Houseplant pests and indoor flower diseases
Content:
It is quite difficult to deal with pests and diseases of indoor plants, so it is better to know in advance how to prevent the occurrence of a problem. To do this, it is important to understand how indoor flower diseases manifest themselves, what pests look like, and how their harmful effects are expressed. Unfortunately, it is not always possible to identify the parasite or notice the pathology at the initial stage of development. In such cases, there is nothing left but to resort to effective methods of dealing with the disease.
Pests
There are many different parasites that pose a threat to house flowers.
White bugs in the ground
If small white bugs appear in indoor flowers in the ground, then we are talking about a whitefly. It is a pest of indoor and garden plants. All of its varieties are easily reproduced at home.
Black bugs on indoor plants
If black insects appear, it means that the plant has been attacked by thrips. Typical signs of infection:
- Silvery spots on the leaves.
- The stems dry out and reshape.
- There is no flowering.
- The leaves turn yellow.
- On the leaf blades, black dots that look like streaks are observed, as well as shiny black drops and dark skins from insect molting.
- Falling pollen in flowering plants.
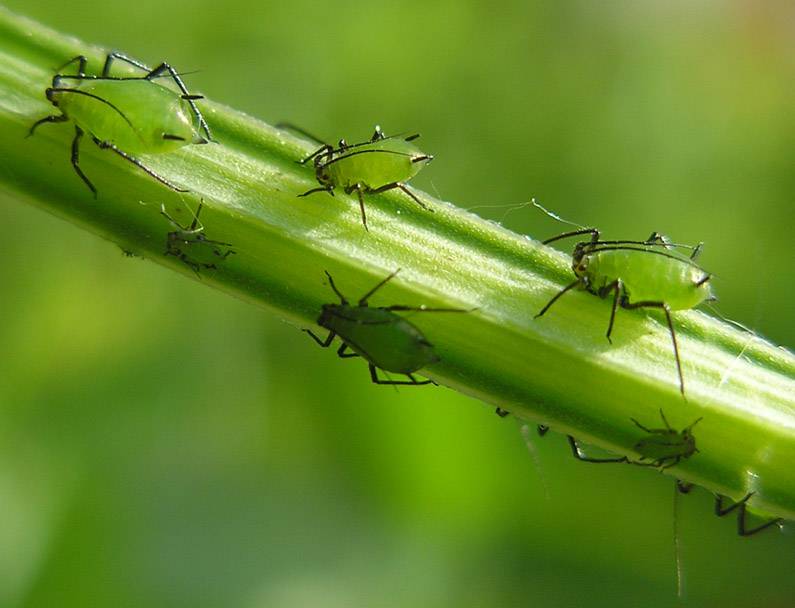
Aphid
It poses a threat to domestic plants, regardless of the season. Insects reproduce very quickly and form colonies. Aphids are quite large in size, they can be easily seen on plant tissues.
To get rid of the problem, you need:
- Cut off the affected stems, cut off the peduncles.
- Treat the leaves of plants that form a rosette with a solution of green potassium soap and rinse under a hot shower. Clean the axils of the leaves with cotton swabs, having previously moistened them in alcohol.
- In case of severe infection, the flower must be sprayed with an insecticide.
- You can use decoctions of wormwood, tansy, dandelion root, yarrow, garlic, onion. Dusting a sick plant with tobacco dust will also be effective.
A plant invaded by colonies often looks like it has dandruff on it.
Also, the disease is indicated by:
- Discolored parts of the shoots;
- Deformed flowers;
- Twisted leaves;
- Yellowed and dying leaves;
- Termination of plant development;
- Lack of flowering (buds do not open);
- Contamination of flowers with sticky mucus.
Onion mite
The body has the shape of a wide oval, the color is light yellow. The surface of the skin is smooth, thin, with a glossy sheen. The parasite feeds on the underground part of plants - bulbs and roots.
The symptoms are as follows:
- Growth inhibition.
- The appearance of red or brown spots on the bulbs. White dust also forms on their surface.
- Yellowing of the leaves.
- Termination of flowering.
- Chlorosis (a sign of starvation).
- Drying of individual branches.
- Fusarium - as a secondary disease due to the fact that infection penetrates into the wounds on the bulbs and roots.
The chance that a mite can grow on a plant increases in conditions of high soil moisture. To prevent the disease, the soil must be disinfected, and quarantine must be organized for all recently acquired plants.
Control methods:
- Affected bulbs and roots are treated with an acaricide solution.
- Any drug based on spiromesifene will also work.
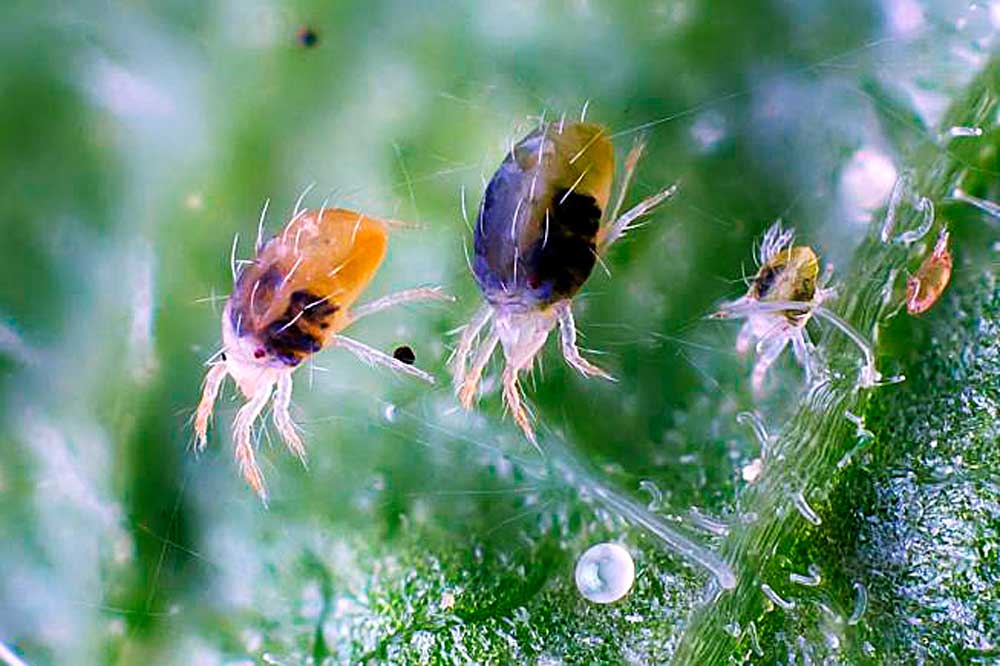
Spider mite
The most common parasite that attacks indoor plants.
Signs:
- The presence of punctures on the sheet plates of a yellowish or whitish color. Over time, the dots merge and turn into spots.
- Leaves lose color, turn gray, then dry out and completely discolor. It also happens that the leaves acquire a red or bronze color.
- The leaves are deformed.
Adult insects are greenish in color and are almost invisible on plant tissues.
Treatment methods:
- Increase air humidity. This will help: wide trays with water; humidifier; table fountain.
- Short-term hot (45-48 degrees) shower. Repeat the procedure after 3-5 days (first water 3-4 times every week, then once every 3-4 weeks). Before showering, it is recommended to apply a layer of tar, green or laundry soap to the plant.
- Application of acaricides or insectoacaricides.
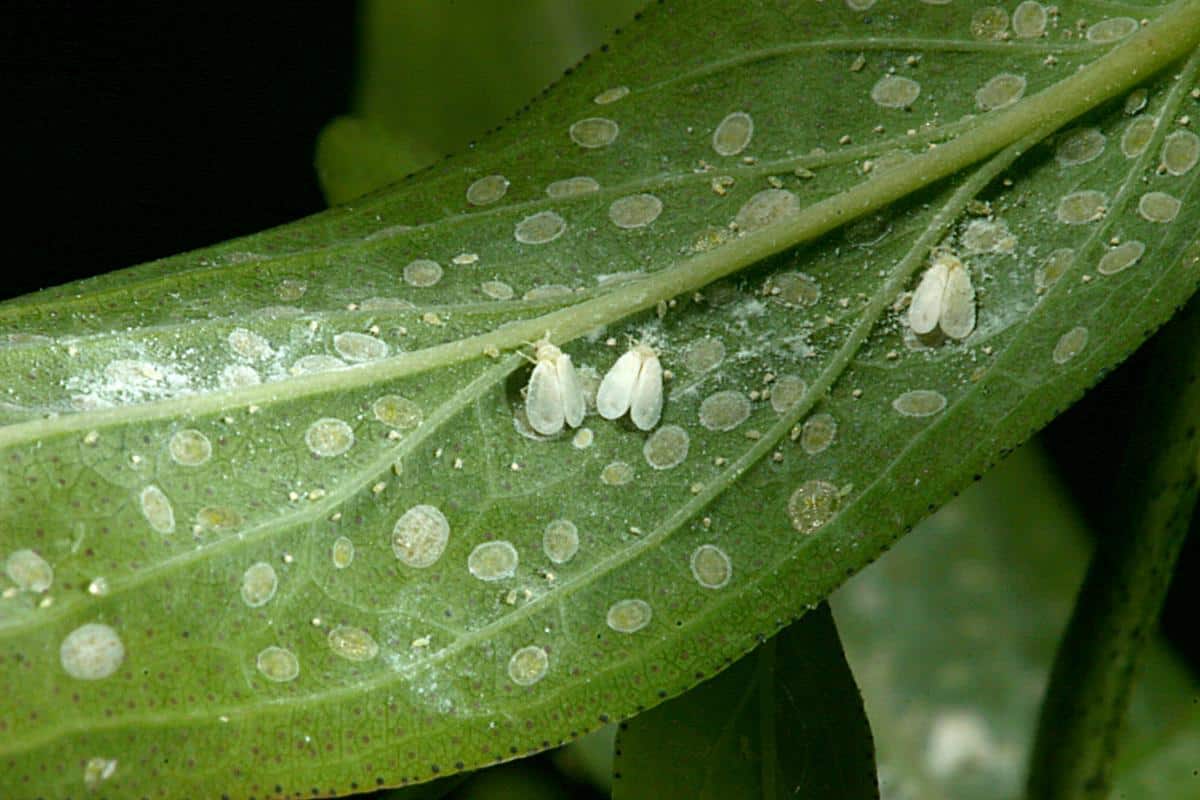
Greenhouse whitefly
According to the external description, this is a small white midge resembling a reduced version of a moth (body length - about 2 mm, has 2 pairs of white wings).
The greenish insect larvae are located on the back of the leaf and suck out the cell sap from it, leaving behind a sticky discharge. Ideal conditions for development:
- The air temperature is from 21 to 27 degrees.
- Air humidity - 60 to 75 percent.
Signs of parasite activity:
- Spots of light yellow or white appear on the leaves.
- Leaves curl, turn yellow and fall off.
Most often, pests suffer from:
- Hibuscuses;
- Begonia;
- Balsam;
- Fuchsia.
Control methods:
- The use of systemic drugs (Aktara, Apache, Confidor, Tanrek). These means are poured over the soil, and the leaves are also sprayed. The drugs are ineffective against larvae, therefore, the treatment is carried out in 3-4 stages every 2-3 days.
- Application of insecticides: karbofos; Pegasus; inta-vir.
- Timely removal of affected leaves.
- It is recommended to hang sticky fly traps near the flower.
Dangerous thrips
Most often, the fly affects garden plants, in particular, peonies, asters and other terry Compositae crops.
An adult insect grows up to 1.5 mm, has an elongated, segmented body with a pair of long antennae and two pairs of wings, completely covered with fine hairs.
Bubble-shaped suckers are located on the insect's legs, thanks to which thrips easily cling to the surface of the leaves and jump quickly (like fleas).
The body of the parasite is equipped with a piercing-sucking mouth apparatus, due to which the insect quickly sucks out the juices of the plant. Thrips larvae can be located in different parts of the plant: most often on flowers, less often on leaves, in some cases on leaves and flowers.
Adult thrips range in color from yellow-brown to brown. The larvae are gray or yellowish.
What to do to cure a flower:
- Systemic insecticides (Aktara, Confidor) will be effective against insects living on flowering plants. Citrus and other fruit-bearing trees need to be reprocessed.
- Contact pesticides (Vermitek, Fitoverm, Aktellik, Karbofos) are suitable for decorative deciduous plants.
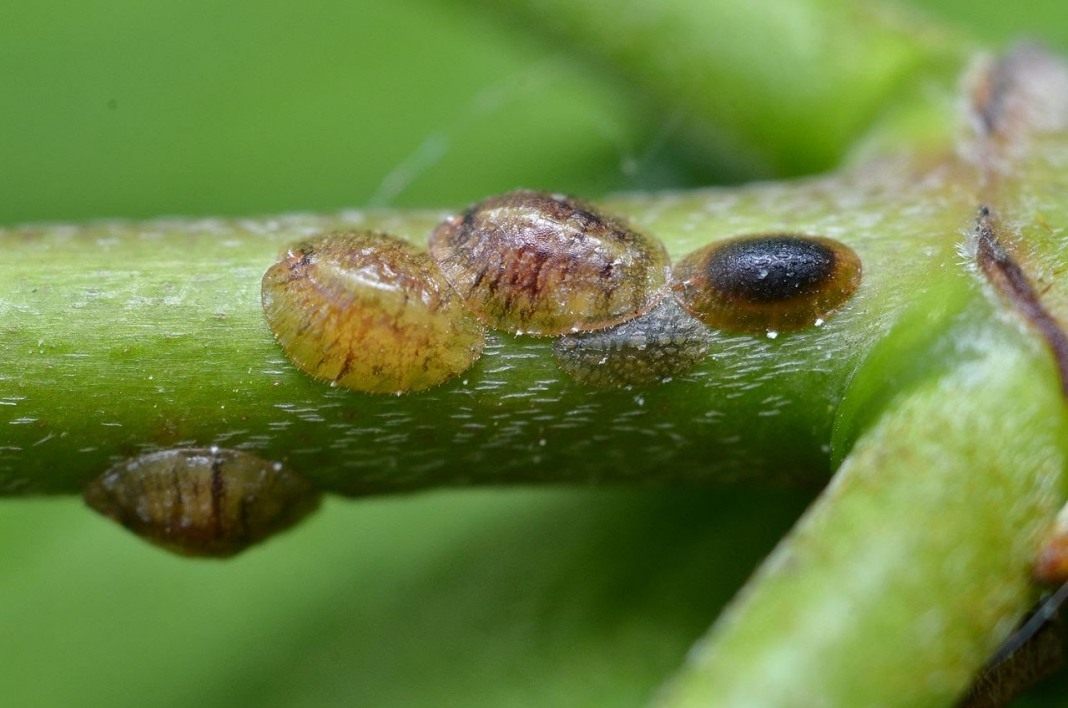
Shields
Infection with this parasite can kill the flower.
Symptoms:
- Yellow spots appear on the leaves, which gradually grow.As a result, the leaf turns completely yellow, curls and falls off.
- The presence of sticky secretions on the leaves.
- Growth stops.
- The branches are bare.
- The bush dries up and the plant dies.
Control methods:
- Isolating the plant from other indoor flowers.
- Mechanical removal of scabbards (with a cotton pad, sponge or toothbrush soaked in soapy water).
- Wash the leaves with laundry soap.
- Hot shower once a week.
- Soaking the infected crown in an insecticide solution.
- Treatment with contact preparations 3 times every 7 days.
Diseases
Due to gross mistakes in caring for home flowers, the latter often fall ill with various pathologies.
White bloom on the soil
White bloom on the ground in pots of indoor plants is of two types:
- Dry. These are saline residues from evaporated hard water. You can fix the problem by watering the plant with soft water. To soften, you will need to boil water or freeze it. You can also use melt water or rainwater.
- Soft and moist. This means that the soil has begun to grow moldy.
White bloom on flowers
If the tissues of the plant began to turn white, it means that the flower was attacked by powdery mildew. The leaves are covered with a white bloom, similar to cotton wool. The reason is infection with a fungal infection. Favorable conditions for its distribution are high air humidity, a sharp change in temperature, excessive fertilizing with nitrogen content, and a lack of calcium.
If on indoor flowers there is a white bloom like cotton wool, how to treat the plant:
- The flower is isolated;
- A systemic fungicide (eg Topaz) is used.
Why does potted soil grow moldy?
Mold on the soil appears due to excessive watering of the plant and high humidity in the room. To fix the problem, you will need:
- Reduce watering;
- Add new soil;
- Treat the soil mixture with an antifungal agent.
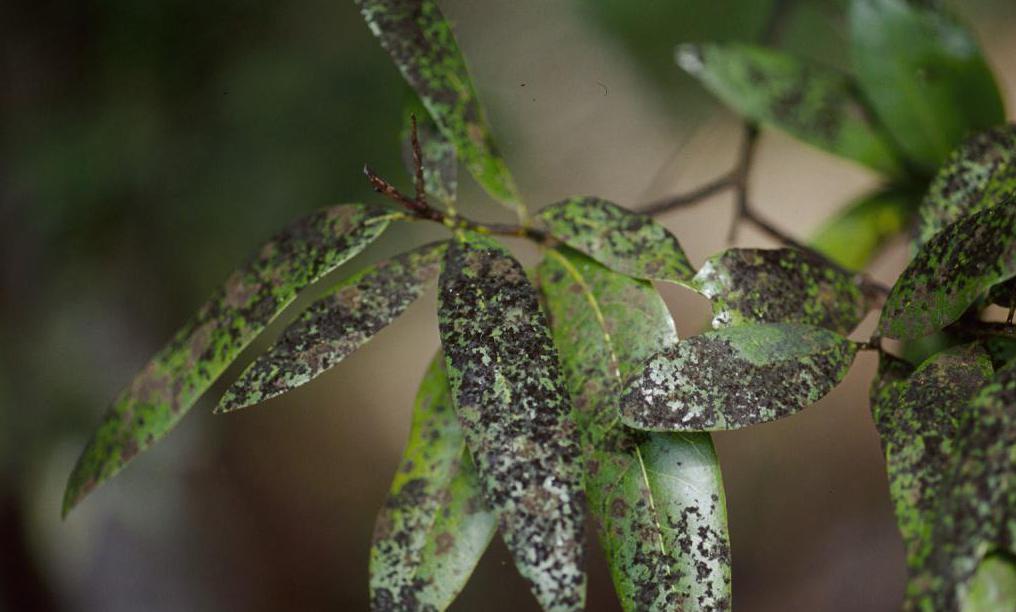
Sooty fungus
In another way, the disease is called rabble. The pathology is fungal in nature and affects mainly young and weak plants. Favorable conditions for fungus are high humidity and poor ventilation in the room.
Symptoms:
- Formation of black or gray streaks on stems, fruits and leaves.
- At first, plaque appears in the form of specks, which then combine with each other.
Treatment and prevention:
- Reducing humidity levels up to 50%.
- Regular ventilation of the room.
- Spacious color content.
- Treatment of trunks before the beginning of the growing season with copper sulfate containing lime.
- Top dressing.
- Treatment of infected plants with insecticides.
- Removing plaque with a wet sponge.
- Removal of severely damaged leaves.
Knowing what pests of indoor plants look like, how their various diseases manifest themselves, and why they arise, will help to notice the problem in time and save the flower from death.
Video