Yellow spots on pear leaves: why and what to do
Content:
Appearing yellow spots on pear leaves are not always a signal of a serious pathology. Sometimes this indicates a violation of care, in other cases the problem may be associated with an infectious lesion of the culture and requires urgent action to cure it.
Why are pear leaves covered with yellow spots
During the growing season, the standard foliage color ranges from green to dark green. The appearance of extraneous streaks or spotting indicates the preliminary preparation of trees for the winter season or health problems.
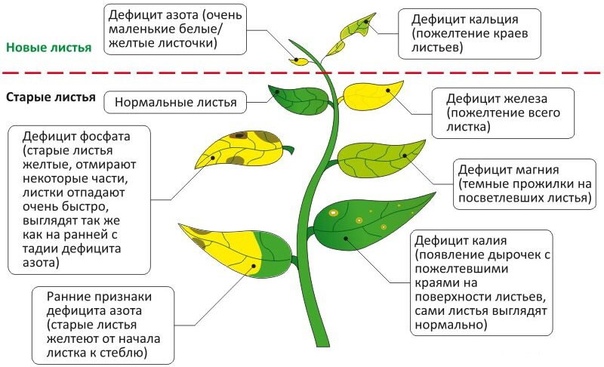
Frequent sources of anomalies include insufficient intake of nutrients or damage to the culture by pathogenic microorganisms that provoke the formation of "rust". In the first option, the gardener must check the amount of fertilizers applied and the presence of nitrogen, iron, zinc and manganese in them, in the second, he must carry out therapeutic procedures to destroy the source of pathology.
To clarify the preliminary diagnosis, it is necessary to take into account the symptoms:
- Lack of iron - manifested by the whitish color of the foliage with yellowness around the edges. With a partial lack of an element, the veins on the leaves remain green, without a visible change in the main color.
- Lack of manganese - determined by yellow-green dots scattered over the surface of the leaf plates.
- Insufficient intake of zinc - provokes thinning of the foliage, a decrease in its size. In some cases, yellowness forms at the ends of young shoots.
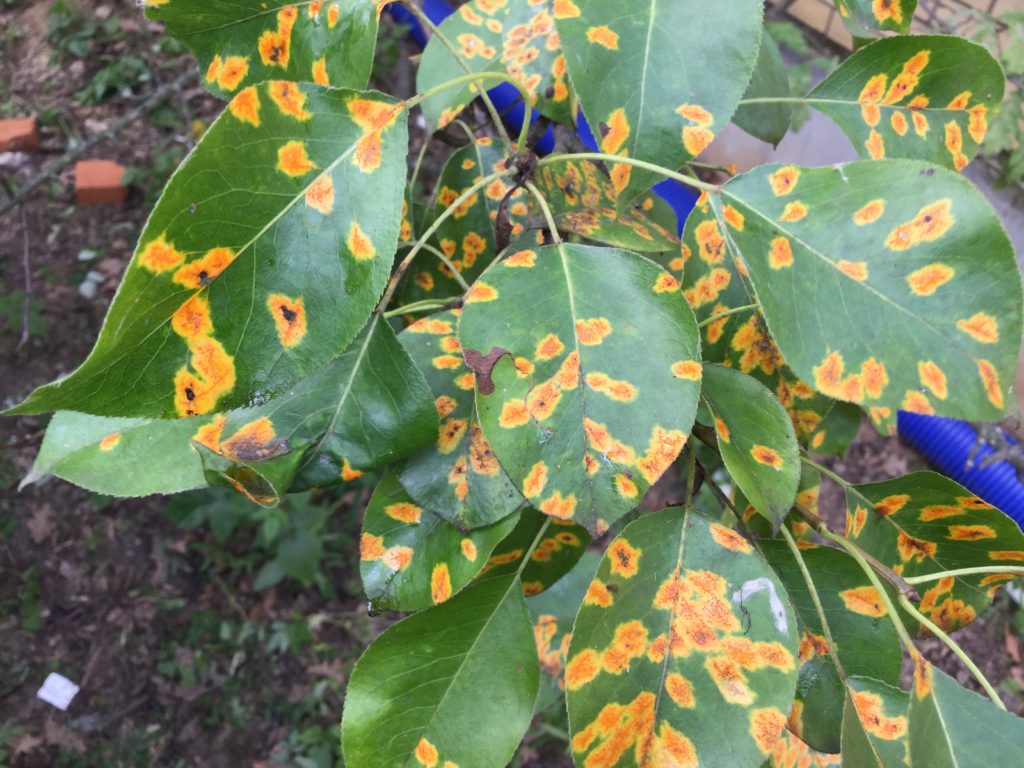
On the pear, orange spots can occur when a fungal infection is affected. An extraneous bright orange color appears in summer days or early autumn, the lesions are sticky to the touch. Ripe spores quickly migrate through the rest of the garden plants with the help of insects, infecting healthy crops.
The appearance of non-standard shades of leaves in spring is a symptom of the development of scab. Over time, foliage takes on a brownish or olive tones at the sites of infection. The disease spreads only in high humidity.
Resistant and unstable varieties
Breeders have developed certain varieties of pears that are resistant to rust. The list is presented:
- Gordzaloy;
- Gulabi;
- Sailo;
- Sugar;
- Suniani;
- Chizhovskaya, etc.
The consequences of inaction when the leaves on the pear turn yellow
The danger of orange spots on pear leaves is determined by the source of their occurrence. Unless seasonal changes are the cause, plants and crops can be severely affected by progressive infection.
Capture of pear rust leads to disruptions in the processes of photosynthesis in foliage, a rapid weakening of the culture.The fruits will become tasteless and small, and with a prolonged illness, over several years, the wood will begin to be damaged and covered with corresponding growths.
Loss of leaves leads to crop depletion, weakening of immunity and vulnerability to pests and diseases. The index of frost resistance decreases, even in the Middle Lane there is a possibility of frost damage to shoots.
A culture that has recovered stops bearing fruit or gives a minimum yield with small and tasteless fruits. To reduce the risk of infection, gardeners prefer to plant varieties that are resistant to rust in their backyards and check the sufficiency of the intake of nutrients.
How the disease develops and spreads through the tree
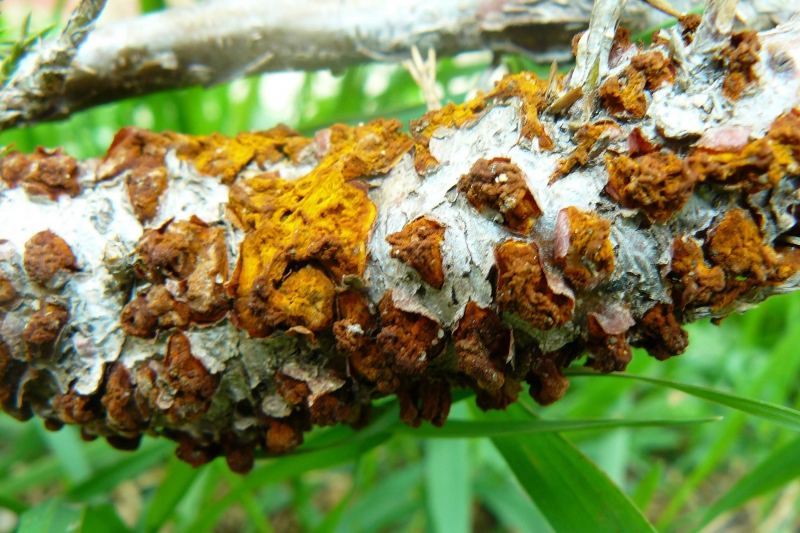
Gymnosporangium sabinae is a two-year cycle parasite that changes two hosts. The first is the Cossack juniper, the second is the pear. The defeat of crops is noticeable from the end of April - small round spots with a yellowish-greenish tinge are formed on the leaves. They do not exceed 0.5 mm in diameter.
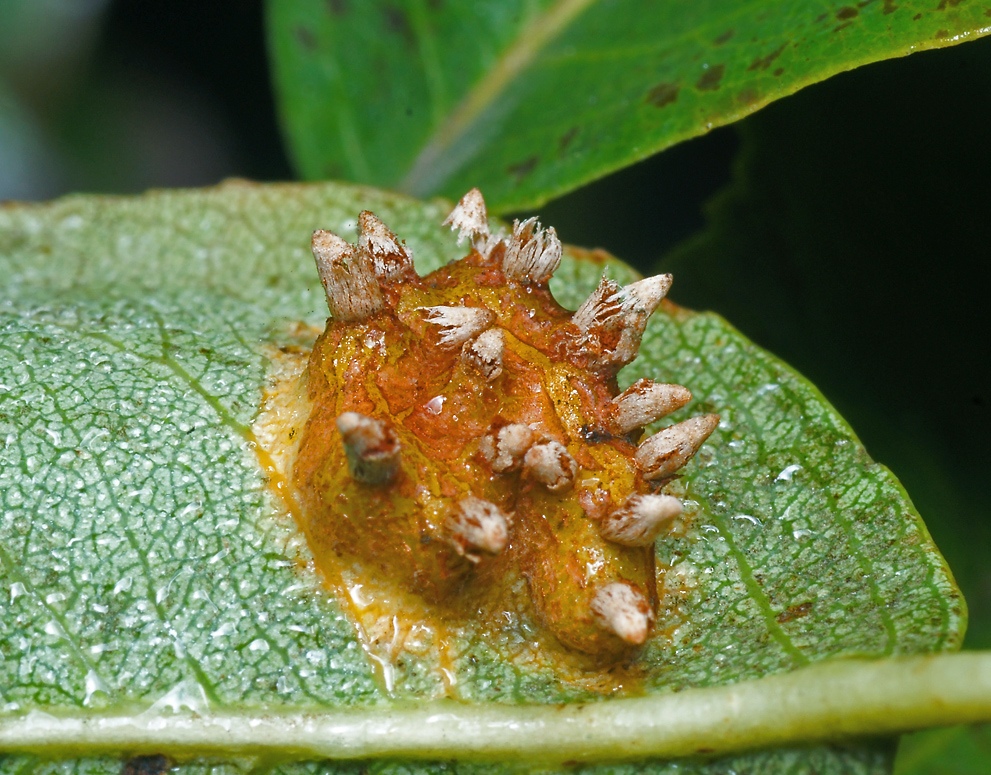
As they spread, they capture the entire surface of the damaged sheet plate, swell. In the affected areas, on the outside of the foliage, spermogonies develop. In the lower part, eciospores with a finely warty surface are formed. On windy days or on the legs of insects, they move around the site, and when they enter a humid environment, they germinate on healthy leaves and form a mycelium.
The mycelium spreads over time through the tissues, activating cell growth and thickening of the affected surfaces. 2-3 years after infection, teliospores are formed on the branches and trunk of the pear, in the form of cone-shaped horn-shaped outgrowths. They are re-formed into basidia, quickly covering the entire surface of the plant with the arrival of spring, moving into the parenchyma and re-forming mycelium.
What to do if the leaves on the pear turn yellow
Dealing with abnormal greenery requires finding the source of the problem. With a pronounced lack of nutrients, it is enough to feed with a complex mineral fertilizer. In other cases, the decision is more complicated, the gardener will have to deal with mechanical cleaning of the affected crop, use fungicidal preparations, etc.
Chemical treatment
The use of industrial solutions is considered the most successful solution in the fight against rust. For therapy, drugs containing copper are used:
- 1% Bordeaux mixture solution;
- "Champion";
- "Kuproksat";
- "Kuproksil".
You can deal with the problem:
- Fundazol;
- Topsinom M;
- Byleton;
- "Kumulus DF";
- "Tiovitom Jet", etc.
Treatment procedures are carried out according to a certain algorithm:
- Primary treatment is carried out before swelling of the buds, in early spring.
- Secondary - after flowering is complete, fungicides are applied.
- The final one - when the size of the fruit is the size of walnuts. Spraying of solutions is carried out 2 weeks after the second manipulation.
For the complete destruction of pathogenic microflora, it is necessary to process plants four or more times per season. The procedures are repeated annually for 2-3 years. The problem is solved only by such an approach that will prevent the death of the crop and normalize the volume of the harvest.
Mechanical wrestling
The physical solution to the problem involves the timely removal of infected foliage, before the kidneys open. The damaged branches are cut 10 cm lower from the places infected with the fungus. Wound black surfaces on the shoots are cleaned to healthy tissue, washed with a 5% solution of copper sulfate.
Acceleration of the healing process takes place by treating the damaged areas with a solution of "Heteroauxin" (in a proportion of 0.5 g per bucket of water) and covering them with "Garden Var". The excised branches and foliage are burned - the specimens left on the site can become a source of secondary infection, help the culture to re-cover with rusty spots.
Traditional methods
Many gardeners have a negative attitude towards industrial remedies for controlling diseases of pear specimens. They prefer to use homemade solutions, the list of fixed assets includes:
- Infusion of wood ash - 0.5 kg of the substance is diluted in 10 liters of liquid and sent to a darkened room for 2 days. The finished mixture is poured into a spray bottle and the affected specimens are treated.
- Manure infusion - the product is diluted with water in a ratio of 1 to 2, kept for one week. The prepared product is diluted a second time by 50% and the diseased culture is watered. For each adult plant, at least 10 liters of infusion are required, for young plants - from 4 to 6 liters.
- Soap-soda solution - 5 tbsp. l. linen soda is mixed with 50 grams of pre-grated laundry soap and diluted in a bucket of water. After half an hour, the garden is sprayed, the composition is best applied after the flowering phase is completed.
- Flower infusion - 0.5 buckets of recently picked marigolds are poured with the same amount of warm liquid. The mixture is infused for 48 hours, filtered and mixed with 50 grams of crushed laundry soap. After the completion of flowering, diseased cultures are treated with a solution.
In case of massive grip of rust or scab of pears, professional store preparations should be used. Solutions are prepared exactly according to the manufacturer's instructions.
Problem prevention
Prevention of the development of pathologies will help to avoid damage to the entire garden. Gardeners recommend not planting junipers next to the crop and regularly examining the plants for rust symptoms. Why the infection cannot appear a second time: the timely removal of the affected branches and foliage will prevent massive infection.
Chemical control
After the foliage falls in the fall, gardeners should sanitize the pears, spray them with fungicides, and prepare them for the next season. With the onset of spring days, therapy continues, it is carried out in three steps:
- before bud break;
- before opening the buds;
- after the end of the flowering period.
Preventive spraying is carried out with 1% Bordeaux liquid or any copper-containing preparation at least 3 times per season. If the pear is unstable to scab, it is treated regularly, but in this case, additional prophylaxis against rust is not used.
Important! If a Caucasian juniper grows next to pears, then it also needs to be constantly examined.
Non-chemical control
Ornamental plants on a personal plot are best planted away from pears and other trees. In this case, the risk of cross-contamination is reduced. Preventive measures of the planned type include the following recommendations:
- regular examinations of rose bushes, junipers and cultivated plants - for the timely identification of foci of a developing disease;
- destruction of weeds next to cultivated plants;
- remove fallen leaves from the root system and remove it immediately outside the site;
- whitewash the trunks and skeletal branches - with a mixture of lime and copper sulfate;
- add suitable nutrients in the fall - potassium chloride, superphosphate;
- make the treatment of the trunk circle with a 7% urea solution - upon completion of the collection of foliage.
Most budding gardeners make a serious mistake when trying to plant conifers and other crops in the immediate vicinity.
In order to prevent rust from appearing on the site, it is important to observe certain conditions: to protect the pear from the neighborhood with juniper or other conifers, to regularly prune and fertilize, to treat it with fungicides in time for prophylaxis. Proper care and timely protection will prevent fungal infections. Rust treatment takes several years and it is difficult to cope with the pathology, it is easier to carry out preventive measures.
Yellowness on foliage can be a sign of illness or improper care of pears. Before starting rescue work, the gardener must make sure that the change in the color of the greens is not associated with a deficiency of nutrients.