Fruit trees and shrubs for the garden, columnar fruit trees
The owners of large backyards and small summer cottages alike love to pamper themselves with fresh fruits and berries. To do this, the garden has to "settle" fruit trees and shrubs, the varieties of which there are a great many. Certain species are especially fond of gardeners.
Juicy fruits from their own trees are a gardener's dream. Even a beginner can get a harvest if he follows the rules for planting and caring for trees. First, it is worth deciding which types of plants are best to plant in a certain area.
Fruit trees
There is a huge list of species and varieties of fruit and berry trees that get along in almost any climate. Now, seedlings for a garden can be safely chosen not only by a resident of the Moscow region or Crimea, but also by a gardener whose site is located in Siberia.
Apple tree
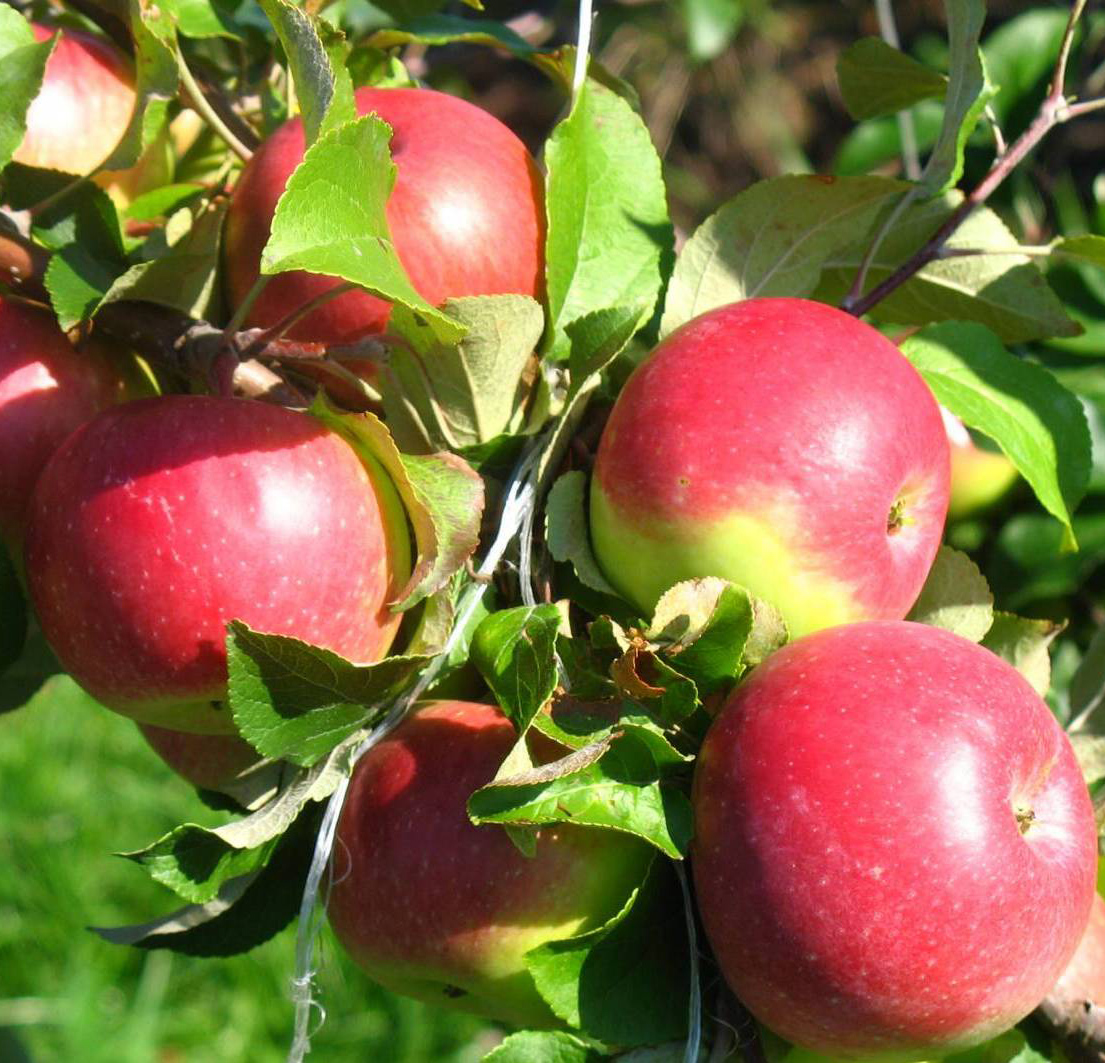
The apple tree is perhaps the most famous fruit variety. Trees are grown in both conventional vegetable gardens and farm gardens. It is a very unpretentious species, yielding quite sweet (depending on the variety), tasty and healthy fruits.
Visually, it is a tree with a spreading crown, with a height of 2.5 to 10 m. There are so many varieties of apple that it is difficult to distinguish common features inherent in all trees of this species.
The beginning of fruiting of an apple tree begins by 4-5 years after planting. In total, a tree can live for about 40 years.
The apple tree is distinguished by good resistance to frost, tolerates shading well. Does not require too frequent feeding. Young fruit trees can be planted both in spring and autumn. It should be borne in mind that the apple tree does not like drafts and stagnant moisture in the soil.
Pear
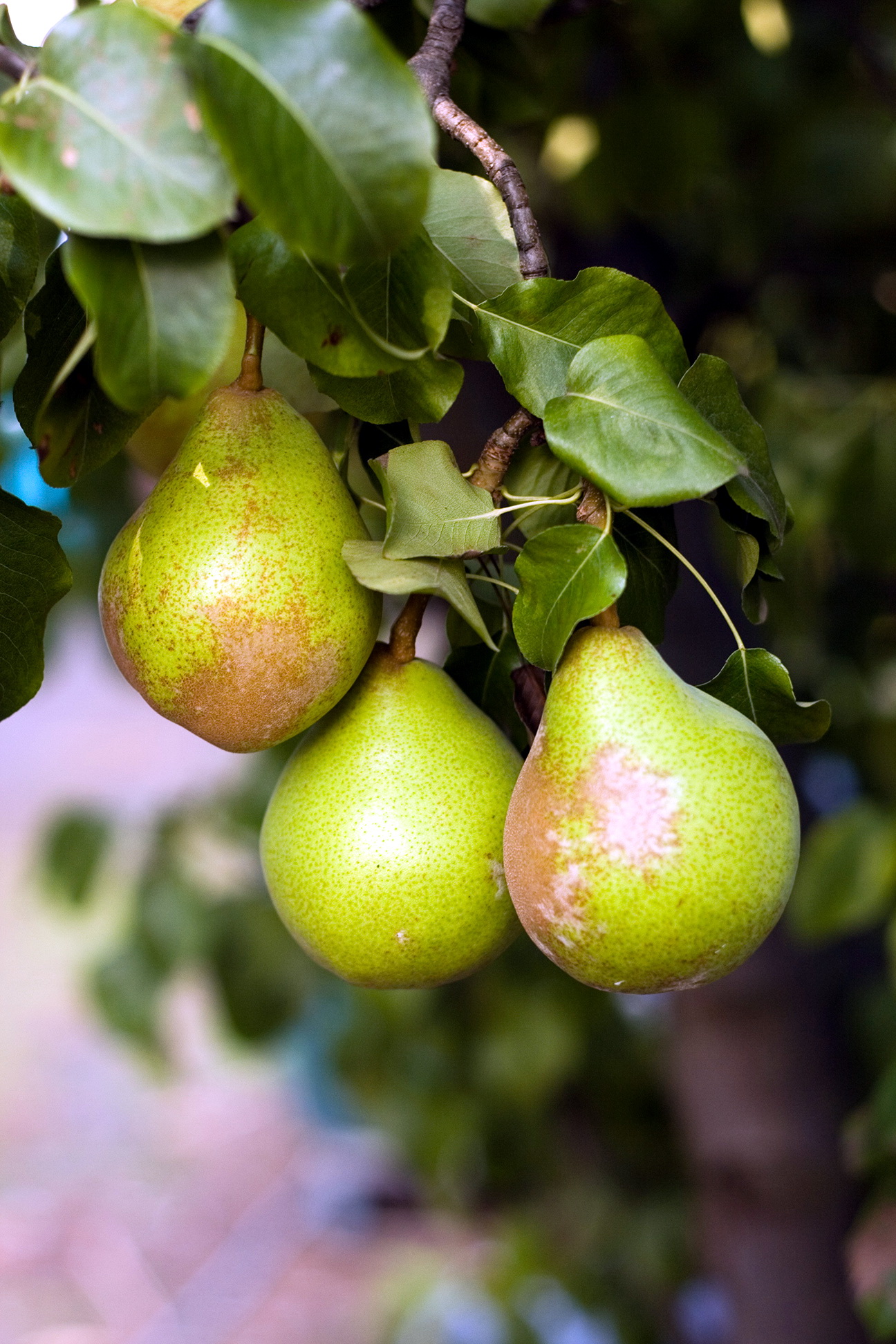
This deciduous fruit tree with dark ovoid leaves and smooth bark is the main competitor to the apple tree. Its lifespan is about 100 years. Garden beauty grows throughout European territory, as well as in Central Asia.
The pear loves loose, nutrient-rich soils, therefore, requires additional feeding and careful selection of a planting site. If the tree has taken root, it is actively growing and can eventually reach a five-meter height.
Planting is desirable in the fall, although it is also permissible in spring. Choose a sunny location with loose soil. The pear gets along well on loams. In the first 4 years of life, the seedling needs nitrogen fertilization and watering in dry weather.
Pear begins to bear fruit in 4-7 years of cultivation.
Plum
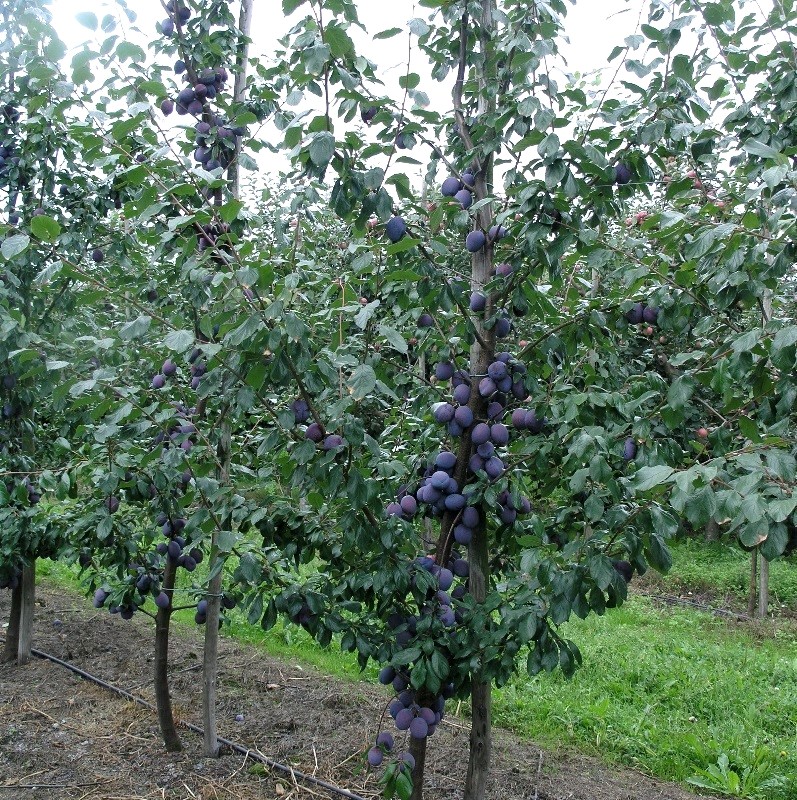
A natural hybrid of blackthorn and cherry-plum - plum, also a frequent guest in the gardens of the European part of Russia. It is a tall (up to 15 m) tree with an ovoid crown. Plum lives up to 25-30 years, of which only 15 bears fruit.
Planting plum trees is best done in spring or early autumn.
Adult trees, as a rule, tolerate winter without problems; it is advisable to wrap first-year seedlings with straw along the trunk. In spring, mature trees need pruning, which is usually done in March.
Apricot
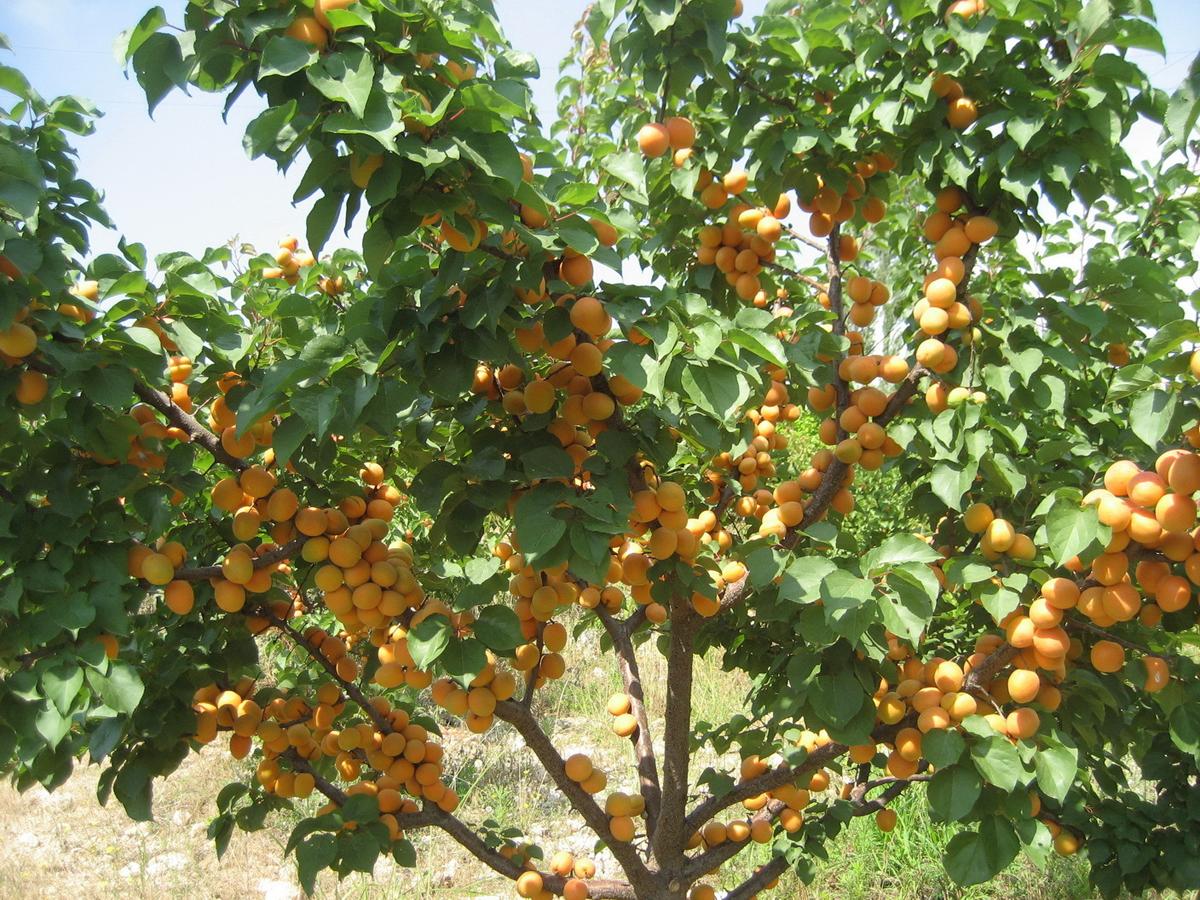
Apricot is a relative of the plum, also belonging to the Pink family. In memory of this belonging, the old Russian name of the tree remained - the yellow-leaved plant.
The apricot is a deciduous fruit tree up to 8 m in height. It blooms in April, and the flowers appear before the leaf plates, which makes the tree very beautiful at this time.
The tree lives for a long time, up to 100 years, begins to bear fruit from the 3rd year of life and continues for 30-40 years. Thanks to a strong root system that penetrates deep into the soil, it is not afraid of drought. Contrary to the opinion that apricot is a southern plant, it tolerates frosts down to -25 ° С, some varieties even up to -30 ° С.
Berry trees
Along with fruit trees, berry trees are welcome guests in the gardens. They also exist in a great variety of species and varieties, with good care they bear fruit abundantly and grow actively.
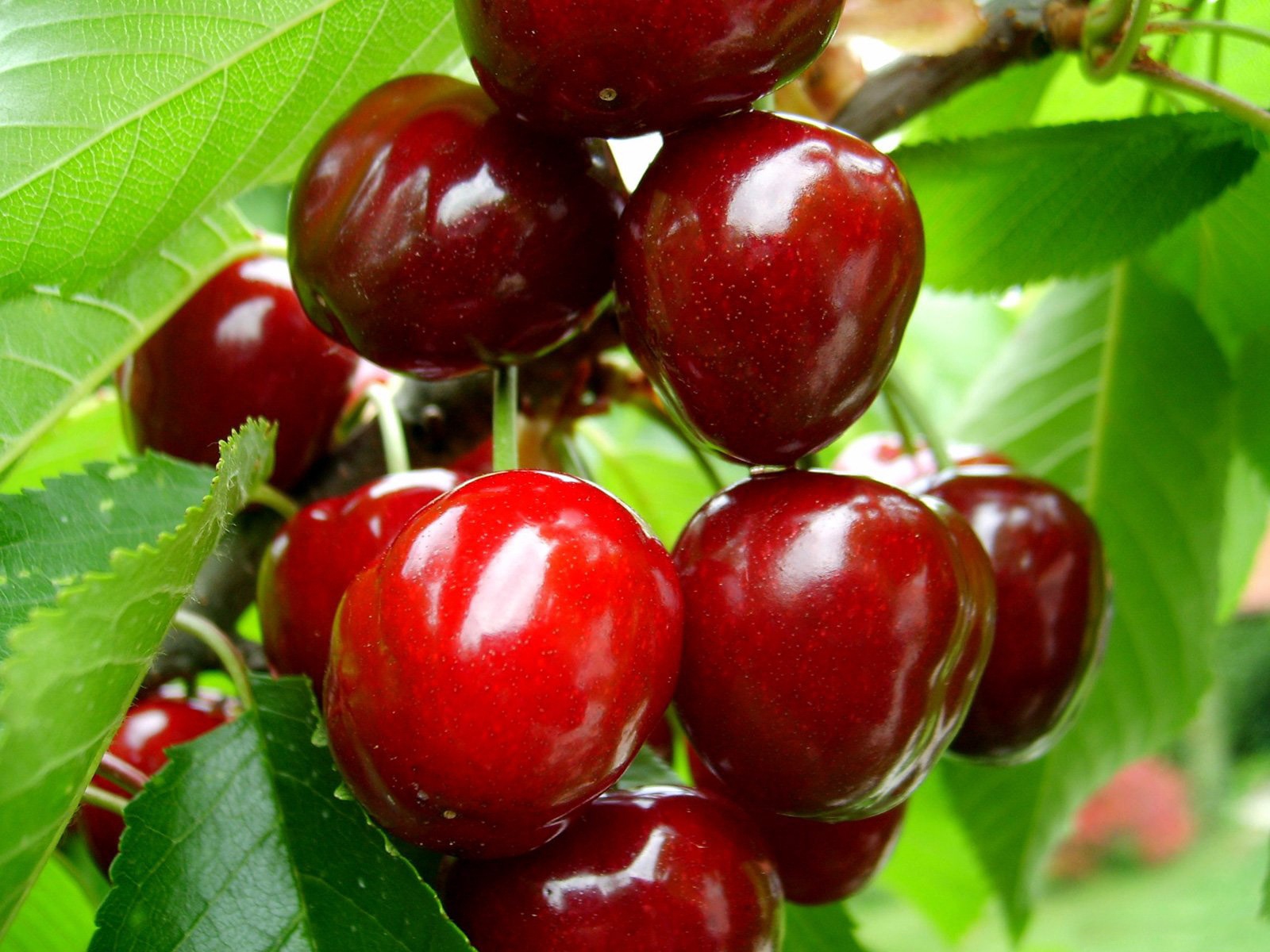
Cherry
Another popular member of the Pink family is cherry. This culture grows both in the form of a shrub plant (up to 3 m) and in the form of a tree (up to 8 m). Moreover, tree-like forms begin to bear fruit a little later than bush ones.
Cherry grows almost everywhere, except for deserts and the extreme north. The tree lives for a relatively short time, about 30 years.
There are a huge number of varieties of this tree, and some of them are self-fertile, others are not. So it is advisable to have several cherries on the site, at least 2 varieties.
For seedlings, it is recommended to find well-lit places with sandy loam soil. Cherry does not like heavy soil and stagnant water at the roots. But it tolerates drought steadily, although it requires summer watering in the first years after planting.
Cherry is resistant to winter frosts, although sometimes at too low temperatures, about 90 percent of its flower buds freeze out. Most of all, the tree "does not like" winter winds and blizzards, in a blown place it can die even with relatively mild frosts.
Cherries
The oldest variety of cherry is cherry (aka bird cherry), it is a fairly tall tree, up to 10 meters. Sometimes there are large size and 30 m in height. The root system is usually horizontal, but under special conditions, vertically directed roots can develop.
Cherry begins to bear fruit from 4-5 years of age, the whole tree can live up to 100 years. This tree, like cherry, does not like stagnant moisture, cold winds and heavily shaded places.
In spring, cherries need formative pruning and feeding (from the 4th year of growth).
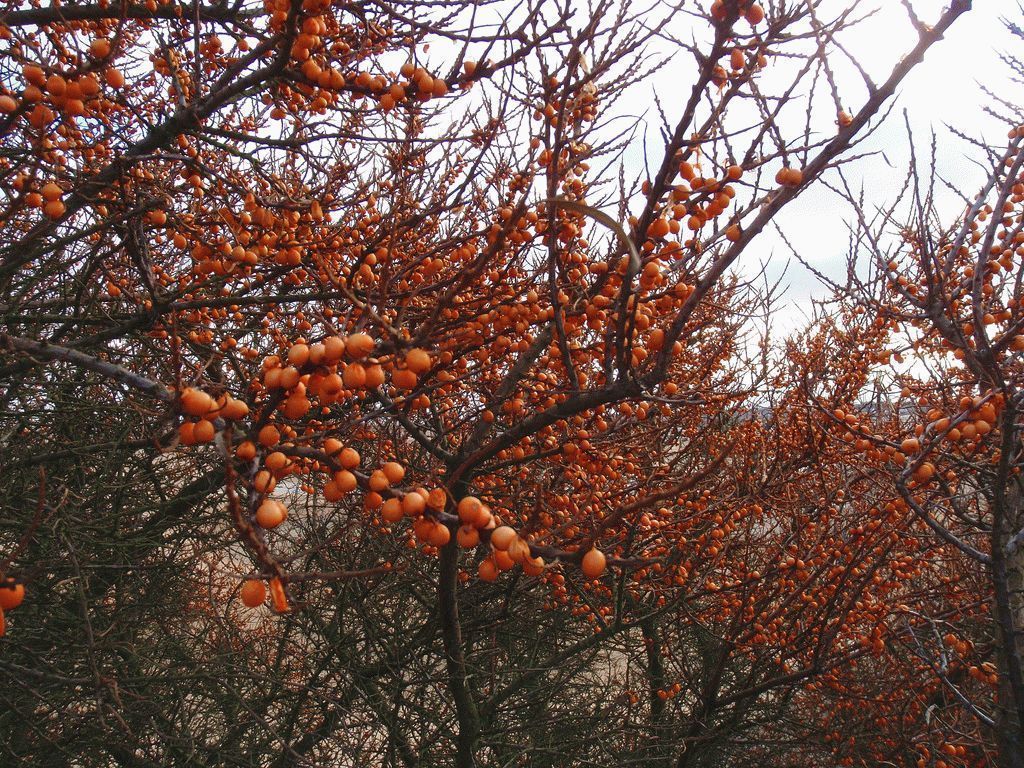
Sea buckthorn
Sea buckthorn is a tree (it can also grow in the form of a bush), which has not only useful, but also decorative properties.
Plant height can reach 10 m, the root system is superficial, highly branched. Sea buckthorn blooms inconspicuously, its real decoration is bright orange berries. They have a specific taste, but they are very useful for health.
It makes sense to plant only female specimens on the site, since male specimens do not give berries.It is easy to distinguish them: the buds on female trees are smaller, with a pair of scales. On men - larger and "shaggy". This becomes noticeable only at 3-4 years of plant life.
The selected place on the site should be well lit, it is not bad if the soil is slightly wet, but without an excess of water.
Features of the root system of fruit trees
Fruit roots are most often powerful, lie deep in the ground. The root system is wider than the crown. The better the soil is fertilized, the wider it grows, becoming more powerful. This ensures the active development of the aboveground part of the plant and its abundant fruiting.
That is why it is so important to loosen, water and fertilize the soil in the tree trunk circle. The nutrition of the plant through the root directly depends on this, which means the yield.
Fruit shrubs
If there is no place for trees with their powerful crowns and roots, you can pick up fruit bushes for the garden.
Berry bushes for the garden
With proper care, each berry bush can produce an excellent harvest. The rules for caring for compact plants are similar in many ways and are not difficult.
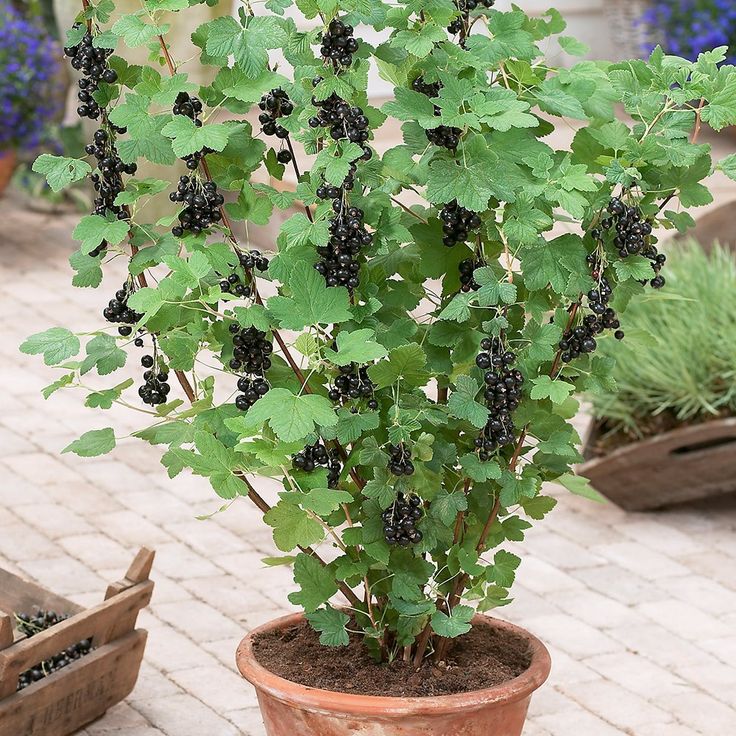
Currant
Currant - a shrub from the Gooseberry family, needs no introduction. In Russia, it was grown in the X century. There are a huge number of recipes using the berries of this plant.
Perennial shrub has many varieties. Some differ in height (there are plants of 300, 500, 800 cm), in compactness, in the color of berries (sometimes black, red, white, golden).
The currant has a strong fibrous root system, thanks to which the bush quickly takes root in a new place. Already in the second year after planting, you can wait for the harvest. With good care, currants will delight with berries up to 15 years.
Well-lit areas with drained soil and no strong winds are suitable for planting.
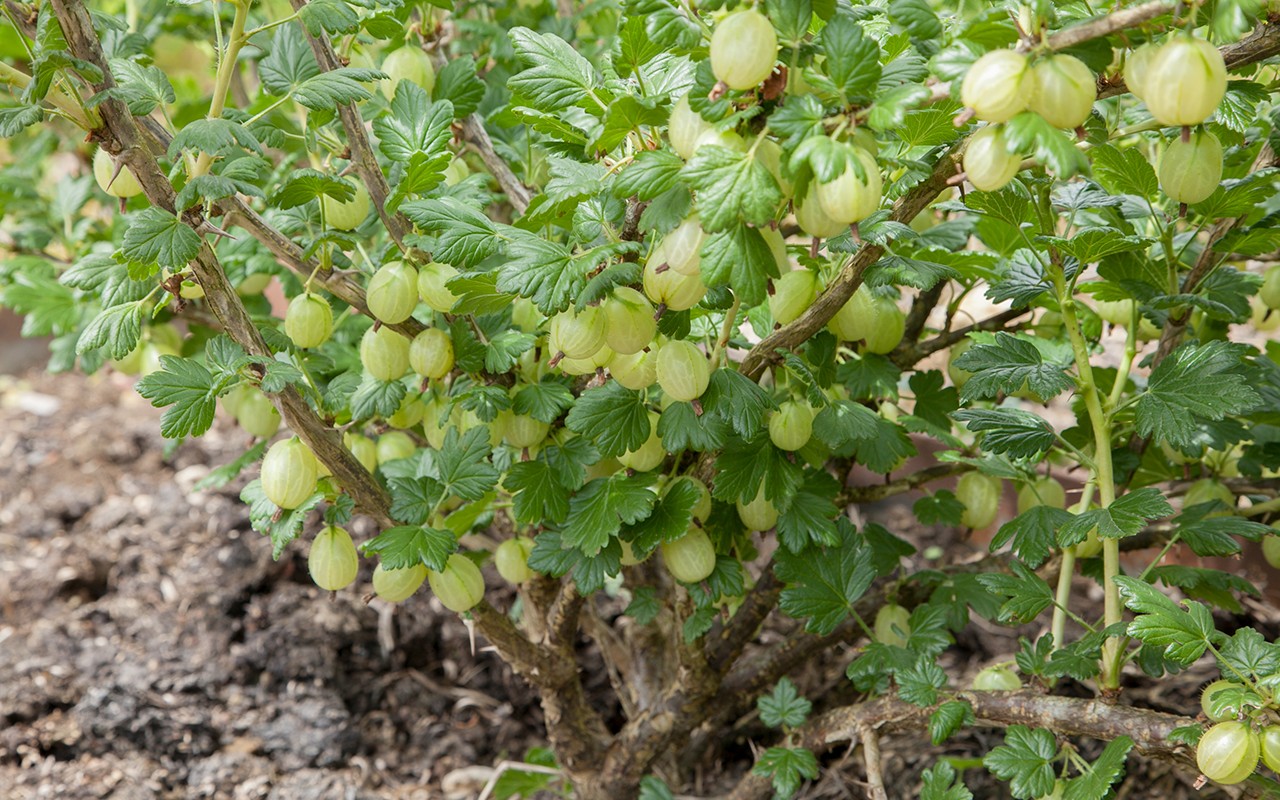
Gooseberry
A relative of currants, gooseberries, are no less common. It is actively grown for the sake of delicious berries. An unpleasant feature of the plant is its thorny thorns, which interfere with harvesting.
Gooseberry is a perennial of small height, with bright, dense leaves. It blooms early, is a honey plant, which attracts beneficial pollinating insects to the site. The main advantage of the shrub is its self-fertility. Only 1 plant on the site is capable of abundant and regular harvest.
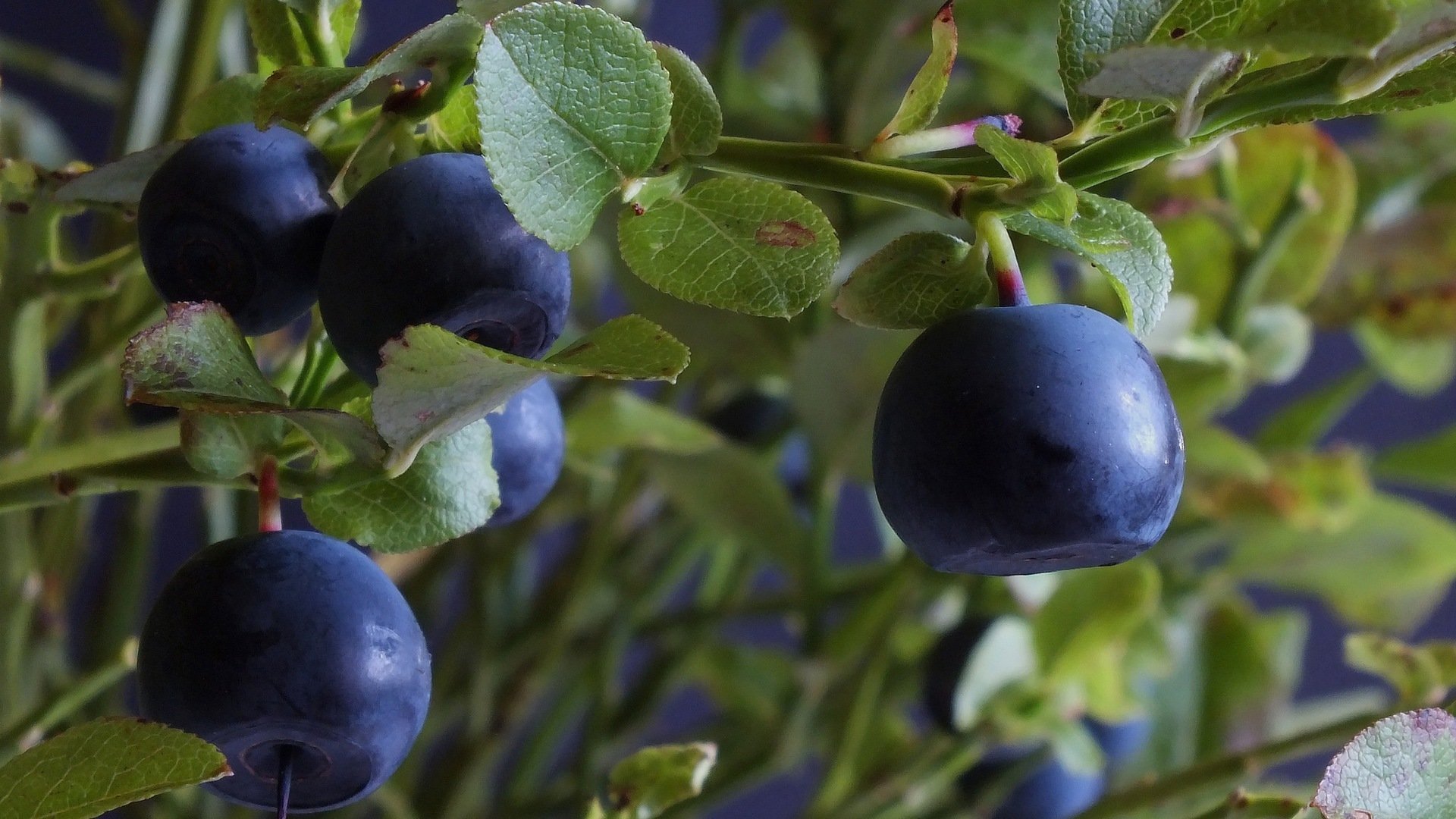
Blueberry
This low (up to 1 m) deciduous shrub did not become as widespread as the ones described above, however, many have tried its fruits.
Blueberries tolerate shade and partial shade well, frequent moisture. Doesn't like drought. Therefore, if a sunny place is chosen for it, you will often have to water and spray with water.
In the central regions, blueberries are planted in autumn, in September-October, in the northern regions, spring planting is preferable.
Blueberries require frequent watering so that the soil at the roots always remains slightly damp. Annual feeding with mineral and organic fertilizers has a beneficial effect on the plant, both under the root and on the leaves.
What shrubs to plant in the shade
When all the bright, spacious places on the site are already filled with vegetation, the question arises of what to plant in the shade. Full shading does not work very well on almost all plants, however, there are shrubs that will not only take up the remaining space, but can also bear fruit under the conditions provided.
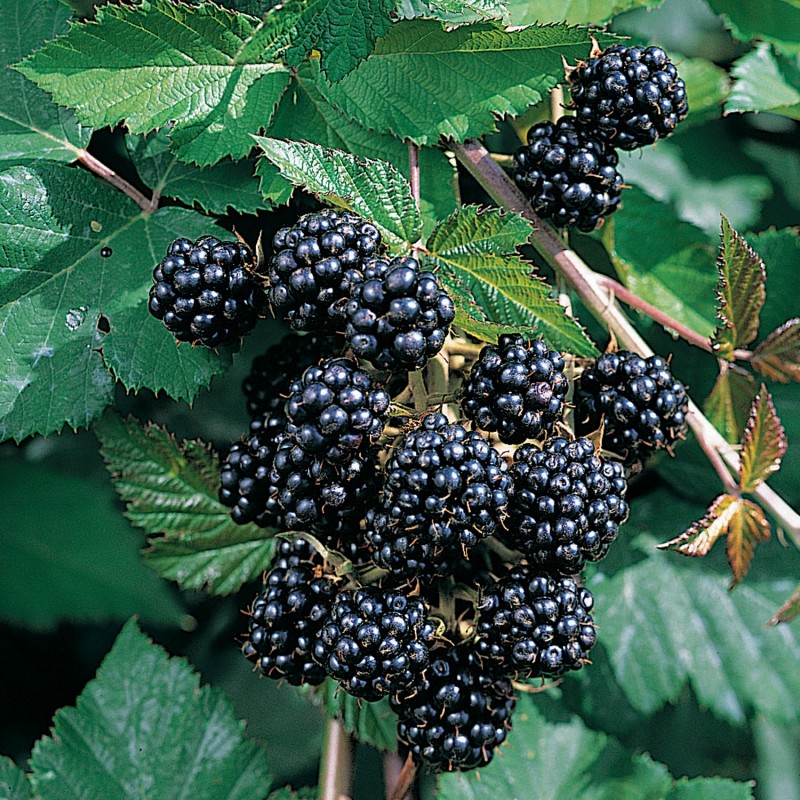
Blackberry
Blackberries often grow on the side of the road, wildly, and so braids everything around that it is impossible for a person to pass in these places.The taste of dark berries is worthy of all the torment that awaits people who have fallen into the thickets of creeping dwarf shrubs.
The yield of blackberries is remarkable, 3-4 times higher than that of raspberries. The similarity does not end there: blackberry shoots, like raspberries, begin to bear fruit only in the second year.
The fruits ripen on the half-shrub in stages, so that the harvest takes a long time.
Another advantage of the blackberry is its decorative effect. Connoisseurs of landscape design advise to plant a plant near a fence, mesh or other support. So over time, you can get a hedge.
Dogwood
Another shade-tolerant bush is dogwood. It is quite high, up to 2 m, with shoots hanging down to the ground. If the branch reaches the ground, it quickly takes root, so it is not difficult to propagate the dogwood.
Among the garden bushes, this owner of scarlet edible berries is a long-liver. The plant can be up to 100 years old.
Dogwood does not like an excess of light, so it is best to find a place for it near a farm building or the edge of a hedge.
It is not difficult to care for this plant. As a basis, you can take the rules of caring for gooseberries or currants: weeding and loosening, timely watering, spring and summer dressings, sanitary and rejuvenating pruning.
Aronia
Aronia, or black chokeberry, used to be grown as an ornamental plant. Then it was cultivated, various varieties were bred, the berries of which are distinguished by good taste.
This branching shrub strikes with its amazing unpretentiousness, grows well in the shade and is not afraid of frost. Due to the shallow root system, stagnant groundwater is not afraid of chokeberry.
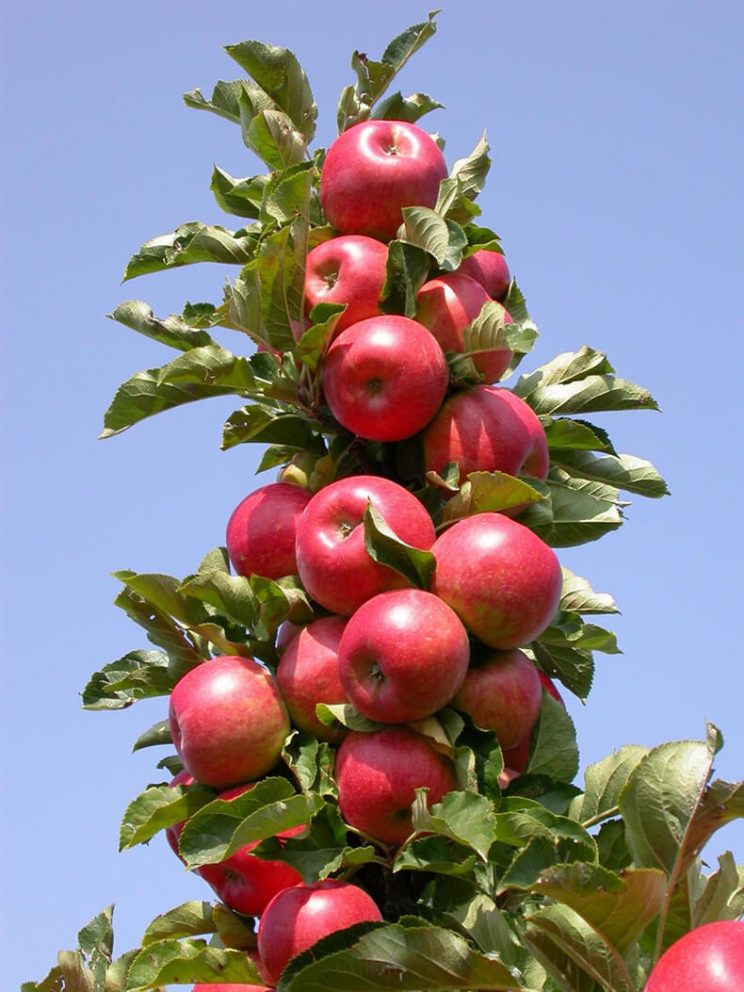
Columnar trees
For those in whose area it is problematic to arrange at least a few spreading plants, columnar trees can be advised. They got their name because of the external resemblance of the form to the column. From a distance, it seems that these plants have no branches at all. This is not so - there are branches, but short.
Features and disadvantages
Columnar trees have their own characteristics and disadvantages associated with their external data.
Benefits:
- Compactness. Such plants do not need a large area;
- Productivity. Trees become fruitful already at 2 years of age;
- Unpretentiousness. No special conditions are required for them;
- Decorativeness. Young trees serve as a decoration of the site.
There are only two disadvantages of columnar trees: fragility (they bear fruit for no more than 20 years) and a higher cost than ordinary seedlings.
How to plant columnar trees
Columnar trees love loose, rich, sandy loam soil and sunlight. They do not tolerate stagnation of moisture at the roots and drafts.
Saplings are planted in spring, at a distance of 1 m from each other. If there are several seedlings, the scheme for planting them is a square, with sides of 1 m.To do this, dig a hole 60 × 70 cm in advance.When the soil settles, you can lay out the drainage on the bottom, add a spoonful of nitrogen and potash fertilizers, sprinkle it with earth a little.
Having straightened the roots, put the seedling in the hole and cover it with earth to the root collar, gently tamping it with your hands. After that, it remains to water the planting abundantly.
How to care
Rules for caring for columnar fruit trees:
- Watering. Young trees are watered once a week in dry summer or less often if it rains frequently. Sprinkling in the heat is also useful for them;
- Top dressing. 1st application on melted snow (nitrogenous), 2nd - during flowering (mullein solution) and the same composition is applied again a week after flowering. 4th application is carried out in the fall (phosphorus and potassium);
- Pruning. This procedure is extremely rare if long side shoots appear. It is important not to forget to lubricate all the places of the cuts with garden varnish.
The variety of garden trees allows you to choose the options that are optimal for the site. It is also easy to find fruit and berry bushes that will delight with the harvest every year. You can safely plant the garden of your dreams.