Rose Ali Baba (Alibaba)
Content:
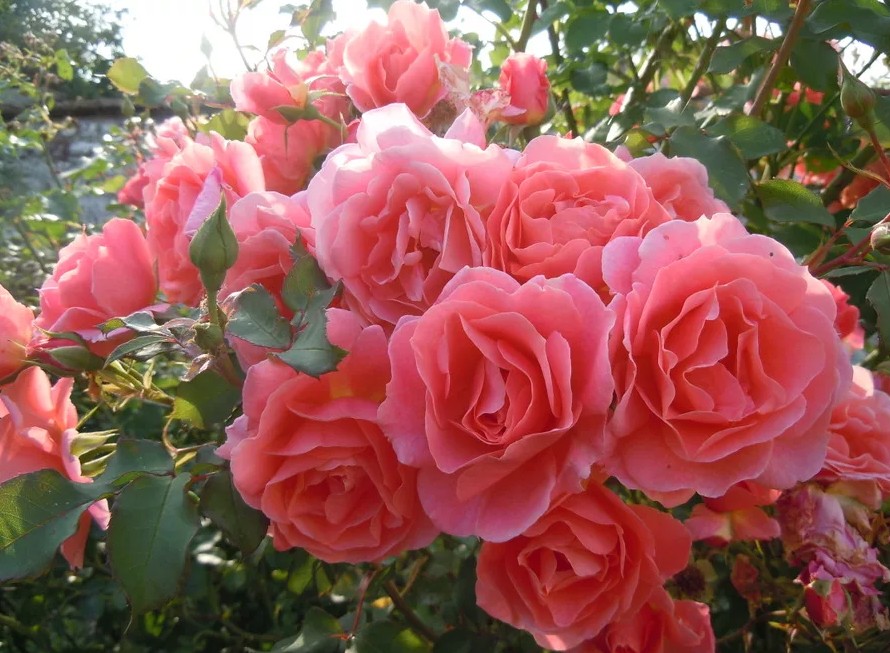
The charming climber Ali Baba deservedly attracts admiring glances. Vigorous growth, excellent health and almost continuous flowering make the rose a desirable specimen in the piggy bank of rose varieties. Delicate play of copper-salmon-pink scalloped petals is complemented by a bright fruity-pink scent.
Characteristics of the variety
Officially, the Alibaba variety was registered in 2007 under the brand name of Alibaba rose (CHEwalibaba, Schloss Bad Homburg ®, Sunset Glow, Ali Baba). The breeding work was highly appreciated by professionals:
- 2007 (Gold Standard Rose Trials) the cultivar was awarded the Gold Standard award in the testing of cultivars in England.
- 2008 Winner at an exhibition in Lyon (France) for aroma.
- 2011 Championship in the category Climbing roses at the exhibition-competition in Italy.
- 2014 bronze award-certificate of the competition in The Hague (Netherlands); bronze medal of the Japan Rose Competition.
Roses of the British breeder Christopher Warner, the originator of this variety, are characterized by resistance to weather whims, originality of colors and high repairability.
Alibaba flowers grow large in optimal conditions (10 - 12 cm), not inferior in size to hybrid tea. The flower is semi-double, airy due to the wavy edge of the petals. The color is complex, changeable during the life of the flower, brightens. The illusion of glow is created by the bright coloration at the base of the petals.
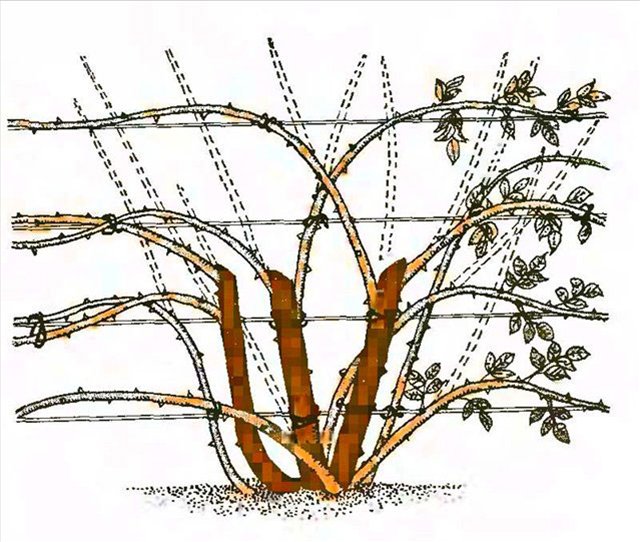
A plant with high vigor, in the first year after planting, it builds up green mass, at the same time produces clusters of buds. Blooms mainly at the ends of the shoots. An adult rose, for abundant flowering along the entire length of the shoot, must be laid on a support (horizontal).
The advantages of the variety include:
- continuous flowering;
- strong pleasant aroma;
- well leafy shoots, not bare at the bottom;
- resistance to rain: the petals are not damaged by moisture, do not rot;
- self-cleaning: wilted flowers crumble and do not require pruning, do not mummify, reducing the decorative effect of the bush;
- high plant resistance to the most common diseases in our latitudes (powdery mildew and black spot).
Do not expect cascades of fragrant bunches in the first year of the plant's life in the garden. In the first 2 - 3 years after planting, the rose adapts to a new place, gaining strength. Flowering may end quickly and the expected aroma may not be heard.
Growing and care
In the description of the variety, it is indicated that the shoots of the rose grow up to 200 - 250 cm. The declared width of the bush is up to 120 cm. It should be noted that in the southern regions the rose is capable of curling more than 3 m in length, and requires shading at midday. Otherwise, the flowers will fade in the sun and fly around quickly.
Landing rules
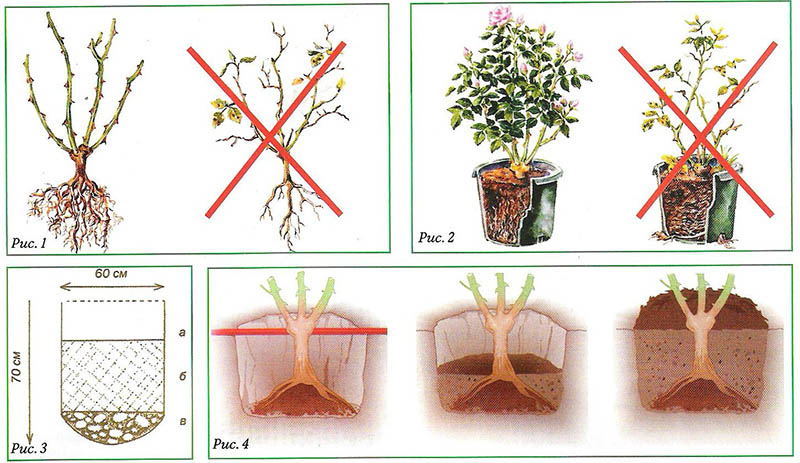
A rose is planted taking into account the dimensions of an adult plant, in a well-lit area, protected from wind and drafts. Low areas should be avoided so that the landing site is protected from excess moisture in rain or during snowmelt. Groundwater close to the surface will also prevent the rose from developing fully. Locking the root system can lead to the death of the plant.
The depth of the planting pit is approximately 70 - 80 cm, with a diameter of up to half a meter. It must be seasoned with a nutrient mixture to provide the young plant with a comfortable development and rapid rooting. For areas with loamy soil, mix in equal parts:
- peat;
- sand;
- sod land;
- vegetable compost.
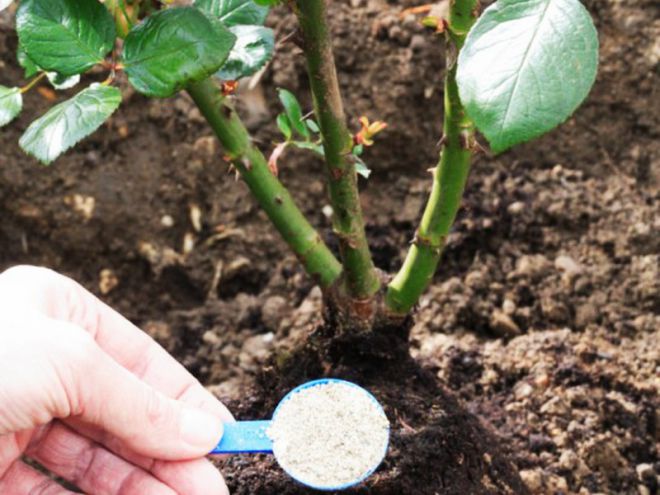
Additionally, it is recommended to fill the pit with 200 g each:
- ash;
- phosphate fertilizer;
- bone or dolomite meal.
In the case when the soil on the site is poor, sandy, the hole should be made deeper, and clay should be used instead of sand. Then the moisture and nutrients needed by the roses will be retained at the roots longer.
Before planting, shoots and branches are shortened to 30 - 35 cm so that the rose spends energy on rooting, and does not feed many buds. The roots should also be freshened. For this, each root is shortened by 2 - 3 cm with a sharp secateurs. The cut reveals white tissue, at the dry roots of a tree-colored tissue, they are cut to live, white. Saplings purchased with an open root system are preliminarily left in a container with water to the level of the root collar for a period from 1 hour to 1 day. A good sign is the presence of small white water-sucking roots on the roots of the plant.
Watering
In the first weeks, it is necessary to monitor the soil moisture at the roots of a young bush. After watering, the drying soil is loosened to avoid cracks when drying out. An adult plant needs regular watering during dry periods. It is enough to moisten the soil around the rose well once every 7 to 10 days. This requires 10 - 12 liters of water, and so that the liquid does not spread over the surface, you can make a small groove around the bush and water it gradually. You can prevent moisture evaporation by mulching the root area. For this, mowed, sun-dried grass is suitable.
Fertilizer
In the first year after planting in a properly filled hole, the rose does not need additional feeding. Enhanced nutrition is necessary for a plant that fully blooms all summer. The rose fertilization system is based on three essential elements:
- nitrogen: the plant's need during the beginning of the growing season, when the plant grows green mass (shoots, foliage);
- phosphorus: a plant that has received the required amount of the mineral actively develops the root system, produces buds;
- potassium: stimulates growth and flowering, works as an immunostimulant for roses.
It is recommended to feed the rose with organic fertilizers (nitrogenous) until mid-summer. Complex fertilizers containing, in addition to potassium and phosphorus, iron, magnesium, sulfur and other necessary elements can be done until autumn.
Top dressing can be:
- root: when fertilizer is poured into the root area or the rose is watered with their solution;
- foliar (by leaf): in this case, the fertilizer solution is made weaker so as not to cause burns to the leaves and spray the ground part of the rose, wetting the leaf as much as possible.
Fertilize roses in the early morning or evening after sunset. It is advisable to carry out foliar feeding in cloudy, calm weather.
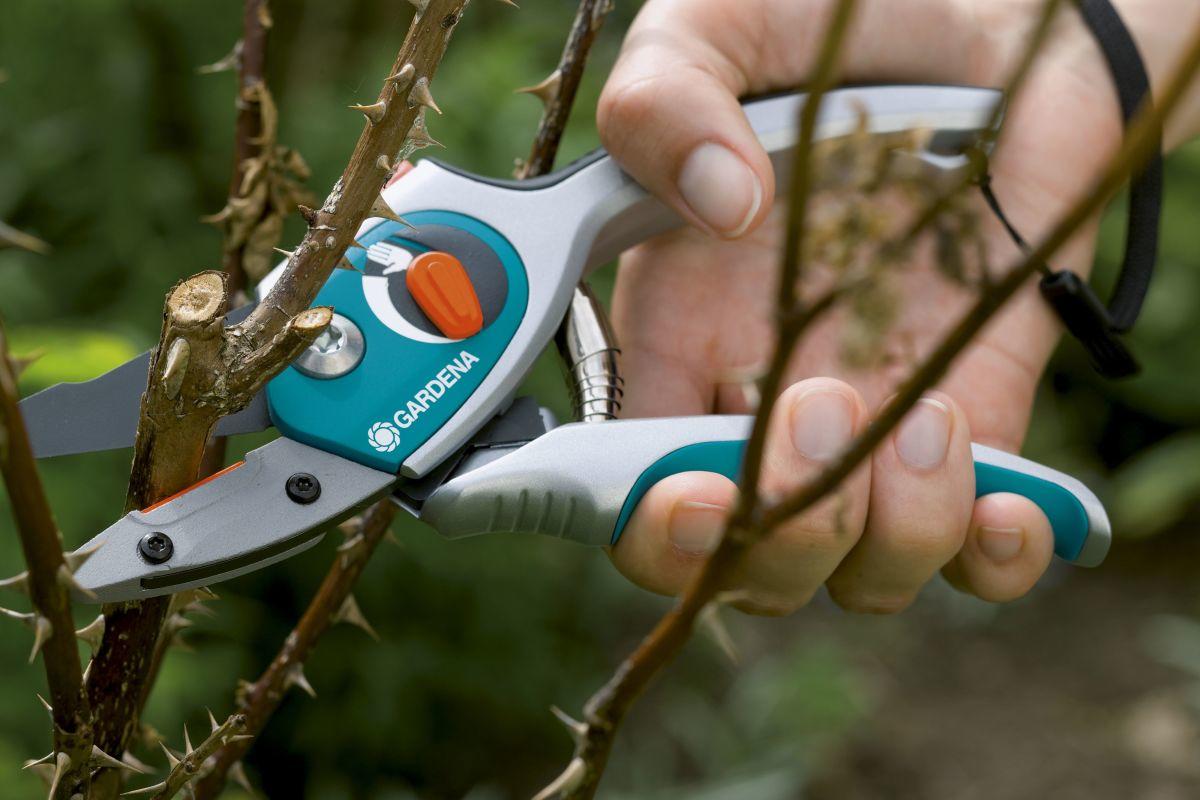
Pruning
There are two main types of pruning: sanitary and formative. Sanitary pruning is done in the spring before the start of the growing season. All dry leaves with signs of damping out or an infectious burn are removed from the rose. Shoots are shortened to healthy wood.
Formative pruning is used to increase decorativeness, as well as to stimulate branching of shoots. Weak lateral branches and branches growing inside the bush are removed. In an adult, more than 5 years old, growing bush, old lignified shoots should be cut out, they bloom less and are difficult to fit under the shelter.
Disease prevention
Rose Ali Baba has good immunity against fungal diseases. In order not to give a chance to infections, it is important to regularly feed and not allow the bush to thicken. Increased humidity levels can also spread the fungus.
Pest control
Young rose buds and leaves attract pests:
- aphids feed on sap at the base of the bud;
- rose leafworm, small green caterpillar, nibbles leaves;
- The rosy sawfly penetrates into the upper part of the shoot, where it feeds on juicy tissues; the pest can be identified by the sloping tops of the shoots.
You can get rid of gluttonous insects by spraying the rose with an insecticide, some preparations require re-treatment.
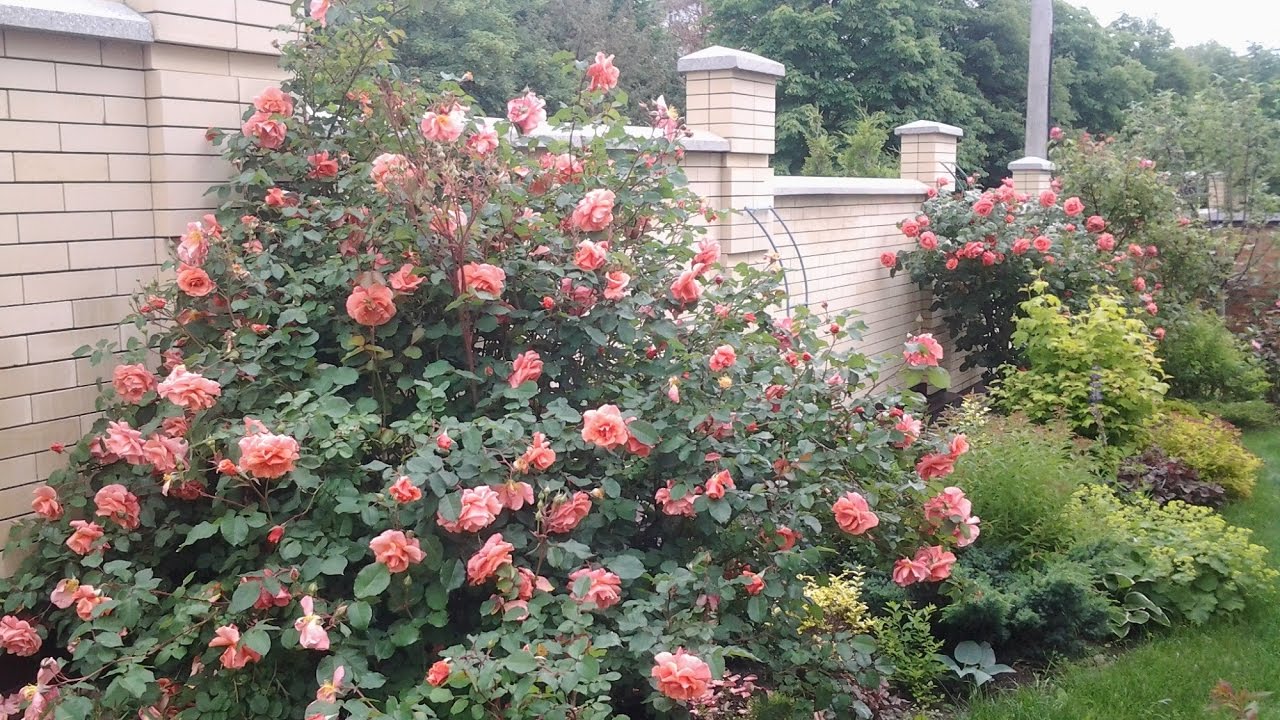
The climbing rose Ali Baba is suitable for growing on arches, supports and pergolas, it can be used to drape an unpresentable corner or wall. Blue and white sage, tall bells look charming in companions to her.