- after destroying the seeds, it changes the skin again;
- eats away the exit and moves to another fruit.
Chrysalis
When it warms up to 8 degrees, the transition to the pupation stage begins. It develops from 14 to 25 days, transforms into a moth.
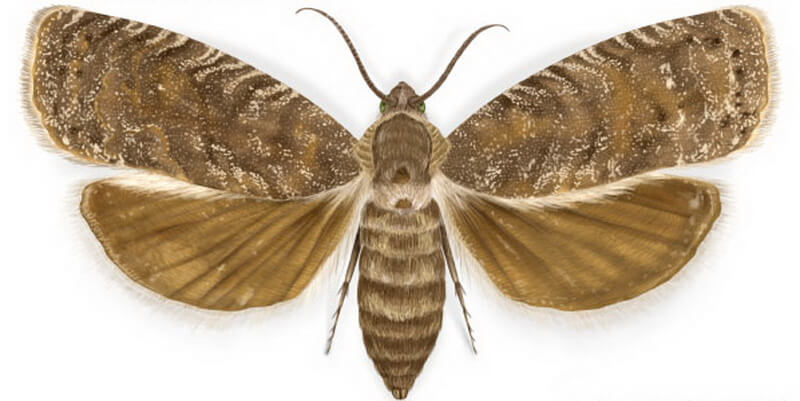
Eastern moth
Distributed in the middle and southern regions, Crimea. The pest infects shoots and fruits, is capable of destroying the entire crop.
Life cycle
The insect goes through standard developmental stages.
Mature individual of the first generation
After warming to 14 degrees, pests begin to fly out, at dusk or in cloudy weather. Laying of eggs of the 1st generation on foliage begins in 72 hours, lasts 1-2 weeks.
Egg
The development of embryos takes from 3 to 12 days - the period depends on the temperature.
Larva (caterpillar)
The formed individuals pass into the apical buds of the shoots, deepen and destroy their structure. Pupation takes place inside the dead part or in cracks in the bark. The pest develops from 10 to 22 days, depending on the generation.
Chrysalis
Moths ripen on an apple tree, the surface of affected apples or under fallen leaves for 5 or 10 days. The next generation forms cocoons in areas of future wintering: in the bark or on the ground.
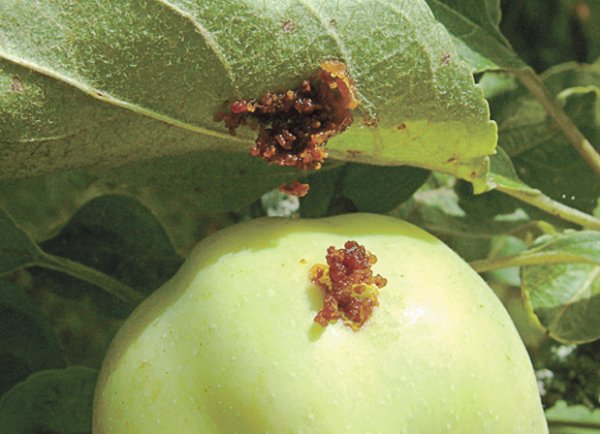
Harm done
The oriental variety seriously infects apple trees, causing:
- loss of frost resistance;
- weakening of immunity to disease;
- dying off of young shoots;
- low yield after treatment.
Reasons for infection
The appearance of a pest on a garden plot is associated with infected seedlings, a transition from a neighboring plot. The defeat is observed in household plots where the rules of agricultural technology are not followed and there is no prevention.
Signs of the presence of a moth
Symptoms of the lesion are presented:
- the massiveness of moths;
- falling apples ahead of time;
- early ripening of the crop.
Apple varieties resistant to moth infestation
The only variety that is not afraid of the eastern variety is Wine. But it also requires compliance with the rules of agricultural technology. There are no resistant species against the codling moth.
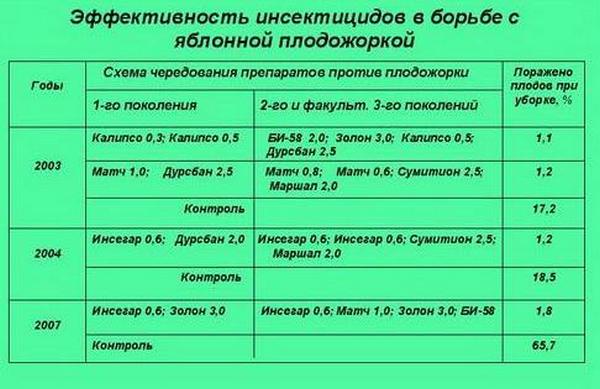
Processing chemicals
Certain drugs are able to protect fruit crops from attacks. They are used strictly according to the manufacturer's instructions - so as not to harm the crop and beneficial insects.
Fitoverm
When a moth is found on an apple tree, control methods require spraying the garden with a special compound. Fitoverm causes her death in 1 day, helps with the massive dominance of the garden.
Can I use a herbicide
The description indicates that this subspecies is not used for manipulation due to the high risk of harm to trees.
Pesticides
They are similar in action to insecticides, cause the death of worms. Treatment is carried out:
- Battering ram;
- Tanrekom;
- Confidor;
- Fastak, etc.
Mixed insecticides
Complex application gives a greater effect. Gardeners prefer the combination of Imidacloprid + Lambda-cyhalothrin, Thiamethox + Chloranthraniliprol.
Organophosphate insecticides
Toxic formulations with high efficiency. Gardeners use Dichlorvos and Karbofos because of the inexpensive price and low consumption.
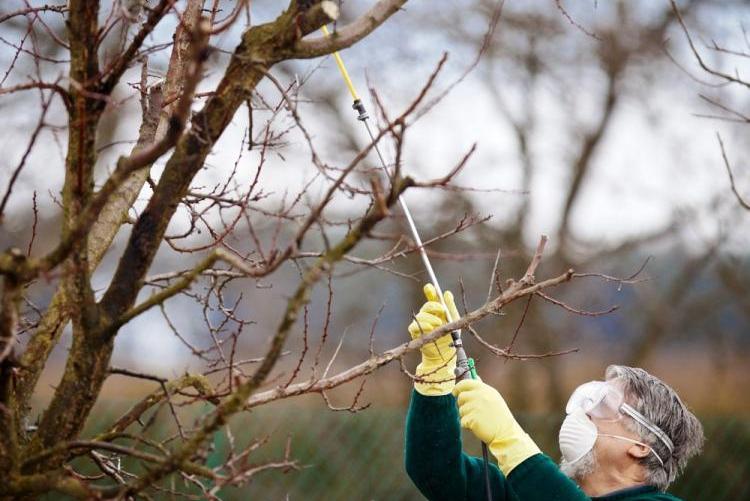
Spraying technology
For the procedure, sprayers are used - they can evenly distribute the compositions. The approach helps to reduce the consumption of substances and increase the effect.
Spraying time
Dates vary according to regional characteristics. Seasonality and climatic conditions play an important role.
In the spring
Spring cleaning begins with the appearance of mature individuals. In the fight, organophosphates are used that destroy both moths and caterpillars.
After flowering
Mass attacks of insects are restrained by spraying apple trees with Dimilin, Gerold, Insegar. The compositions kill adults, and the larvae that appear die when they try to eat the treated surfaces (after pouring drugs on them).
During the period of fruit ripening
Biological means, traps and trapping belts, homework are used. Chemical poisons during ripening and harvesting of fruits are prohibited.
Dates in autumn
Cleaning begins after the leaves fall: the accumulated debris is removed, the trunks are prepared and whitewashed. In the fall, you can spray the garden after the area and trunks are completely cleaned.
How often to spray
The work calendar is associated with the regional location of the garden:
- with a cycle of 2 generations - processed 2-4 times;
- with 3 or 4 generations - from 4 to 8 times during the growing season.
Spraying terms in the regions
The work is carried out every 12 days after flowering - in the southern part of Ukraine, the Stavropol Territory and the Volga region. 10 days after budding in Krasnodar and the region, in the North Caucasus.
Environmental control methods
Safe products are intended for direct destruction of pests.
Pheromone traps
The design resembles a prism with 3 edges, which contains the bait. The drug contains pheromones that attract moths. Once inside, the moth sticks to adhesive tape and dies in 6 hours.
Fighting the moth on an apple tree with folk remedies
Homemade preparations are decoctions, infusions, mechanical removal of debris from the region of the peri-stem circle. To create folk medicines, makhorka, tomato and potato tops, wormwood are used.
Methods without chemistry
The common methods include the preparation of a special "compote": a lot of sugar is added to an ordinary drink. The finished liquid is poured into a deep plate and exposed to the trees.
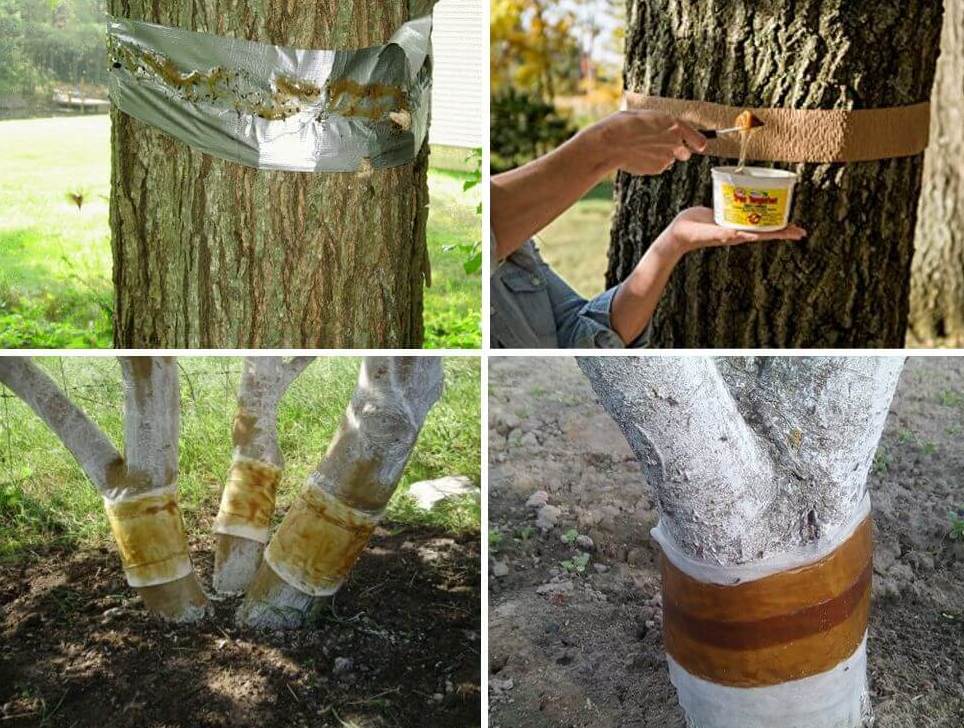
Trapping belts
The creation of specialized belts is considered an effective and proven technique in helping to breed butterflies. A dense fabric (burlap, etc.) is moistened in a poisonous substance and tightly wound on the trunk. The procedure is carried out before the first exit of insects.
The composition of the glue
The specialized formulation is easy to prepare at home. To create a poisonous substance, take:
- sap - 10 hours;
- garden pitch - 2 hours;
- rosin and paraffin - 1.5 tsp each
The ingredients are poured into a bowl, heated and stirred into a homogeneous mass. As a result, the drug should resemble a thick paste.
Integrated protection
This is a set of procedures that help to destroy the number of moths in the main phases of life (caterpillars, butterflies). Proven methods include the phased application of mechanical, agrotechnical and physiological methods. Preventive measures reduce the risk of pest attacks to a minimum, and timely care eliminates their presence.
The danger of moths lies in the massive destruction of the crop. Regular inspection of fruit trees in the summer, in June-July, will prevent their reproduction, laying of eggs and further development in cycles.