Plum diseases - black, yellow and brown spots on the leaves
Content:
To ensure an annual harvest of delicious fruits, gardeners should become familiar with the possible manifestations of plum disease and their descriptions. This will help to provide assistance to the affected seedlings in time.
What can a tree get sick with
Despite the fact that plum is a relatively hardy tree to various diseases, it can be attacked by:
- viruses;
- fungus;
- scab on the plum;
- bacterial infections;
- insects - plum pests.
Fungal diseases
The fungus is easily transmitted from an infected culture to a healthy one. This is due to the high level of moisture and thickening of the crown. Fungi can actively spread during warm and humid summers by rooting in tissues. In this case, a mycelium is formed, contributing to the rapid destruction of trees. After all, the disease of this category affects fruits, leaves, shoots.
Coccomycosis
In late spring and early summer, small specks with a brown tint appear on the foliage of trees, which can still turn red. This is a disease of plum coccomycosis. Around the middle of summer, there are such a large number of formations with a diameter of about 2 mm that they begin to merge into several large ones. On the seamy side of the leaves, pinkish and gray-white pads with fungal spores inside are formed. Before autumn, the affected foliage turns yellow, sometimes acquires an orange tint, curls and falls off.
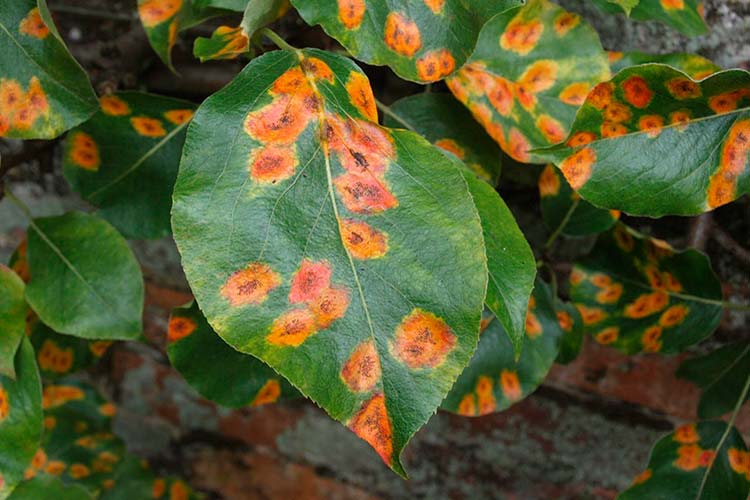
Rust
Many gardeners are wondering if there are rusty spots on the plum leaves, what to do. This often happens in the middle of summer. If there are rusty spots on plum leaves, small and angular darkening appears between their veins. Then rust on the plum is supplemented with pads of red summer fungal sporulation, which consist of urediniospores, which have an ellipsoidal or ovoid shape. They are characterized by thickening at the tops and are equipped with finely spiked shells. Over time, teliospores begin to appear among the urediniospores - winter mushroom spores, which look like pads of dark brown shades. Teliospores usually have spines on the surface, rounded at the tips, slightly taut.
Brown spot
Brown spot of stone fruits appears on plum leaves in the form of small spots, their color is different. It depends on the kind of fungus that has infected the plant. The specks on the foliage are brown, and the yellow spots on the plum can be framed with a dark border. After a while, many small black dots, called mushroom spores, form on the spots on both sides of the leaves.
To properly fight and cure stone fruit diseases, you need to remove the affected branches and familiarize yourself with how to process the plum. It is recommended to clean and disinfect young branches with a 1% solution of copper sulfate. To prepare it, it is enough to dilute 100 g of the drug in 10 liters of water. Then you can rub the wounds with fresh sorrel leaves and cover with garden var.
Plum pockets
Symptoms of infection develop on the fruit about 21 days after the petals have fallen off. The causative agent of plum disease is a marsupial mushroom. Infected fruits visually become noticeably larger than healthy ones, acquire a flattened shape, a soft structure, which is indicated by the name of the disease that needs to be treated.
As pathogens develop, the surface of the fetus becomes covered with a whitish coating, which becomes brown over time. Fruit disease consists in drying out on the tree, sometimes falling off.
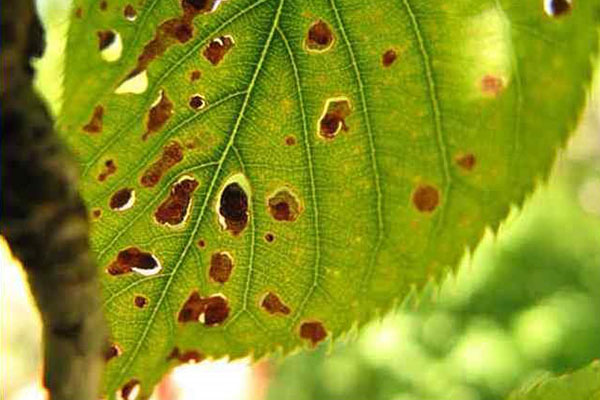
Clasterosporium disease
The disease is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- damage to buds, leaves, flowers, fruits with brown spots with a red border;
- the formation of holes in the foliage from spots;
- spotted shoots;
- cracking of the bark;
- shedding flowers;
- drying of leaves;
- the formation of reddish spots, swelling on the fruit, the release of gum, sometimes like a tear or wart on a tree.
With this disease, spores are actively produced. They are small in size and fly well, spreading through the garden. They are carried by wind, insects, tools. The yield of the tree is reduced to a complete loss.
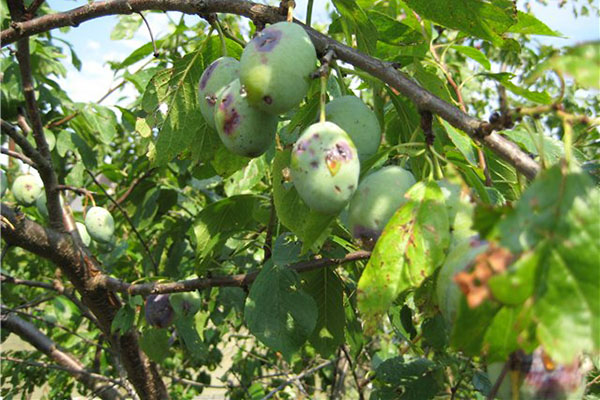
Stone fruit moniliosis
The causative agents of moniliosis strike most often during the flowering period. Infection occurs through the bark of a tree. The incubation period lasts up to 14 days, after which the foliage and flowers gradually turn brown, wither and die. On rainy and warm days, small white pustules with fungal spores may appear on the pedicels and leaf petioles on the underside. They are carried by the wind or garden pests of plums, and must be dealt with immediately. Brown specks may appear on the fruits, which gradually grow and cover the entire surface.
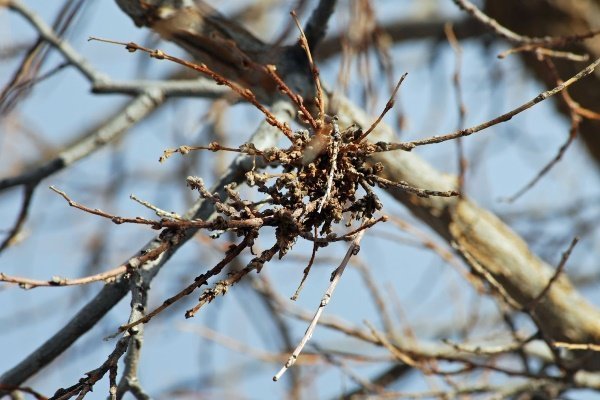
Witch's broom plum
This type of disease is popularly called bushiness or plum sprouting. At the site of the lesion, all parts of the plant suffer. The development of the disease is facilitated by various damages on plants, some of them appear as a result of the vital activity of insect pests.
In the place of localization of fungi, thin, sterile shoots grow en masse. They are visually similar to brooms. On the affected shoots, the foliage becomes smaller and soon crumbles. Towards the end of summer, a gray bloom appears on the leaves, which is the spores of the fungus.
Milky shine
When a grower discovers a silvery tint on plum leaves that can glisten, this is a signal of infection with a dangerous fungus. On young foliage, air voids appear under the upper plates on the skin. Then the leaves dry out and the branches die off. There are 2 forms of the disease:
- plum fruit disease caused by unfavorable growing conditions of the tree, which include cold winters and freezing of planting;
- the second form is parasitic, caused by a fungus.
According to experts, the second parasitic form often appears as a consequence of the first.
Fruit rot
Sources of infection:
- affected fruits left hanging on the tree after harvest;
- dry twigs affected by moniliosis, which were not removed during sanitary pruning.
The first signs may appear with carrion, from which spores are transferred to healthy fruits.Rotten fruits hanging on trees are mummified and remain carriers of the infection for 2 years. Through the stalks, the fungus gets to the fruit twig and nearby shoots, where it hibernates. With the onset of spring, it passes into a young ovary, causing wilting and death of overgrown branches.
Plum tinder fungus
Polypore grows mainly on trees of the Rosaceae family, especially on plums. Like most representatives of the genus fellinus, it causes a sign of brownish with a woody tone on the fruit body with small pores, it can turn red. It is characterized by cushion or semi-spread basidiomas, which often form tiled groups.
Sooty fungus
A particular danger of the disease lies in the weakened immunity of young crops that have not yet matured. In the autumn, with fallen leaves, the fungus can enter the soil and overwinter.
When spring comes, it begins to activate and destroy garden crops. The mob attacks pi at an elevated temperature against a background of high moisture. Plaque clogs foliage and interferes with photosynthesis. Over time, individual parts of the tree begin to die off.
Viral diseases of plum trees
Any gardener, especially a beginner, should know the most common viral diseases that are known in the Moscow region and other regions of the country.
Plum Pox (Sharka)
The first sign of smallpox is the appearance of lines and specks on the foliage of the plum tree, which differ in color from healthy tissues and are slightly translucent. Ring-shaped spots can also be seen on fruits that are affected. They become unusable and fall off early enough - everyone understands why.
Plum dwarfism
This type of disease hinders good foliage growth on the plum tree. They become small, uneven and narrow. There are especially many such leaves on the tops of the shoots that are affected by the disease. The growth of an infected plant slows down noticeably, after a few years it dies.
Plum tree bacterial diseases
It is also worth considering what diseases of a bacterial nature exist.
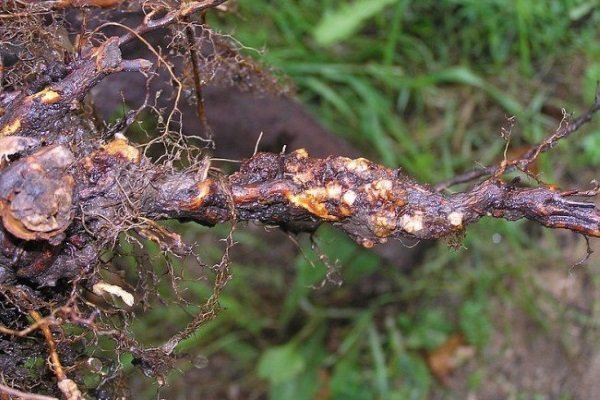
Root cancer
Cancer contributes to the defeat of fruit crops. Under the influence of parasitic bacteria, the tissues of the root system or neck grow, and growths are formed. They pose the greatest danger to the root collar. On seedlings 3-4 years old, tumors sometimes reach the size of a fist and weigh 5 kg or more.
Bacterial burn
The fruit tree, when it starts to hurt, gradually withers, its inflorescences die, the foliage dries up and curls, ulcers appear on the bark, exudate is released on the affected shoots.
Non-communicable diseases
There are diseases that are not associated with fungi and bacteria. They are called non-infectious.
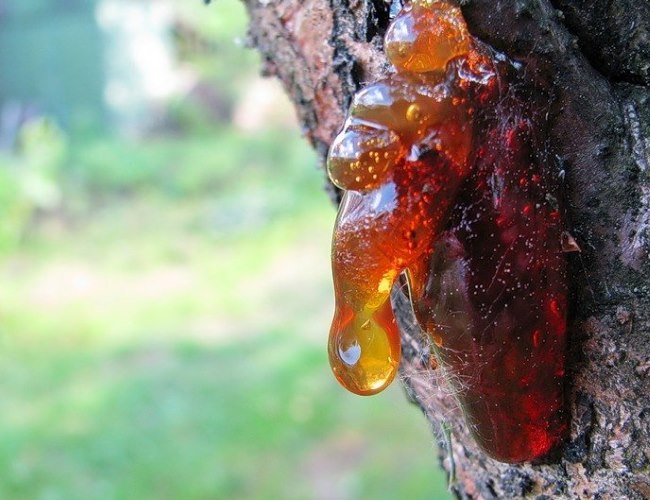
Gum therapy
Frozen crops or those that are already affected by the fungus are susceptible to this disease. There are also factors that increase the risk of the disease. These include high soil moisture and a large amount of applied fertilizers. Gommosis is recognized quite simply - gum is released from the trunk and branches. After the substance solidifies, a transparent drop of any size forms in its place.
Shrinking
If the conditions necessary for the normal growth of horticultural crops are not followed, drying out may occur. The reason lies in the close occurrence of groundwater, soil acidity, freezing, gum flow. The leaves begin to dry out first.
The meaning of the spots on the leaves
Periodically, the gardener can observe the appearance of various shades on the foliage of the crops of his site, which also indicate the unhealthy state of the plants.
Leaves turn yellow and dry
The main cause of chlorosis in plums is poor stock compatibility of grafted trees or poor quality grafting. Also, the state of the foliage is affected by mechanical disturbance of the roots, insufficient or excessive amount of moisture in the area of the root zone.
Brown spots on plum leaves
The appearance of brown spots on the foliage indicates the defeat of the garden culture by insects, fungus. It can also be the reason for the lack of trace elements important for plant nutrition.
Plum leaves turn black
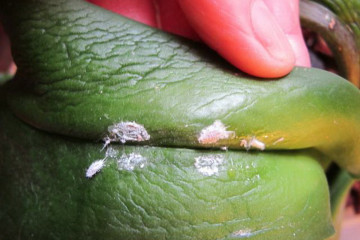
If the plum leaves are visibly covered with a sticky black bloom, often in the company of fruits, this is a sign of an aphid attack. It contributes to the weakening of the culture and carries with it the spores of the sooty fungus.
White bloom on plum leaves
A white sticky coating on the foliage of a plum tree is a symptom of powdery mildew. The disease contributes to the defeat of all parts of the culture and affects the general condition of the garden.
Pale and light leaves
The pallor of the sheets should alert the gardener. After all, it can be a physiological or pathological sign. Most often, the reason for this is:
- lack of nutrients;
- missing amount of nitrogen in the earth;
- lack of potassium-phosphorus fertilizers;
- lack of potassium, manganese, iron or copper.
Preventive treatment
Preventive measures include:
- collection and destruction of the remnants of the affected plum tree, as well as fruits, both crumbling and remaining on the tree;
- cutting and burning affected shoots and fruits;
- digging up the soil in the peri-stem circle during early spring;
- treatment of cracks in the bark;
- removing weeds in garden plots;
- processing the culture with Bordeaux liquid or a solution of copper sulfate with soap.
It is necessary to spray the affected plums at least three times a year: in the fall - after harvesting the garden, in early spring - until the buds open and after the end of flowering.
Owner care and attention, as well as timely treatment, is the best way to preserve the health of the garden and reap a rich harvest.